Dark discharge during menopause. Discharge during menopause
Menopause is a special period in the life of every woman. During and after this period, many things change; this is directly related to changes in a woman’s hormonal levels. A drop in the level of sex hormones also affects the nature of vaginal discharge in women. However, in some cases such a picture is the norm, in others it is a sign of an incipient pathology.
It all depends on the color, consistency, smell of mucus, and the presence of other pathological signs. During and after menopause, women should pay special attention to their own health, since a sharp change in hormones can be an impetus for the development of many dangerous diseases, including cancer. Timely diagnosis greatly facilitates treatment in this case.
Causes and types of pathological discharge during menopause
In most cases, small, mucous, odorless, watery discharge from the female genital organs is considered normal.
 Treatment in this case is not required. They serve as a natural lubricant during sexual intercourse, and are also designed to absorb and remove all kinds of harmful bacteria from the woman’s body. This is how local immunity of the female reproductive system is formed.
Treatment in this case is not required. They serve as a natural lubricant during sexual intercourse, and are also designed to absorb and remove all kinds of harmful bacteria from the woman’s body. This is how local immunity of the female reproductive system is formed.
During and after menopause, women's local defenses decrease due to an imbalance of sex hormones. The amount of normal discharge decreases; at first, many ladies complain of vaginal dryness, and then completely different, pathological discharge may take the place of the “correct” discharge. Let's consider each of their types separately, which are the norm, which are pathology.
 First, let's look at the signs of discharge, which are considered the absolute norm for women, including during menopause, as well as after it:
First, let's look at the signs of discharge, which are considered the absolute norm for women, including during menopause, as well as after it:
- odorless;
- watery or slimy consistency;
- are released in moderate quantities;
- their appearance is not accompanied by any other pathological symptoms.
It is important to observe the color and nature of the discharge; after any changes, you should contact a doctor who will prescribe treatment, if necessary.
White curdled vaginal discharge
Such discharge may indicate the onset of a disease such as vaginal candidiasis or thrush; the causes of its occurrence are varied. This disease is familiar to many women, but during menopause and after it, women reproductive system becomes especially vulnerable to the uncontrolled proliferation of the Candida fungus. In addition to discharge, thrush is characterized by the following symptoms:

For staging accurate diagnosis you need to contact a gynecologist. In most cases, for the treatment of candidiasis, local antifungal suppositories are prescribed in combination with suppositories that restore normal microflora vagina (Clotrimazole, Metronidazole, etc.).
Copious mucous or watery discharge
Although clear mucus from the genitals is not a sign of pathology, a change in the amount of discharge toward a significant increase may indicate the development of an infectious disease such as chlamydia. This insidious disease can for many years do not talk about your presence in any way, however, during a decrease in immunity, it can manifest itself in the form of unpleasant symptoms:

Treatment is prescribed by the doctor after receiving test results; the disease is treated with antibiotics.
Purulent discharge from the genital tract
May be a sign inflammatory process pelvic organs. As a rule, this disease is accompanied the following symptoms:
Review from our reader Maria Krasnikova
I recently read an article that talks about the natural healing mixture “Monastery Anti-climax Tea”, which helps you forget what menopause is. With this tea you can get rid of increased sweating, frequent headaches, irritability, muscle pain...
I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered one package. I noticed changes within a week: constant hot flashes, pressure surges, bad dream and the mood swings that had tormented me in recent months receded, and after 2 weeks disappeared completely. Try it too, and if anyone is interested, below is the link to the article.
Treatment is prescribed by a gynecologist after determining the cause and nature of the inflammatory process. In most cases, this kind of pathology is treated both during menopause and after it with antibacterial drugs of both local and systemic action.
Bloody discharge
This kind of discharge should especially alert a woman. Their appearance is a reason to consult a doctor. Their reasons are quite varied. There are two main types of discharge of this type:

Pathological brown and pink discharge during the period after menopause can be caused by precancerous or even cancerous processes in a woman’s body, namely in the area of her reproductive organs.
Cervical cancer is one of the the most dangerous diseases, which can develop against the background of hormonal changes during menopause and after it.
The causes of cancer are still not fully understood. If such symptoms appear, you must immediately consult a doctor; delay in this case is truly like death, and timely treatment can save a life.
