Glaucoma signs of treatment. Symptoms and signs of glaucoma. Non-traditional and folk methods of glaucoma treatment.
Glaucoma is a disease characterized by damage to the optic nerve. This pathology becomes the main cause of deterioration, and in the future, complete loss of vision. The disease can occur at any age, regardless of gender and lifestyle. The treatment is a medications or performing an operation. determined and appointed by a specialist, taking into account the stage of development of the disease.
Eye Clinic of Ludwig Maximilian University. Imagine that you are going to an ophthalmologist to have your visual acuity checked. At the front desk, you will be given an information sheet informing you of the recommended glaucoma screening exam, which in most cases is not covered by health insurance companies. At the end of the page, you must state your consent to conduct your own investigation.
But you don't want that, especially not before you've seen the doctor. You will then be asked at the counseling center to sign that you will not take this exam. A tick box is provided for this purpose. Do you support: why sign if you don't want an investigation? “For legal reasons,” the expert replies. "In case someone later wants to make the doctor responsible for forgetting the link to this investigation, we will sign it." But if this investigation was medically necessary, wouldn't it be covered by health insurance?
What is glaucoma and how is it treated?
Glaucoma of the eye is a disease that results in damage to the optic nerve and retina eyeball. As a result, there is a loss of visual fields, which, if left untreated, can lead to absolute blindness.
The main cause of the formation of pathology is high intraocular pressure. In the normal state, the fluid contained in the anterior chamber of the eye washes and is the main source of tissue nutrition. Accumulation of this fluid leads to increased pressure inside the eye, and damage to the optic nerve results.
The ophthalmologist also cannot explain to you what legal reasons are required for this signature - his professional association recommended that he request a signature for legal reasons. But he tells you in detail why the investigation makes medical sense.
They apply in writing to the professional association of ophthalmologists. The first answer remains unclear, as with the doctor: "Forensic reasons" is a conversation, and then medical reasons, the danger of glaucoma or green stars, which for a long time not recognized, but by responsible ophthalmologists in a timely manner Preventive examination.
The disease is almost asymptomatic. It is impossible to completely get rid of glaucoma, but with the right treatment, you can stop the pace of its development and reduce the area of distribution.
Medicines are used to treat disease laser treatment or surgery. Therapy is prescribed by a specialist individually for each patient.
You again ask about the association: Has an ophthalmologist ever been condemned because he did not tell the patient about the danger of unrecognized glaucoma and the possibility of salvation through timely early detection? Therefore, "judicial" reasons are completely absent, but only advanced. In fact, the psychological pressure is mounting.
Patients believe that this investigation is standard, perhaps even a matter of course, and refusal is something unusual, perhaps even dangerous. These are sales methods that are known from the oriental bazaar, but are not expected in the office of a German doctor. They are especially dangerous for patients with cash because they want to " medical services» charged directly to your insurance company. They are looking for trust in their doctor - and not that they need to separate and defend themselves from salespeople who want to convince them to do something.
First initial stages treatments are prescribed eye drops . Their action is aimed at reducing intraocular pressure, which leads to damage to the optic nerve. They must be used strictly following the recommendations for dosage and frequency of use. At further development pathology, glaucoma is removed surgically or under the influence of a laser.
“Benefits that exceed the level of medical medical care, should be credited to the doctor only if they were provided at the request of the payer. This is even more clearly claimed by many medical organizations, such as the "Kassenarztiche Verinigung Bavaria".
How useful, important and necessary is glaucoma screening?
The initiative for private treatment should be based on the patient. Of course, it is possible that ophthalmologists are correct in their opinion that screening for glaucoma is actually very important, and it is medically careless, and does not allow them to perform regularly from a year of age. This, however, would be a medical justification, not a judicial one.
Glaucoma causes
The main cause of glaucoma is fluid that accumulates in the anterior chamber of the eyeball and creates additional internal pressure on the optic nerve.
And if they are indeed right, then why don't doctors use every means to ensure that the investigation is funded? According to the Joint Federal Committee's Health Investigation Manual. "Screening for glaucoma cannot be recommended for early disease detection based on current scientific knowledge."
AT explanatory note This directive takes several arguments. First, it has been shown that early treatment can slow the progress of glaucoma. In addition, it is currently unclear what tests should be performed, for example, and by whom, to determine the value and use of general glaucoma screening. This requires “very long follow-up periods and very large numbers of patients.”
Depending on the causes of the formation of the disease, several types of glaucoma are divided: primary, congenital, secondary.
- Primary glaucoma appears in middle-aged people as a result of myopia, heredity, diabetes, dysfunctions nervous system, thyroid gland, unstable blood pressure.
- congenital glaucoma develops as a result of failures in embryonic development organs of vision in the fetus. Also, the reason may be inflammatory process, trauma, tumor during pregnancy.
- Secondary glaucoma: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention, depend on the underlying disease, which subsequently led to the formation of pathology.
The main secondary glaucoma are:
Further rationale for excluding glaucoma screening from the box office catalog is provided in the press release. So too many healthy people are suspected to be ill, and subjected to unnecessary additional examinations; On the other hand, but also perhaps really sick patients are not recognized and not treated.
What does this mean for you and your ophthalmologist?
Both of them would not be accepted in a democracy that would commit itself to the implementation of the will of the citizen and the transparency of his decision-making processes. Ask your eye doctor why glaucoma screening is not covered by your insurance company. Means pass the test, for example, in diabetics who already have changes in the eyes, and often even if they participate in a special diabetic treatment program; In case of eye injury; Before eye surgery, where glaucoma must be ruled out; In case of complaints; In cases of glaucoma and in patients on cortisone therapy.
