How much is a fecal analysis done for a coprogram. What does a scatological examination show? How to collect feces for analysis in an adult
Research method stool occurs through coprological analysis, which allows obtaining objective quantitative data on pathological dysfunctions in organs gastrointestinal tract, as well as the functional state of the rectum. Coprology can determine the presence of inflammatory processes and oncological diseases on early stages development in the digestive system.
The coprological method of studying feces proceeds at three levels: physical, microscopic and chemical, which allows you to get a complete and detailed picture of the presence or absence of diseases. Coprology accurately reveals the degree of deviations from the norm, and also marks and indicates the presence of certain diseases.
Upon completion of the diagnosis, the obtained quantitative data allow the specialist to give a qualitative assessment of the state of the digestive organs, as well as to determine the localization of a specific problem.
The coprological method is one of the best and most reliable research methods. digestive system. This simple and informative diagnostic method has no age restrictions.
Experts recommend scatology not only as a method of detecting various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or rectum, but also as a preventive measure. Preventive diagnostics are indicated both for children at least twice a year, and for adults. Early diagnosis will make it possible to timely establish the development of any pathological processes and a number of others. dangerous diseases. The presence of disorders in the digestive system is reflected in a special form, which is referred to as a transcript.
The procedure for donating feces does not require special preparation. It is enough to withstand all the standard recommendations of specialists. It is recommended not to take the day before the study medications, which can affect the functional activity of the digestive system. It is necessary to exclude the intake of vitamins and other preparations containing such substances and chemical compounds like iron, barium. Before taking the test, it is not recommended to put enemas, suppositories and eat food that can stain the feces. Failure to comply with the recommendations, interpretation of the analysis may carry unreliable information about the state of the digestive system.
The main reasons that can provoke unreliable results
The above recommendations are due to the fact that in the normal state, stool in adults and children is a cylindrical shape, which consists only of particles of food debris. If the digestive system is without pathologies, only semi-digested residues are observed. The decoding of such an analysis will be characterized as the norm. If there are inflammatory processes in the organs, as well as serious diseases, then the consistency, color and smell of feces undergo significant changes. There are such inclusions as blood, mucus, clots and natural color, purulent discharge. Feces with such inclusions will indicate the presence of dysfunction of the digestive system. All these signs can significantly confuse even an experienced specialist, and the decoding of the analysis will be considered unreliable. In such situations, a qualified doctor is likely to prescribe a second test. It should be noted that the results may be unreliable as a result of improper collection of feces.
In order to avoid unreliable results, in order for the diagnosis of fecal masses to be as informative and accurate as possible, it is necessary to pay special attention to a number of recommendations for collecting feces. The stool collection algorithm is the same for both adults and children. It is not recommended to take the analysis:
- during the menstrual cycle;
- with exacerbation of hemorrhoids;
- with loose stools;
- after taking laxatives,
- after an enema;
- after the introduction of suppositories into the anus.
Additional procedures before collecting feces include the following manipulations: it is strongly recommended to wash yourself thoroughly, and also be careful not to get drops of urine into the biomaterial. You can not collect and donate fragments of feces from the toilet. These recommendations apply to both adults and children.
For a child up to a year old, the procedure for collecting feces is carried out using a sterile stick, it is recommended to collect feces from a clean diaper or diaper. It is advisable to be sure before taking the biomaterial that the child did not write into this diaper. For older children, feces are collected from a pot. The pot must be thoroughly washed beforehand.
Features of the collection and deadline for the delivery of biomaterial
Stool collection should be done in the morning for both adults and children. There is an obvious problem - getting a child to go to the pot early in the morning. In such cases, experts recommend that parents massage the child's tummy with smooth circular movements for 15-20 minutes. If the child does not have frequent constipation, then this method, as a rule, especially works in the morning.
Feces are recommended to be taken in a special sterile glass container or plastic cup. Such dishes can be purchased at any pharmacy or laboratory. Biomaterial for analysis must be delivered to the laboratory as soon as possible. Its long-term storage can lead to the loss of quantitative and qualitative information content. Fecal collection should get to the laboratory within an hour.