Another common cause of spotting is the pathological growth of uterine tissue; this is a specific reaction of the body to a drop in the level of sex hormones in the body. Although this symptom itself is not as dangerous as oncological process, yet many doctors tend to regard it as a precancerous condition. Also, brown or pink discharge during menopause may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid or pancreas, that is, be evidence of serious endocrine disorders.
It's worth saying that spotting During menopause, small amounts may appear after intimate relationships. In this case, sex also becomes quite painful. However, this does not yet indicate the development of any disease.
 It’s just that during menopause, the secretion of natural vaginal lubrication is significantly reduced, so the mucous membrane becomes quite vulnerable to various kinds of mechanical damage that are inevitable during sexual intercourse. In this case, doctors advise the use of special lubricants and lubricants that completely solve the problem.
It’s just that during menopause, the secretion of natural vaginal lubrication is significantly reduced, so the mucous membrane becomes quite vulnerable to various kinds of mechanical damage that are inevitable during sexual intercourse. In this case, doctors advise the use of special lubricants and lubricants that completely solve the problem.
Menopause is a natural age-related phenomenon in a woman’s life, which usheres in a new period. In order for hormonal changes to take place without much discomfort, it is necessary to promptly apply for medical care, competent treatment will help cope with all problems.
Are you still sure that it is impossible to delay menopause or reduce its symptoms to a minimum?
Have you ever tried to get rid of the symptoms of menopause or delay its onset? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, victory was not on your side. And of course you know firsthand what it is:
- hot flashes, excessive sweating...
- Frequent pressure surges and hypertension...
- sudden mood swings, irritability, tearfulness...
- loss of strength, depression, apathy...
- change in body weight...
- severe headaches and dizziness...
Now answer the question: are you satisfied with this? Can ALL THESE SYMPTOMS be tolerated? How much time, effort and money have you already wasted on ineffective treatment? After all, sooner or later the SITUATION WILL GET WORSE and any help will be useless! That's right - it's time to act! Do you agree? That is why we recommend that you familiarize yourself with real story Lyudmila Kudryashova, about how she managed not only to cope with CLIMAX, but also to feel like a real woman...
Menopause occurs when a woman is 50 years old. Clinically, it is expressed as cessation menstrual cycle, the cause of which was age-related ovarian dysfunction.
Menopause does not occur instantly. For 9 to 12 months, a woman experiences premenopause - a restructuring of the body, which is characterized by:
- irregular cycle,
- spotting instead of regular discharge.
The appearance of spotting is associated with the gradual cessation of ovarian function. During premenopause, their presence is not dangerous.
Menopause is characterized by a long absence of critical days (about 12 months). Spotting and spotting that appears 1 year after the last menstruation may indicate the presence of a serious gynecological pathology or disease.
What can cause discharge during menopause?
| Possible reason | Detailed Description |
|---|---|
| Age-related changes in vaginal microflora | With the onset of menopause, the ovaries stop producing estrogen-type sex hormones:
This leads to a change in the qualitative composition of the cervical mucus and thinning of the epithelium - the mucous membrane lining the vagina. Any mechanical injuries and minor damage can lead to bleeding. Usually their secretion increases after sexual intercourse. |
| Inflammatory processes of the genital tract | The most common types of inflammation are:
|
| If a woman who has reached menopause continues to be sexually active, the cause of the inflammatory process can be infections and STDs. | Bloody discharge is caused by the following types of bacteria:
|
| Cervical polyps | The formation of a polyp leads to the proliferation of the epithelial membrane. Its tissues are easily damaged, which also leads to discharge. |
| Exchange disorders | According to data medical research, the presence of spotting during menopause is associated with disturbances in carbohydrate and fat metabolism. The appearance of secretion can be caused by the following pathologies:
|
| Causes of discharge that appears due to removal of the ovaries | Women of reproductive age who have had surgery However, they are susceptible to menopause syndrome. In patients, the secretion of female hormones decreases, which leads to inevitable restructuring of the body and changes in the mucous membrane:
Minimal trauma and microcracks usually lead to brown bloody discharge. |
How to determine the cause of the pathology?
In order to establish the cause of vaginal bleeding, the gynecologist uses complex methods research. Typically they include:
- palpation of the uterus,
- examination of the pelvic organs using ultrasound,
- tissue biopsy - collection of biological material for clinical trial for availability degenerative changes,
- other laboratory methods for studying vaginal microflora.