- inflammation of the eyes;
- lens shift;
- cataract;
- mechanical damage to the eye;
- tumor.
Intraocular pressure rises due to age-related changes, insufficient amount of fluid in the body, endocrine diseases, intoxication of the body, long-term use hormonal drugs, obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous system.
Until such a request is made, and then pass by, the ophthalmologists will offer you an examination as a self-paying service, and you must decide, as a mature client or self-aware consumer, whether you succumb to pressure or withstand. The eye disease, also called the "Green Star", affects about 1,000 Germans. If glaucoma is not treated on time, you may become blind. It is not necessary, say, ophthalmologists, because the suffering is detected early, it can be treated well. But what is glaucoma?
In glaucoma, the optic nerve disappears
How will you know it and who is at risk? In glaucoma, the cells of the optic nerve gradually die. The reasons for this process are manifold: often too much eye pressure plays an important role. Apart from a few exceptional cases, the patient is not sick and cannot recognize defects associated with glaucoma, in facial area until most of the optic nerve is irrevocably destroyed. There is a risk that patients will become blind.

Prevention of glaucoma and cataracts
The disease can develop as a result of age-related changes or genetic failures. It is possible to save vision and stop possible pathologies with the help of preventive measures.
A green star is more dangerous than a cataract
Glaucoma - also called "Green Star" on People's Day - should not be confused with horror. The latter means the opacity of the ocular lens, which can be easily removed with surgery. In the case of glaucoma, on the other hand, vision restrictions are no longer reversible, the disease can only be stopped.
"Green Star" did not cause any complaints at the beginning. Rings around light sources were often affected as the first symptom. Later on, the visual field course may fail, i.e. blind spots appear in certain areas of the facial field. On the early stages the progress of the disease can be stopped.
- Regular medical examinations. At least once a year, it is recommended to undergo an examination by a specialist for people whose work activities are associated with a computer or require constant attention and eye strain. It is also necessary to visit an ophthalmologist for people with thyroid diseases, diabetes, with high blood pressure.
- Physical activity. To reduce the level of intraocular pressure, improve nutrition and blood supply to the retina and optic nerve will help sports, walking in the fresh air. At the same time, it is forbidden to lift heavy objects and stay with your head down for a long time, alternate physical exercise and rest.
- Proper nutrition. Foods, which are the main source of nutrients and trace elements, will help maintain vision. The daily diet should include protein, fiber, polyunsaturated fatty acid. It is recommended to consume more vegetables and fruits, cereals, whole grains, fish.
- Rejection bad habits . Nicotine and alcohol impair blood circulation in the organs of vision, saturate the blood with carcinogenic substances.

From 40 regularly to the ophthalmologist
In the Green Star, prevention means timely visits to the eye doctor. The risk of the disease increases already at the age of 40 years. Therefore, the professional association of ophthalmologists advises regular early detection. This exam costs between 15 and 30 euros, and only in exceptional cases, health insurance. This is the case, for example, if there is an increased risk, for example due to family pre-stress, or increased pressure on the eye has already been found in an earlier study.
Can glaucoma be cured without surgery?
Used to treat glaucoma drug therapy, laser exposure and surgery. The method of therapy is prescribed by a specialist, depending on the stage of development of the disease.
With timely diagnosis, glaucoma therapy consists of several stages:
With a combination of different examination methods, ophthalmologists can recognize glaucoma at a time when vision has not yet been damaged. The disease process can then be stopped with eye drops that reduce eye pressure. The treatment is simple and less stressful. If the effect of the drops is not enough, laser treatments and surgeries help.
Glaucoma is also called "green star" and refers to increased eye pressure in one or both eyes. In a healthy eye, a clear liquid is constantly formed, the so-called water humor. The production of this liquid takes place in a certain area in back eye, ciliary body. Subsequently, aqueous humor flows through the pupil into the anterior region of the eye. The discharge of water in the chamber occurs through the so-called chamber angle, so that there is a constant circulation of chamber water in the eye and a balance between the production and excretion of a healthy eye.
- Prescribing drugs, the action of which is aimed at lowering the level of intraocular pressure: drops, ointments, foams. They must be used according to the instructions for use from 2 to 4 times a day, depending on the type of medicine.
- Taking medications that improve nutrition and blood supply to the eye.
- Appointment and use of vitamin complexes to restore vitality and improve the condition of the body.
To improve the effect of drug treatment, physiotherapy is carried out in the complex: exposure to currents, a magnetic field.
If the flow is obstructed, the balance is disturbed, and visual pressure increases, glaucoma or a green star. In all our pets, eye pressure can be measured with special equipment that occurs on the awake animal and is not painful.
What are the causes of glaucoma? Basically, one differs between two types of glaucoma, namely primary glaucoma and secondary glaucoma. When primary glaucoma in many cases, no other disease can be found in the affected eye that would be responsible for the increase in intraocular pressure. Also congenital glaucoma, as well as open angle glaucoma, belong to this group. Defective chamber angle formation can be determined by gonioscopy on an alert animal under local anesthesia and is not painful or stressful.
In cases of absence positive effect from the use of drops and medications or progression, there is a need for surgical intervention. Surgery is necessary for a congenital disease. In the secondary form of glaucoma treatment, it is carried out in parallel with the treatment of the main problem.