The results of the analysis and its interpretation should be provided by a laboratory specialist the very next day. Laboratory data can be sent to the clinic or personally to the patient himself. The decoding shows only quantitative data, and the attending physician gives a qualitative interpretation of the state of health. Only after studying the results of the analysis, the doctor makes a diagnosis.
 The results of the analysis and its interpretation should be provided by a laboratory specialist the very next day.
The results of the analysis and its interpretation should be provided by a laboratory specialist the very next day. Consistency and color of feces
Experts point out pathological processes associated with the functional activity of the gastrointestinal tract can be determined by the consistency and color of feces:
- If the feces are very dense, this indicates the presence of stenosis or inflammation of the colon. A mushy consistency indicates the presence of colitis, an inflammatory process of peristalsis, as well as fermentative dyspepsia. Plasticine-like feces indicate a violation of pancreatic secretion, a chronic course of pancreatitis and cholecystitis. Liquid consistency indicates the presence of violations of digestion in small intestine, as well as for the presence of acute infection, often occurs in children under 3 years of age.
- In children at breastfeeding feces are characterized by a golden yellow color. At artificial feeding light and dark brown. In older children and adults - brown. If black or dark brown, then there are violations in the upper sections of the gastric tract. Reddish color occurs in ulcerative colitis and inflammatory processes in the rectum. Gray color indicates the presence of hepatitis and blockage of the bile duct.
Mucus and blood in the feces during scatological diagnostics
The presence of mucus in the feces of a child during breastfeeding should normally be observed in the form of small inclusions, since in babies the stomach adapts to fatty foods, in this case, milk. In artificially fed children, as well as in adults, mucus should be completely absent. Any manifestations of mucus indicate diseases such as:
The detection of blood in the stool is an alarming sign. Usually the appearance of blood indicates serious diseases of the digestive system. Blood, even in the form of inclusions at any age, refers to the pathological development of the gastrointestinal tract. The main reasons for the appearance of blood are:
- cracks in the anus;
- stomach ulcer or duodenum;
- oncology - a benign or malignant tumor of the intestine or rectum;
- acute infection;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hemorrhoids at the stage of acute inflammatory process.
Timely diagnosis of fecal masses will avoid serious problems associated with the functional activity of the digestive system. Knowing how to collect and donate biomaterial will allow you to receive accurate quantitative and qualitative data, which means that any specialist will be able to make the correct diagnosis. And all together will help to solve almost any problems related to the health of the intestines and rectum.
Human health largely depends on the state of the gastrointestinal tract. Diagnosis of diseases of the digestive system is a difficult task for any doctor. It is almost impossible to get a complete picture of the work of the small and large intestines without the use of invasive examination methods, but their use is not always justified. If any pathology of the gastrointestinal tract is suspected, the patient is primarily recommended a stool coprogram.
When is a study appointed, and what is its essence?
Fecal analysis is considered one of the most important tools for assessing the functionality of the intestines, liver, pancreas and gallbladder, allowing you to make a preliminary diagnosis to the patient. Like clinical analysis urine, coproscopy gives a detailed physical characteristic (according to appearance), and also allows you to determine the microscopic and chemical composition of the studied biomaterial with the help of special reagents. Scatology is a way to detect bacteria and occult blood that are not visible to the human eye.
A complete fecal analysis is rarely prescribed to a patient separate study and often acts as an additional, but extremely informative diagnostic tool. He is appointed:
- during preventive examinations of children and adults in the clinic (medical examination);
- with suspicion of dysbacteriosis and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS);
- in case of malabsorption (celiac disease, NUC, malabsorption);
- in the complex diagnosis of secretory insufficiency and inflammation of the upper gastrointestinal tract (duodenitis, GERD, gastritis);
- with acute and chronic hemorrhoids, rectal hernia;
- in the diagnosis of genetic pathologies, oncology, HIV infection.
A coprogram is also a way to detect the antigen of a rotavirus infection in case of infection with it. In addition to the above, the study allows you to learn about the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment for gastrointestinal diseases.