The menopause period is considered the most dangerous for a woman. Due to the cessation of hormone secretion by the ovaries, the mucous membrane ceases to perform barrier functions - the functions of protecting the body from microbial pathogens of gynecological pathologies. If bloody discharge occurs, the patient should immediately consult an experienced doctor to eliminate the risk of cancer.
At a certain age, every woman faces decline reproductive function, this period causes concern both physically and psychologically. Discharge during menopause, which does not always have the normal biological nature of the female body, is of particular concern. When should you not worry? What symptoms should you immediately consult a doctor for?
Normal discharge during menopause
Natural vaginal discharge accompanies women throughout their lives, and menopause is no exception. But in order for them not to be a symptom of any pathological processes in the body, it is necessary to know the very mechanism of their formation. Vaginal discharge helps avoid dryness of the mucous membranes of the female genital organs and protects against infections.
Their normal intensity depends on many factors:
- woman's age;
- hormonal stability;
- level of sexual arousal;
- quality and frequency of sexual contacts;
- absence of diseases of the genital organs.
 Vaginal discharge contains dead skin cells, mucous fluid, natural bacteria and a large number of microorganisms. The vagina has an acidic environment, the discharge may have a sour smell - this is normal.
Vaginal discharge contains dead skin cells, mucous fluid, natural bacteria and a large number of microorganisms. The vagina has an acidic environment, the discharge may have a sour smell - this is normal.
At the initial stage of menopause, a woman’s hormonal levels begin to malfunction, while the body adapts to new living conditions. The quantity and quality of discharge changes, vaginal dryness appears due to a lack of natural lubrication. This process is accompanied by disruption of menstrual flow. They do not disappear immediately with the first symptoms of menopause.
Menstrual flow becomes irregular and its intensity decreases each time. Against this background, daily discharge may contain bloody clots, which is normal in most cases. A physiological process occurs - the vaginal tissues lose their elasticity, without lubrication they dry out and die.
Deviations from the norm during menopause
 During menopause, discharge is a natural process of extinction of reproductive function. With the right approach, a woman can even slow down this process; doctors assure that an active lifestyle, a balanced diet and, oddly enough, regular sex life will help maintain the health of the genital organs longer.
During menopause, discharge is a natural process of extinction of reproductive function. With the right approach, a woman can even slow down this process; doctors assure that an active lifestyle, a balanced diet and, oddly enough, regular sex life will help maintain the health of the genital organs longer.
But the beautiful half of humanity at climatic age must responsibly and carefully monitor changes in the body. After all, vaginal discharge can indicate pathological conditions.
During menopause, discharge, indicating a deviation from the norm, has a characteristic appearance and composition.
Discharge like water
Moderate amount vaginal discharge, not exceeding the daily norm of 5 ml, are considered normal physiological characteristics female body during menopause. Abundant watery leucorrhoea from the vagina should worry a woman; it is extremely dangerous when it has an unpleasant odor and causes discomfort. This is the first signal of a malfunction in the hormonal system; a medical examination and adequate treatment are required.
DO YOU STILL THINK THAT IT IS IMPOSSIBLE TO GET RID OF THE SYMPTOMS OF CLIMAX?
What does yellow discharge mean?
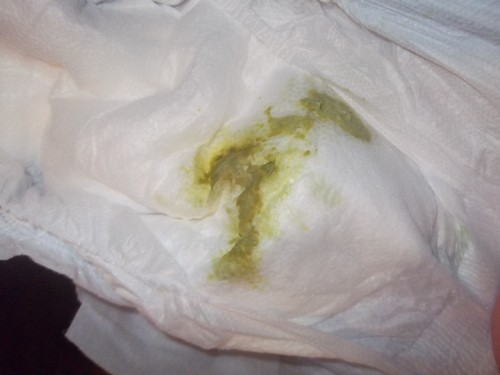 In the female vagina there are various bacteria that form normal acidity and microflora. Together, they protect the genitals from infections and fungi. In adulthood, the number of bacteria decreases, this happens both for natural reasons and due to improper hygienic care. Yellow vaginal discharge is characteristic of bacterial vaginitis, cervical erosion and inflammation fallopian tubes. They are accompanied painful sensations after sexual intercourse, a woman feels a burning sensation in the external genitalia. Often during menopause, the discharge turns yellow and comes out along with bloody clots. Foamy consistency yellow discharge from the vagina - a sign of the development of gonorrhea, chlamydia and other diseases, as well as a combination of two infections at once.