In secondary glaucoma, there is an increase in intraocular pressure due to another eye disease. The disease may occur simultaneously or may be prolonged. A common cause of secondary glaucoma is a change in the position of the lens in the eye. In this case, the lens can be torn off only partially or completely from its attachment in the eye, and then moved "free" into the eye or sit in the internal structures of the eye.
In these cases, we speak of the primary dislocation of the lenses. These dogs should not be bred due to heredity as they can pass the disease on to their offspring. In older dogs and cats, the fixation of the lens may weaken due to age-related degenerative symptoms, and then lead to lens dislocation. Glaucoma can also occur as a consequence and complication after intraocular interventions.
Surgical treatment is used when there is a high probability of loss of vision. The effect of the operation can last about 5 years, then the fluid inside the eye begins to accumulate again and put pressure on the optic nerve.
Glaucoma symptoms and treatment
Eye diseases is not characterized by pronounced symptoms, so it is difficult to determine without consulting a specialist. The main symptoms of the development of the disease are:
You should know that glaucoma is always associated with massive pain for the animal! The increase in pressure in the eye results, depending on altitude and speed, sometimes severe, unbearable headaches. Some animals rub their heads above the ground or avoid touching the affected head.
Many animals are lethargic due to pain, sleep a lot, or show reduced appetite. The normally clear and transparent cornea of the eye becomes milky opaque and the pupil no longer contracts with light. In the case of prolonged existence, an increase in the eye and obvious visual disturbances up to a complete loss of vision occur. The eyes of cats and horses often tolerate the intraocular changes mentioned longer than the eye of a dog, so eye pressure in these animals often increases over a longer period of time, which does not mean that these animals do not have pain.
- changes in the shape and structure of the optic nerve;
- high, palpable pressure inside the eyeball;
- deterioration in the quality of vision;
- reduced visibility.
The main reason for the development of glaucoma is the internal pressure of the eye. Signs of its rise are:
- pain near the eyes of low intensity;
- low ability to see in the absence of lighting;
- feeling of excess moisture in the eye;
- pain sensations;
- hazy effect with eye strain.
Manifestations of pathology are characterized by intense cutting pain in the eyes, which goes to the temples, ears, nausea, vomiting. You can clearly see the symptoms and consequences of the disease on video.
For the treatment of pathology, two methods are divided: conservative treatment, surgical intervention.
Conservative therapy consists in the use of eye drops that help reduce fluid in the eye chamber or improve its outflow. It is impossible to get rid of the disease with the help of drops. They simply stop its development.
With a high probability of complete loss of vision, an operation is performed to form new outflows of intraocular fluid.
Glaucoma treatment with folk remedies
depend on the stage of development of pathology and the reasons for its formation. In the early stages of the development of the disease, in combination with traditional treatment you can use folk remedies.
- You can use an eye wash to wash your eyes. aloe. To prepare it, you need several leaves of the plant and boil a glass of water for about 5 minutes. It is necessary to wash the eyes with medicine at least 5 times within 14 days. A month later, the course of treatment must be repeated.
- Dill contributes to the normalization of intraocular pressure. dill seed in the amount of a tablespoon boil in 100 ml of water for several minutes. Then the medicine should be infused for about 2 hours, after which it must be filtered. It is necessary to take the drug 30 minutes before meals, 3 tablespoons for 3 weeks. Then you need to take a ten-day break and repeat the course of treatment again.
- For food eyeball, a remedy is used, which includes honey and bow. From several onions it is necessary to squeeze the juice and strain. Add honey to it in a ratio of 1:1. The mixture of ingredients must be boiled in a water bath for several minutes. Cooled medicine should be instilled in the eyes 2-3 times, 1 drop each.
Do you know this disease? glaucoma? Causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention match? Leave your opinion or feedback for everyone on the forum
Glaucoma is a disease that damages the optic nerve and results in blurred vision or blindness. This disease can occur at any age from birth, but is most common in the elderly and older. Currently, there are no common ideas about the causes and mechanisms of development of this disease.
Glaucoma usually occurs due to increased intraocular pressure (IOP). In front of the eye, between the lens and the cornea, there is a small space called the anterior chamber. A clear liquid circulates in it, washing and nourishing the surrounding tissues. When intraocular fluid begins to drain too slowly from the anterior chamber, its accumulation causes an increase in intraocular pressure. If left unchecked, it can lead to damage to the optic nerve and other structures in the eye, and then to loss of vision.
Types of glaucoma
Symptoms of glaucoma
In the early stages, most cases of open-angle glaucoma are not accompanied by any symptoms and manifestations: normal vision is maintained, there are no pain sensations or other changes in well-being. Sometimes patients may complain about the temporary appearance of iridescent circles before the eyes, the phenomenon of asthenopia. Since they are not specific to glaucoma, this can lead to underestimation of the condition and, as a result, a delay in diagnosing the disease. However, despite the absence of symptoms in the early stages of the disease, irreversible damage can occur in the optic nerve.
If glaucoma remains undiagnosed for a long time, then the symptoms described below may subsequently appear. The main one is the deterioration of peripheral vision. A person sees well straight ahead, but objects located to the side and at an angle may not be noticed. At first, the narrowing of the visual field occurs mainly from the side of the nose, and later it can cover the peripheral sections concentrically up to its complete loss. It is also possible the appearance of a translucent or opaque spot in the field of view.
The patient may notice a decrease in dark adaptation, which consists in a deterioration in vision during a rapid transition from a brightly lit room to a dark one, and also, sometimes, the appearance of color perception disorders. In some cases, there is an uncorrectable decrease in visual acuity, which already indicates a severe, advanced stage of the disease, which is accompanied by gradual atrophy of the optic nerve fibers.
The most striking symptomatology is observed in an acute attack of angle-closure glaucoma. In this case, the following manifestations of the disease can be detected: - pain in the eye and headaches with irradiation along the course trigeminal nerve(frontal, zygomatic, temporal areas); - blurred vision; - rainbow circles around light sources; - photophobia; - redness of the eye; - nausea and vomiting; - decrease in the number of heartbeats.
It should be noted that often the general symptomatology is more pronounced than the eye. Patients are often restless, in some cases they may experience pain that radiates to the heart and abdomen, similar to the manifestation of cardiovascular pathology. Slit lamp examination reveals clouding of the cornea due to edema. The pupil is greatly dilated, the reaction to light is sharply weakened or absent. On palpation, the eyeball is hard as a stone.
All of the above symptoms of an acute attack of glaucoma require emergency medical attention. If, within the next few hours after the development of an attack, the pressure is not reduced with the help of medications or surgically, the eye is threatened with irreversible loss of vision!
Diagnosis of glaucoma
The main problem in diagnosing glaucoma, especially open-angle glaucoma, is the absence of typical symptoms in the early stages. Many people who have this disease are unaware of it. Therefore, it is very important, especially in old age, to undergo regular examinations by an ophthalmologist. There are several methods for diagnosing glaucoma.
Eye pressure is measured by tonometry. Checking eye pressure is an important part of diagnosing glaucoma. High intraocular pressure is often the first sign of an illness. In some cases, anesthetic drops are instilled into the eyes before the measurement. With the help of a special device - a tonometer - the resistance of the cornea to pressure is measured. Normal intraocular pressure is considered to be from 10 to 21 mm Hg. (P0-true). However, in people with normotensive glaucoma, in which IOP is less than 21 mm Hg. Art., damage to the optic nerve and loss of visual fields may occur.
Gonioscopy (examination of the angle of the anterior chamber) allows you to get a clear picture of the state of the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye to determine the type of glaucoma. It is difficult to do this during normal inspection. The use of a specular lens makes it possible to examine the anterior chamber angle and determine the presence of open-angle (if the anterior chamber angle is not functioning effectively) or angle-closure (if the anterior chamber angle is at least partially closed) glaucoma or a dangerous narrowing of the anterior chamber angle (when the iris is so close to the drainage system eyes, which can block it).
Ophthalmoscopy (examination of the optic nerve head to detect signs of damage) is performed using an ophthalmoscope, an instrument that allows you to view the internal structure of the eye in magnification. At the same time, the pupil is dilated with the help of special drops. Glaucoma damages the optic nerve, causing the death of its constituent fibers. As a result appearance it changes, it starts to resemble a bowl. If its size increases, "dark" spots appear in the field of view.
Perimetry (read more) reveals "dark" spots in the field of view. The test results will show their presence and localization. Some of them the patient may not even notice. The test is performed using a cup-shaped instrument called a perimeter. Only one eye can be tested at a time, so the other eye is covered with a bandage during the examination. The patient should look strictly straight at the mark. The computer gives a signal and glowing dots flash randomly inside the device. The patient must press the button when he sees them. Not every beep is accompanied by a dot. Perimetry is usually done every 6-12 months to monitor changes.
Pachymetry is the measurement of the thickness of the cornea. This indicator can affect the accuracy of IOP measurement. If the cornea is very thick, then the intraocular pressure will actually be lower than according to tonometry. Conversely, with a very thin cornea, the true intraocular pressure is higher than the measurement shows.
Treatment methods for glaucoma
Glaucoma is treated with eye drops, tablets, laser surgery, conventional surgery, or a combination of these methods. Their purpose is to prevent loss of vision, irreversible in glaucoma. The main goal of treatment is to reduce IOP to an acceptable level, which is achieved in two ways: reducing the production of intraocular fluid and improving the outflow of fluid. It is encouraging that the course of glaucoma can be managed with early detection, and due to conservative and / or surgical treatment, most patients with glaucoma do not lose the ability to see.
The tactics of treating glaucoma depends on its type, the cause of development, the severity of the course of the disease.
Medical treatment of glaucoma
Eye drops are the most common treatment for glaucoma. They lower intraocular pressure in two ways - by reducing the production of aqueous humor or by improving its outflow through the angle of the anterior chamber.
Drops should be instilled daily. Like any other medication, it is important to take them regularly, as directed by your ophthalmologist. Never change or stop taking your medicine without talking to your doctor. If for some reason you are going to stop using it, check with your doctor about what you can replace it with.
Glaucoma surgery
Some patients with glaucoma are surgery, which improves the outflow of intraocular fluid, thereby reducing eye pressure.
Laser trabeculoplasty. This surgery is often used for open-angle glaucoma. There are two types of trabeculoplasty: argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT) and selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT).
During ALT, the laser makes thin, evenly distributed burns in the trabecular meshwork. It does not create new drainage holes, but stimulates a more efficient operation of the outflow system.
In SLT, the laser is used at different frequencies to allow operation at low power levels. At the same time, a certain type of cells is affected, and the filtering channels, like the networks surrounding the iris, remain intact. SLT may work in patients who have not been successfully treated with conventional laser surgery or eye drops.