In the female vagina there are various bacteria that form normal acidity and microflora. Together, they protect the genitals from infections and fungi. In adulthood, the number of bacteria decreases, this happens both for natural reasons and due to improper hygienic care. Yellow vaginal discharge is characteristic of bacterial vaginitis, cervical erosion and inflammation fallopian tubes. They are accompanied painful sensations after sexual intercourse, a woman feels a burning sensation in the external genitalia. Often during menopause, the discharge turns yellow and comes out along with bloody clots. Foamy consistency yellow discharge from the vagina - a sign of the development of gonorrhea, chlamydia and other diseases, as well as a combination of two infections at once.
Brown color
During menopause, discharge that is brownish in color is most often not an anomaly. Brown leucorrhoea appears with aging of the uterine tissues and mucous membranes. This occurs due to a delay in menstrual flow, with which dead and discolored biological materials are released.
Vaginal discharge may also be dark brown in color and is clotted blood from the uterus or cervix. They occur as a result of microtraumas of the internal genital organs and can be a sign of dangerous diseases.
Discharge with an unpleasant odor
 Reproduction pathogenic bacteria in the genitals leads to an imbalance between them and beneficial microorganisms. Due to the large number of waste products of these bacteria, during menopause, the discharge acquires an unpleasant odor. At the same time, the woman suffers from constant itching and burning of the external genital organs.
Reproduction pathogenic bacteria in the genitals leads to an imbalance between them and beneficial microorganisms. Due to the large number of waste products of these bacteria, during menopause, the discharge acquires an unpleasant odor. At the same time, the woman suffers from constant itching and burning of the external genital organs.
A decrease in lactobacilli or their complete destruction occurs with bacterial vaginosis. The acidity of the vagina decreases, an inflammatory process begins, in which pathogenic microorganisms affect the entire area of the mucous membranes. The same effect on the body is exerted by fungal infections, for example, candidiasis.
Greenish color, odorless
Any inflammatory process in the female organs is accompanied by green discharge during menopause. This color of leucorrhoea is obtained due to higher level leukocytes. There is no burning, itching or unpleasant odor from the vagina. Such a benign picture is not always safe, because the greenish color of odorless vaginal discharge can signal an infectious origin. A disease such as trichomoniasis spreads not only to the internal genital organs, but also to the entire genitourinary system.
Bloody
 Copious discharge with blood is the most dangerous phenomenon during menopause. Against the background of a decrease in the production of sex hormones, age-related changes in the uterus, leading to its vulnerability from external influences. Bleeding may appear after physical activity, sexual intercourse, also without any external influence. Bloody discharge together with other signs (burning, itching, pain in the groin and abdomen) indicate the presence serious illnesses. It could be:
Copious discharge with blood is the most dangerous phenomenon during menopause. Against the background of a decrease in the production of sex hormones, age-related changes in the uterus, leading to its vulnerability from external influences. Bleeding may appear after physical activity, sexual intercourse, also without any external influence. Bloody discharge together with other signs (burning, itching, pain in the groin and abdomen) indicate the presence serious illnesses. It could be:
- polyps in the cervix or the organ itself;
- uterine fibroids;
- malignant tumors (cervical and endometrial cancer).
Such anomalies in female body require timely diagnosis, prompt and effective treatment.
Curdled
Almost every woman has encountered discharge with a cheesy consistency in her life. After all, candidiasis is the most common disease affecting females at any age. During menopause, fungal “thrush” is even more common. Additional symptoms of Candida infection are severe itching of the genitals and redness. In adulthood, the development of this disease is explained by a decrease in immunity and sexual function, while a cheesy discharge may appear on the mucous membranes of the genitals and oral cavity.
Purulent
 Infections of the genital tract, accompanied by purulent leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor, increased body temperature, and pain in the groin area indicate a neglected condition of the female organs. The above diseases, such as bacterial vaginitis, gonorrhea and chlamydia, without timely treatment led to intoxication of the body. In this situation, the woman will have to resort to antibacterial therapy. And the sooner treatment with antibiotics begins, the less consequences there will be from an irresponsible attitude towards one’s health.