Even if laser trabeculoplasty has been successful, most patients continue to take medication. For them, this method does not give a long-term effect. Approximately half of those who underwent this intervention, within 5 years, there is again an increase in intraocular pressure. Many patients who have had successful laser trabeculoplasty have to go through it again.
Laser trabeculoplasty can also be used as a first line treatment for those patients who are unwilling or unable to use antihypertensive eye drops.
Laser iridotomy. Laser iridotomy is indicated for the treatment of patients with angle-closure glaucoma or very narrow anterior chamber angle. The laser makes a small hole the size of a pinhead in the upper part of the iris and thus improves the outflow of aqueous humor through the angle of the anterior chamber. This hole is hidden upper eyelid, which makes it invisible from the outside.
Peripheral iridectomy. When laser iridotomy is unable to stop an acute attack of angle-closure glaucoma or is not possible for other reasons, peripheral iridectomy can be performed. A small area of the iris is removed, which gives aqueous humor access to the draining system of the eye. Due to the fact that most cases of angle-closure glaucoma can be cured by taking glaucoma drugs and laser iridotomy, peripheral iridectomy is rarely used.
Trabeculectomy. In a trabeculectomy, the sclera (the white tissue that covers the eye) is formed into a small valve. A filter pad, or reservoir, is created under the conjunctiva, the thin tissue that covers the sclera. Once formed, the pad appears as a bulge or blister on the white part of the eye above the iris, usually hidden by the upper eyelid. As a result, aqueous humor can drain through the valve created in the sclera and collect in the pad from where it will be absorbed. blood vessels eyeball.
Eye pressure is effectively reduced in 3 out of 4 trabeculectomy patients. Although regular check-ups with an ophthalmologist are necessary, most patients do not need eye drops for a long time. If the newly formed filter channel closes or too much fluid begins to flow out of the eye, additional surgical intervention is necessary.
Surgery with drainage devices (bypass surgery) If trabeculectomy cannot be performed, surgery with drainage devices is usually successful in lowering intraocular pressure.
A shunt is a small plastic tube or valve connected at one end to a reservoir (round or oval plate). It is an artificial draining device implanted into the eye through a thin incision. With an increase in IOP above certain numbers, the shunt redirects aqueous humor into the sub-Tenon space (under the Tenon capsule that covers the eyeball outside the palpebral fissure), from where it is absorbed into the bloodstream. When everything has healed, the reservoir can only be seen if, when looking down, the eyelid is lifted.
Folk remedies in the treatment of glaucoma
On the Internet, you can find many recipes for the treatment of glaucoma with decoctions and tinctures of herbs, vitamins, various lotions, etc. It is no coincidence that ophthalmologists are extremely negative about such advice. Practice has not confirmed the effectiveness folk remedies in the treatment of glaucoma. Relying on them will only delay the visit to the doctor and the timely start of proper treatment. And the disease, meanwhile, will progress, which will result in an increase in the degree of irreversible loss of vision.
Risk factors for developing glaucoma
Risk factors are factors that increase the likelihood of developing a disease. However, glaucoma can be diagnosed in the presence or absence of the factors described below. However, the more of them present, the higher the risk of developing this pathology. If you notice any of these factors, tell your doctor. This will help reduce the risk of developing pathology.
Risk factors for developing glaucoma include:
1) The presence of glaucoma in close relatives This disease can be inherited. However, if one of your relatives suffers from glaucoma, this does not mean that you will definitely develop the disease.
2) Race In black people, open-angle glaucoma occupies a leading position among the causes of blindness and occurs 6-9 times more often than among the white population. It should be added that the risk of developing pathology in blacks increases after 40 years. Eskimos and Asians are less at risk than others.
3) Age According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, the risk of developing glaucoma increases after age 50.
4) High intraocular pressure People with elevated intraocular pressure have a higher risk of developing glaucoma. Increased intraocular pressure is more than 21 mm Hg. Art. (P0 - true).
5) Thin cornea Last big clinical researches showed that patients with more thin cornea are at greater risk of developing glaucoma. It has also been found that African Americans have thinner corneas than fair-skinned people.
6) Refractive errors The presence of myopia leads to an increased risk of developing open-angle glaucoma, and farsightedness - angle-closure.
7) Regular long-term use of steroids / cortisone Long-term use of all forms of corticosteroids increases the risk of disease
8) History of eye injuries and operations Injuries can damage the structures of the eye, which is accompanied by a deterioration in the outflow of intraocular fluid. Complications of eye surgery can also lead to the development of glaucoma.
In addition to the above risk factors for glaucoma, some studies point to causes such as high levels of blood pressure, obesity, cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. However, there is not enough convincing evidence to support this view.
Just having one or more risk factors does not mean that you will inevitably develop glaucoma. However, in conjunction with the symptoms of this disease, this is an occasion to consult a doctor as soon as possible. In addition, even in the absence of symptoms, it is advisable to regularly (once a year) visit an ophthalmologist for a preventive examination.
Glaucoma is an eye disease, the main symptom of which is an increase in intraocular pressure. There are primary and secondary glaucoma. The etiology of primary glaucoma has not been elucidated. Secondary glaucoma can develop as a complication of a number of eye diseases (iridocyclitis, intraocular tumor, etc.).
There are two clinical forms primary glaucoma: congestive and simple. With congestive glaucoma, pain in the eye area, blurred vision, vision of rainbow circles around the light source periodically occur; on examination, changes are found in the anterior part of the eye - vascular hyperemia, some swelling of the cornea, pupil dilation. Simple glaucoma is asymptomatic for a long time and is detected during examination by a decrease in visual acuity, a narrowing of the visual field.
According to the stage of the process, initial, developed, advanced, almost absolute and absolute glaucoma are distinguished. With initial glaucoma, visual acuity and visual field are not changed. Developed glaucoma is characterized by a narrowing of the field of view by 15-20°; with advanced glaucoma, there is a more significant narrowing of the visual field, usually from the nasal side. Almost absolute glaucoma is characterized by reduced vision, and it is preserved only from the temporal side, with absolute glaucoma there is not even light perception. The deterioration of visual functions in glaucoma is associated with atrophic changes in the optic nerve.
There are four degrees of intraocular pressure compensation in glaucoma: compensation - intraocular pressure does not exceed 28 mm Hg. Art. (norm - from 18 to 27 mm Hg), subcompensation - from 29 to 35 mm Hg. Art. non-compensation - above 35 mm Hg. Art. and decompensation, or an acute attack of glaucoma, in which intraocular pressure can rise to 70-80 mm Hg. Art.
The course of primary glaucoma is varied. It usually develops gradually. An acute attack (decompensation) of glaucoma is observed infrequently, accompanied by acute pain in the eye and surrounding areas (temple, forehead), deterioration of the general condition. Nausea and vomiting are often observed. The eyeball is hyperemic, the pupil is wide, visual acuity is sharply reduced.
In the chronic course of glaucoma, early diagnosis and timely treatment are important to preserve vision. With intraocular pressure equal to 27-28 mm Hg. Art. a complete examination for glaucoma is necessary (performed by an ophthalmologist).
The prognosis for glaucoma is always serious, and the preservation of vision often depends on the timeliness of diagnosis, adherence to the regimen and accuracy of treatment.
Glaucoma is treated by an ophthalmologist. Its appointments can be performed by nursing staff. In an acute attack of glaucoma, frequent instillations of miotic (pupil constricting) agents (2% solution of pilocarpine, etc.) into the sore eye are necessary, administration of diacarb (fonurite) 0.5-0.25 g or glycerol (a mixture of equal amounts of glycerol and isotonic sodium chloride solution) at the rate of 1-1.5 g of glycerol per 1 kg of the patient's body weight, leeches on the temple, hot foot baths, saline laxative. If the attack does not stop, urgent antiglaucoma surgery is necessary (the patient should be referred to a specialized hospital).
In chronic glaucoma, instillation of miotic agents into the conjunctival sac is prescribed: 1, 2 and 6% pilocarpine solution, 0.25% ezerin solution, 0.5% prozerin solution (1-2 drops 1-6 times a day), 0.02 % solution of phosphacol. 0.005% solution of armine (1 - 2 drops no more than 2 times a day), etc. Diacarb (fonurite) is prescribed inside, 0.125-0.25 g 2-3 times a day. Apply various vitamins (B1. B2, B6. B12. C, PP) and other means.
Indications for surgery in glaucoma are persistently elevated intraocular pressure with a progressive deterioration in visual functions, especially narrowing of the visual field, despite conservative treatment. Fistulizing operations are the most widespread. As a result of these operations, artificial way outflow of intraocular fluid from the anterior chamber of the eye. After fistulizing operations, an elevation of the conjunctiva is formed at the site of the incision of the sclera - the so-called filtration cushion. A bandage is applied to the operated eye. Bed rest for 1-2 days.
Patients with glaucoma should follow a certain regimen. It is necessary to limit fluids to 5 glasses a day, regulate bowel activity, and improve sleep. Strong tea is excluded. natural coffee and spirits. Belladonna and caffeine preparations are contraindicated. Avoid prolonged exposure to darkness. Reading and more visual work allowed. The use of green glasses is recommended. Employment includes a number of activities that facilitate the work of patients with glaucoma: work during the daytime and in a bright room, work breaks; nervous and physical tension, overwork, etc. should be avoided.
Glaucoma most often begins and often goes unnoticed. If patients, especially the elderly, complain of decreased vision, pain in the eye area, the paramedic should promptly refer them to an ophthalmologist. The most effective in terms of maintaining vision is the dispensary method of servicing patients with glaucoma, which provides for the active identification of people suspected of having glaucoma, systematic monitoring of them, early diagnosis of glaucoma, timely and correct treatment.

Rice. 3. Glaucomatous excavation and atrophy of the optic nerve papilla.
Rice. 4. Normal fundus: 1 - uniform color of the fundus; 2 - parquet fundus; 3 - fundus with a small amount of pigment.
Rice. 5. Separation of the optic nerve. Rice. 6. Multiple ruptures of the choroid.
General information about glaucoma
Glaucoma belongs to the category of diseases that cannot be completely cured, often its appearance is associated with high blood pressure inside the eye, which affects the optic nerve and causes damage to the visual fields, which, if left untreated, leads to permanent loss of vision.

In most cases, glaucoma is a bilateral process. An important factor is hereditary predisposition. In those whose parents suffered from glaucoma, intraocular pressure must be carefully monitored.
As a rule, a patient in the first stages of the disease has an increased intraocular pressure, which over time has a detrimental effect on the optic nerve. The optic nerve dies irrevocably, the patient complains of decreased visual acuity, narrowing of the visual fields. As a result, blindness develops. However, even if the eye has lost the ability to see, the development of glaucoma may continue. The patient may begin pronounced headaches and eye pain. In some cases, to relieve pain, you need to remove the eye.