Infections of the genital tract, accompanied by purulent leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor, increased body temperature, and pain in the groin area indicate a neglected condition of the female organs. The above diseases, such as bacterial vaginitis, gonorrhea and chlamydia, without timely treatment led to intoxication of the body. In this situation, the woman will have to resort to antibacterial therapy. And the sooner treatment with antibiotics begins, the less consequences there will be from an irresponsible attitude towards one’s health.
A doctor can prescribe a specific drug only after identifying the causative agent of the infection. To do this, in a laboratory setting, a smear is taken from a woman’s vagina, this biological material is placed in a Petri dish, and bacteria multiply under the influence of the thermostat environment. After a few days, the smear filled with bacteria is studied according to various parameters and the specific type of infection is determined. After the research, laboratory technicians expose the pathogen to various antibiotics. This is done in order to determine which types of antibacterial drugs there is resistance to and which ones are sensitive to.
What to do - how to treat?
To treat women, doctors prescribe hormonal drugs, their action is aimed at reducing or eliminating the symptoms of menopause, including various discharges. The effect of taking the drugs is to saturate the body with synthetic hormones, which to some extent replace human ones. But such treatment is contraindicated for most women in adulthood due to concomitant diseases and side effects. Hormonal drugs at any age should be taken with extreme caution, because they positive influence on the human body is closely combined with possible dangerous disorders. What to do in this case? Use alternative medicine.

If there is any suspicion caused by unnatural discharge, the woman needs the help of a medical specialist. At this age, even the slightest disturbance in the functioning of the body can lead to dire consequences. Therefore, it is important to start treatment at the first stage of the disease, especially if a woman wants to prolong her quality of life and do the things she loves. Even in old age, a woman can not notice her age and enjoy the calm flow of events or, conversely, actively spend her everyday life.
If you experience discharge during menopause, what are the possible options? Which discharge is considered normal, and which, on the contrary, will indicate pathological process? These are the main questions that worry women during menopause. Naturally, they have different characters, and only a lady’s attentive attitude to her own health can protect her from harm.
IN menopause Women experience serious changes in the nature of their discharge. This is associated with changes in the functions of the reproductive system, hormonal changes and the accompanying decrease in hormone concentrations. Discharge during menopause is not always abnormal, but any representative of the fair sex should have information about in which cases she should immediately visit the doctor.
So it is precisely when non-mucous discharge is detected that a doctor’s consultation is required, as well as a determination of the causes, diagnosis and further therapeutic therapy.
Experts classify different ones based on their consistency and nature:
- mucous membranes (transparent discharge or yellow discharge);
- purulent, creamy white or yellow);
- curdled (white color, sour smell, similar to cottage cheese);
- bloody (spotting, bloody or reminiscent of menstrual bleeding).
On top of that, vaginal discharge may or may not have an odor. As a rule, most of such discharge indicates pathology.
Mucus discharge
Such leucorrhoea is generally not a pathology. They have the following characteristics:

But in certain situations, discharge in the form of mucus can also indicate pathology:
- foamy consistency;
- unpleasant odor;
- allocation in significant volumes or, conversely, scarcity.
Often, such discharge during menopause is characteristic of an infectious and inflammatory process or is a manifestation of chlamydia.
Curdled discharge
If the vaginal discharge has a thick, cottage cheese-like consistency, this usually indicates candidiasis. The disease has accompanying symptoms that only strengthen suspicions of pathology:
- there is itching;
- heavy discharge;
- the presence of a sour odor;
- burning during urination;
- irritation of external organs reproductive system.
The disease can be treated with an integrated approach to therapy: antifungal drugs (Amphotericin, Nystatin) are prescribed, as well as vaginal suppositories to restore the microflora. However, you should not engage in amateur activities in this matter, since treatment should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor.
Purulent discharge
Discharge, including pus, is a clear sign of a sexually transmitted disease (gonorrhea, chlamydia), and may also be a signal of the development of bacterial vaginitis. Often, purulent discharge in women is also associated with the following symptoms:

In such circumstances, you should not delay visiting the doctor, since it is extremely important to establish the correct diagnosis and begin adequate treatment as soon as possible. Typically, therapy includes the following aspects:
- anti-inflammatory and antimycotic agents;
- antiseptic douching;
- vaginal suppositories;
- vitamin complexes;
- a course of antibiotics;
- therapeutic diet.