Glaucoma is divided into several types:
congenital,
closed and open angle
secondary, that is, caused by other diseases.
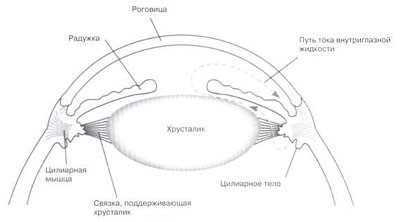
According to anatomical landmarks, glaucoma is divided into:
open-angle, in which the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye is open, through which the outflow of intraocular fluid occurs;
closed-angle, in which the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye is closed or it is very narrow. In this case, the fluid from the eye flows very slowly, due to the violation of the outflow, high intraocular pressure appears.
Also, glaucoma can be primary and secondary. Secondary glaucoma is caused by some additional factors such as: operations inside the eye, intraocular changes, taking medications, injuries, etc.
Symptoms of glaucoma
The number of patients with closed glaucoma is 20% of all patients diagnosed with glaucoma. It usually appears in people with farsightedness, as they have an anatomical predisposition to develop a closed anterior chamber angle. People over 40 suffer from this form of glaucoma.
Open-angle glaucoma, as a rule, also develops after 40. In the initial stages, there are practically no pronounced symptoms. In some patients, due to increased pressure inside the eye, headaches appear, iridescent circles around the light source, and vision becomes blurred from time to time. Over time, the clinical picture intensifies, narrowing of the visual fields appears, and visual acuity decreases.
Causes of glaucoma
The following factors influence the progression of primary glaucoma:
local: changes in the microvessels and drainage system of the eye,
general: hemodynamic and neuroendocrine disorders, heredity.
Due to changes in the drainage system, poor outflow of intraocular fluid from the eye begins, intraocular pressure increases, pressure appears on the fibers of the optic nerve, which causes the progression of glaucoma atrophy of the optic nerve.
Representatives of the middle age group, as well as the elderly, suffer from primary open glaucoma. Often in their body changes are determined that are characteristic of this age category. There are several factors that negatively affect the prognosis and course of primary open-angle glaucoma: the presence of cervical osteochondrosis. low blood pressure, sclerotic changes in the vessels of the neck. All these factors cause a deterioration in the blood supply to the eye and brain. This contributes to a decrease in visual functions, disruption of the usual metabolism in the tissues of the optic nerve and the eye.
Prevention of glaucoma
You can prevent the occurrence of glaucoma if you regularly see an ophthalmologist. It is necessary to carefully monitor intraocular pressure so that it does not rise above the permissible norm. If the parents suffered from glaucoma, you need to more closely control the pressure and regularly undergo examinations of the optic nerve, conduct its tomography. If the doctor prescribes anti-glaucoma drops, you need to use them regularly, without missing a single day. Only in this case, the patient has a good chance to preserve his vision and prevent a decrease in visual functions.
Complications of glaucoma
Glaucoma is an incurable disease that eventually leads to blindness. In some patients, the development of glaucoma causes severe corneal degeneration, tearing, pain, the patient cannot open his eyes. A similar condition is characteristic of the terminal stage of glaucoma, that is, the latter. If intraocular pressure is greatly increased, pain can be so severe that strong medications are needed to stop them. If such drugs do not have the desired effect, the patient's eye is removed.
Diagnosis of glaucoma
To make a diagnosis of glaucoma, the patient needs to consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will measure intraocular pressure. This procedure is done using a pneumotonograph - a special device that fixes the pressure inside the eye using compressed air, or by placing special weights on the eye for 1-2 seconds. Be that as it may, the pressure inside the eye should not be higher than 24-25 mm Hg. Art. The examination also includes examining the eye under a microscope - a slit lamp, examining the optic nerve and the fundus, performing tomography of the optic nerve using a special eye tomograph. It is very important to examine the patient's visual fields, to determine the sensitivity of the optic nerve. In addition, it is possible to conduct an examination of the eye using ultrasound, the study of the angle of the anterior eye chamber (gonioscopy), to determine how damaged the drainage system is.
Glaucoma treatment
Glaucoma therapy is associated with an influence on the main factor in the progression of optic nerve atrophy, that is, a decrease in pressure inside the eye. There are three methods of glaucoma treatment: microsurgical, laser and drug.
When the diagnosis of "glaucoma" is confirmed, the patient is prescribed drops that need to be instilled regularly. If, against the background of this, intraocular pressure returns to normal, the patient should, without stopping the use of drops, regularly consult an ophthalmologist in order to undergo a complete ophthalmological examination and control intraocular pressure. All this is necessary so that if the glaucoma process begins to progress, the doctor can intensify the drug treatment in a timely manner, add medicine for instillation.
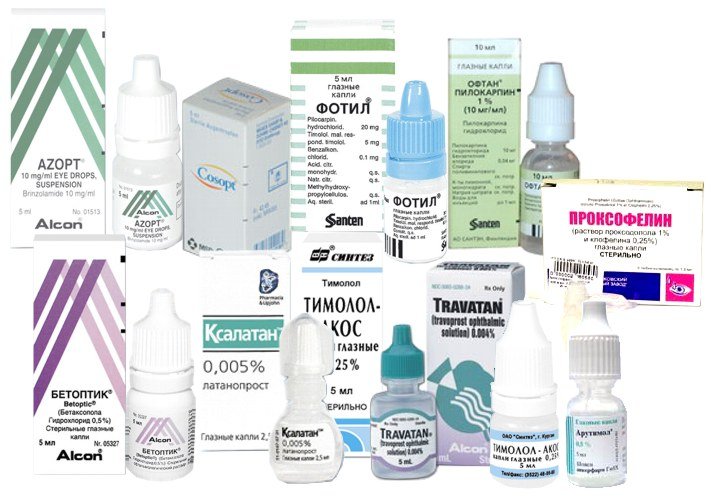
The drugs most commonly used for drug treatment glaucoma: betaxalol, timolol maleatpilocarpine, latanoprost, dorzolamide or combined drugs.
If treatment medicines does not give the desired effect, or if "angle-closure glaucoma" is diagnosed, the patient is prescribed laser treatment. This type of therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis. With the help of a laser, small holes are made inside the patient's eye, as a result of which the intraocular pressure should return to normal, and the intraocular fluid should flow better.

If the intraocular pressure is still high, and laser treatment does not work or is contraindicated to reduce pressure, the patient undergoes a microsurgical operation. Perform it in the operating room, after making the patient a local anesthesia. New ways of outflow of intraocular fluid are indicated, due to which the pressure inside the eye returns to normal, which can become a guarantee of the safety of the optic nerve fibers and prevent the progression of blindness.
Be that as it may, the patient must be under the constant supervision of a doctor, examine visual functions and measure the pressure inside the eye. To maintain the function of the optic nerve, the patient is prescribed medications that improve the blood supply to the brain, and vitamin therapy is also prescribed.
Lifestyle with glaucoma
In view of the fact that glaucoma belongs to the category of vascular diseases, a patient with glaucoma must comply with some restrictions that are characteristic of vascular patients.
It is better not to visit baths and saunas. An increase in blood pressure should be avoided. If a person has angle-closure glaucoma, he should not read in low light, dark rooms should be avoided. It is important to constantly monitor the level of illumination. Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise.
Symptoms of glaucoma.
Glaucoma usually develops slowly and insidiously. Therefore, by the time symptoms appear, chronic eye damage may already be quite significant.
There are two main forms of primary glaucoma - open-angle and closed-angle. Open-angle glaucoma is associated with changes in the drainage system of the eye (outflow of intraocular fluid). The disease usually develops imperceptibly for the patient, sometimes there are complaints about a feeling of fullness in the eyes, headache, blurred vision, the appearance of iridescent circles when looking at the light. Vision gradually deteriorates until blindness.
In angle-closure glaucoma, the angle of the anterior chamber of the eyeball is blocked by the root of the iris. It is characterized by patient complaints of pain in the eye and headache, blurred vision, the appearance of iridescent circles around the light source. The disease proceeds in the form of acute attacks, which are accompanied by acute pain in the eye and head, general malaise, often nausea and vomiting. The eye noticeably reddens, the cornea is edematous, the pupil is dilated. Vision is sharply reduced.
Narrowing of the field of vision is possible, the so-called tunnel vision appears, which can develop to complete loss of vision. An acute attack of glaucoma is accompanied by a sharp pain in the eye, in the forehead, deterioration of the general condition, the appearance of nausea, vomiting.
Treatment of glaucoma.
With angle-closure glaucoma, the main task is to lower intraocular pressure, and therefore drugs are prescribed both inside and in the eyes that contribute to this. Treatment of open-angle glaucoma begins with the use of local agents that reduce intraocular pressure, as well as vasodilators. It is necessary to observe a general sparing regimen, a diet with fluid restriction (5-6 glasses a day), salt. It is necessary to exclude strong tea, coffee, alcoholic beverages from the diet, stop smoking.
Depending on the form of glaucoma, medications taken by mouth, eye drops, laser surgery, conventional surgical methods. Treatment of severe forms of glaucoma is surgical.
Medicines for the treatment of glaucoma as prescribed by an ophthalmologist:
Vasodilators
Vinpocetine (Cavinton)
Local means to relieve intraocular pressure
Clonidine (Bapresan, Gemiton, Katapresan, Chlofazolin)
Pilocarpine (Oftan Pilocarpin, Humacarpin)
Timolol (Glaumol, Glukomol, Okukap, Okumed, Okumol,
Fumigated, Optimol, Oftensin, Timohexal, Timopress,
Non-traditional and folk methods of treating glaucoma
home remedies for glaucoma
Dissolve 0.2 g of mummy in 1 glass of water. Drink 2 times a day on an empty stomach, before dinner and at bedtime. The course of treatment of glaucoma - 20 days.
Herbs and fees for the treatment of glaucoma
Pour 1 tablespoon of cleanly washed and chopped duckweed grass with 1 glass of vodka, leave for 4 days, strain. Take a tincture of 20 drops with 2-3 tablespoons of water 2-3 times a day to treat glaucoma. You can use duckweed fresh with an equal amount of honey, 1 teaspoon 2 times a day.
Take 35 g of oregano herb, white mistletoe herb, 30 g of common cocklebur herb. Pour 2-3 tablespoons of the mixture in a thermos with 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 1-2 hours, strain. Take orally 0.3 cup 3 times a day after meals for the treatment of glaucoma.
Take 2 parts of blood-red hawthorn fruits, 1 part of small periwinkle herb, white mistletoe herb, common yarrow herb, horsetail herb. Pour 1 tablespoon of the collection with 1 cup of boiling water, heat in a water bath for 15 minutes, leave for 30 minutes, then strain. Take 0.5 cup 2-3 times a day with increased intraocular pressure.