Bloody discharge
Bloody discharge can rightfully be called the most dangerous sign that occurs after menopause. Experts point to two types of such secretions. In the first case, bloody or brown marks are noted. They are often provoked by malfunctions in the woman’s reproductive system. It should be noted: this is a very common pathology among women who have crossed the line of 45 years. As a rule, this phenomenon occurs after a missed period.
Bleeding is also observed, lasting from two weeks to several months and having varying degrees of intensity. They start in the background hormonal treatment or for diseases of the thyroid, pancreas and metabolic disorders.
In the second case, such discharge is observed in postmenopause. Often they indicate an oncological process, for example, of the cervix, but such discharge can also appear due to erosion. Such discharge should serve as a signal to contact a doctor, since early detection dangerous pathologies gives good chances for a future healthy life.
If a representative of the fair sex is diagnosed with erosion, as a rule, it just needs to be cauterized. When oncology is detected, in most cases a supravaginal hysterectomy is performed. In women after menopause, not only the uterus, but also the appendages are removed.
Diagnostics
As soon as a woman has atypical discharge, she should immediately go to the doctor. A visit to the doctor at the beginning of the development of many diseases can literally save a life. It is dangerous to forget that women who have entered menopause are especially susceptible to cervical cancer. Only its early detection and timely treatment help avoid serious consequences.

At the appointment, the doctor especially focuses on the patient’s complaints, as well as on taking an anamnesis. During the examination, the gynecologist uses the following diagnostic methods:
- palpation method for palpating the uterus;
- Ultrasound to study the condition of the pelvic organs;
- two-finger vaginal examination method;
- determination of pathogens using ELISA, RIF, PCR methods;
- laboratory tests: bacterial culture and detection of sensitivity to antibiotics;
- examination using mirrors to detect inflammation, erosion, polyps or oncological processes;
- hysteroscopy and diagnostic curettage;
- biopsy to exclude or confirm possible cancer.
It should be noted: not all women with discharge of a pathological nature undergo a full examination. It is irreplaceable only in certain cases. So, uterine fibroids or uterine bleeding - serious reason, which is considered a significant basis for complex diagnostics.
Treatment
Of course, each case of pathological discharge in women requires its own therapeutic methods. So, with mucous, cheesy and purulent discharges, it is quite possible to get by drug therapy and carrying out certain procedures (douching, administering suppositories). However, with regard to blood discharge, things are somewhat more complicated. They can be treated using conservative and surgical methods.
The conservative method includes the following steps:
- hormonal therapy (lasting up to 3 months);
- use of hemostatic medications;
- use of restorative therapy.
It should be noted that therapy for bloody discharge always pursues the following goals:
- cessation of intense bleeding;
- elimination of the causes of the phenomenon;
- carrying out measures to restore blood loss.
When a woman experiences severe bleeding during menopause or intense uterine bleeding, she should seek emergency medical help. If this is not done, complications such as severe anemia or hemorrhagic shock are likely.
If, during the examination, a woman was diagnosed with a malignant tumor, then, alas, in this case it is impossible to do without surgical intervention. However, even after the operation she must undergo a course preventive treatment and for the rest of her life she is obliged to monitor her own body signals as closely as possible.
We recommend similar articles
This restructuring normally begins at 50-51 years of age. We can talk about its beginning when 12 months have passed since the last menstruation. It is caused by the depletion of egg reserves in the ovaries, which begin to be reduced as unnecessary. Because of this, the concentration of female sex hormones in the body decreases and hormonal changes occur.
Those organs that are accustomed to the proper concentration of estrogens and gestagens begin to age, wear out and become decrepit over time. A woman’s mood becomes labile and changeable, wrinkles appear on the skin, osteoporosis appears in the bones, and atherosclerosis develops in the vessels. Female genital organs that have lost their function also undergo changes. In particular, menstruation stops in women and, due to the above reasons, they cannot reappear in any way. Therefore, any non-mucous discharge during menopause should be considered pathological, and if it appears, you should contact a gynecologist.
What kind of discharge can occur during menopause?
According to its composition and appearance Vaginal discharge may be:
- Mucous (transparent, sometimes with a yellowish tint)
- Purulent (white or yellow, creamy)
- Curdled
- Bloody (red)
- in the form of ordinary blood
- spotting (with a small amount of blood)
Also, discharge can be with or without odor.
Normally, mucous discharge should be in small quantities, free of odors and impurities, and may resemble rice water. They should never cause discomfort, itching, burning, pain, or irritation. Excessive or scanty mucous discharge, foamy, especially with an unpleasant odor, may be a sign of an infectious disease.
For example, with chlamydia, the discharge is scanty, transparent with a yellowish tint, and often creates discomfort when urinating.
Purulent discharge
Purulent discharge also indicates a genital infection (bacterial vaginitis, chlamydia, gonorrhea). They are accompanied by fever, symptoms of intoxication, pain and itching in the pelvic organs and external genitalia. As a rule, all this is accompanied by an unpleasant odor, similar to the smell of rotten fish.
In this situation, a course of antibacterial therapy is indicated. Before choosing an antibiotic, it is advisable to determine the pathogen. This can be done using the bacteriological method (culture method). In this case, the secretions are lubricated with a special nutrient medium in a Petri dish and placed in a thermostat so that the bacteria multiply there. After a few days, they are removed and the type of pathogen is determined by shape, color and other parameters. In addition to everything, using this method you can also determine which antibacterial drugs These pathogens will be resistant and which ones will not be (testing for sensitivity to antibiotics).
When treating such diseases, it is logical to use vaginal suppositories containing the necessary medicinal substances(antibiotics, antimycotics, anti-inflammatory drugs). Douching with various antiseptics(eg chlorhexidine) are also given positive effect. Besides local treatment you must try to maintain your immune system proper rational diet, vitamins, in an active way life. If there is a concomitant pathology, then it also needs to be adequately treated.
 Curdled discharge is a sure sign of candidiasis, commonly referred to simply as “thrush.” They are thick in consistency, resemble lumps of cottage cheese, and their quantity exceeds the norm. At the same time accompanying symptom there will be itching and irritation of the woman’s external genitalia.
Curdled discharge is a sure sign of candidiasis, commonly referred to simply as “thrush.” They are thick in consistency, resemble lumps of cottage cheese, and their quantity exceeds the norm. At the same time accompanying symptom there will be itching and irritation of the woman’s external genitalia.
Candidiasis is caused by yeast fungi of the genus Candida and is treated with special antimicrobials(nystatin, amphotericin, griseofulvin). But candidiasis can also indicate a significant decrease in immunity, for example, with AIDS, especially if it is present not only on the vaginal mucosa, but also on the oral mucosa. Therefore, in this matter, consultation with a specialist doctor is always necessary.
Bloody discharge
Bloody discharge is the most dangerous discharge during menopause. In combination with the appropriate age, they can indicate oncological diseases of the female genital organs (erosion or cervical cancer). You cannot turn a blind eye and ignore this, since oncological diseases respond well to treatment and have a favorable outcome only at the very beginning of the disease (stage 1-2). And if erosion of the cervix can simply be cauterized, then cancer of the uterus or its cervix is fought with supravaginal amputation of the uterus and extirpation of the uterus. And during menopause, the uterus is removed along with the appendages.
Examination of a woman with the appearance of pathological discharge during menopause
If pathological discharge appears during menopause, a woman needs to be examined by a specialist. This is due to the fact that an older woman is always at risk for developing cancer, and if any symptoms that are suspicious in this regard are added to this, then a full examination will dispel these unpleasant doubts. This is precisely where the preventive orientation of medicine manifests itself, which, unfortunately, is so poorly developed in our country. In contrast, Cuba's preventative healthcare system is showing amazing results. And even the World Health Organization recommends that everyone follow this small socialist country in this matter.
The examination of a woman begins with identifying complaints and finding out a detailed anamnesis (history) of this disease. Only after this you need to move on to other examination methods, which include:
- palpation (palpation) of the uterus
- two-finger examination of the vagina and uterus
- examining a woman in the mirrors
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
- Hysteroscopy with biopsy
- Bacterial culture and antibiotic sensitivity testing
- Identification of the pathogen using other various laboratory methods examinations (ELISA, PCR, RIF and others).
Of course, all these methods are carried out only when indicated (for example, uterine fibroids, uterine bleeding), since many of them can cause complications. But if these indications exist, then it is better to carry out these examinations, since it is easier to prevent or cure the disease in its initial stage than in a neglected one.
Video: vaginal discharge