Coprogram indicators
Coprological analysis includes macroscopic indicators of the obtained sample: volume, consistency, smell, shade, nature of possible impurities. Biochemical research reveals pigments, protein structures, fats and hemoglobin. Stool microscopy determines the presence of leukocytes, erythrocytes, fibers and crystals.
To decipher the data received from the laboratory, you can use the summary table below. Usually, the coprogram includes a number of indicators and looks like this:
| Norms for adults | |
|---|---|
| Consistency | Dense |
| The form | decorated |
| Color | Brown |
| Smell | Fecal, unsharp |
| pH (acidity) | 6.0–8.0 (neutral, slightly acidic, slightly alkaline) |
| Slime | A small amount of |
| Blood | (–) |
| Undigested foods | (–) |
| Reaction to stercobilin | Positive |
| Bilirubin, ammonia | (–) |
| Protein | (–) |
| reaction to occult blood | negative |
| Protein fibers with striation | (–) |
| Protein fibers without striation | (–) |
| Connective fibers | (–) |
neutral fats, fatty acid and their salts | (–) |
| Digestible fiber | Single |
| Starch (intra- and extracellular) | (–) |
| Pathological impurities | (–) |
| Soaps | In a small amount |
| Eosinophils | (–) |
| Leukocytes | Single |
| red blood cells | Single |
| epithelial cells | Single |
| Crystals (triple phosphates, cholesterol, uric acid, hematoidin, Charcot-Leiden) | (–) |
| Hemoglobin, haptoglobin | (–) |
| Detritus | Available in various sizes |
| Salts (oxalates) | Missing |
Causes of deviation from the norm
Feces are formed from the remains of the food bolus in the large intestine. It consists of detritus, dietary fiber, epithelium, water, bile and enzymes. Their number and type depends on nutrition and other factors. Analyzing all the data obtained from the study, the doctor will determine in which part of the intestine pathological changes have occurred, whether there is an enzyme deficiency.
Macroscopic indicators
Thick, hard-textured stools are considered normal. This indicates a sufficient amount of liquid in it. When plant foods with a high fiber content predominate in the diet, intestinal motility increases, feces become mushy. If with liquid feces an increase in the frequency of defecation is noted, then they speak of diarrhea (diarrhea).
Hard stools are the result of slow peristalsis and dehydration of the feces. This condition occurs with constipation or hemorrhoids. These disorders appear with malnutrition, as well as in men with prostatitis, in women during pregnancy and after childbirth.
The smell of feces changes with the abuse of protein foods. Offensive occurs with putrefactive processes in the lower intestines, with cholecystitis or pancreatitis. The sour smell is the result of fermentation.
The color of the stool is determined by a pigment called stercobilin, and varies depending on the diet, the use of iron-containing drugs (for example, Maltofer). A colorless stool indicates a violation of the outflow of bile due to stones in the biliary tract (often with cholelithiasis), occurs with cirrhosis of the liver, jaundice. With hepatitis A and C, the pigment level also decreases. A light color is possible when taking antibiotics or the abuse of fatty foods, as well as in pregnant women due to the increased load on the digestive organs.
Too much dark stool caused by an excess of stercobilin. Dark brown occurs with pleiochromia ( high content bile pigments in bile). Black feces can appear after using certain medications, in particular, De-Nol.

Biochemical indicators
A pH below normal with an acidic reaction occurs due to problems with the metabolism of fatty acids, as well as an increase in the fermentative microflora. The increase in pH (alkaline reaction) is due to the large amount of meat protein in the diet. In this case, the decay of protein elements occurs. A sharply alkaline reaction is characteristic of putrefactive dyspepsia.
Fatty acids should not be observed in the stool. At healthy person they are absorbed by the body. If the number of fats is several times higher than the reference values, then steatorrhea is diagnosed. As a rule, it is observed with problems with the outflow of bile, such as cystic fibrosis. Soaps in the coprogram indicate dysfunction of the pancreas.
The detected native protein means the development of inflammation in the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract (colitis, enteritis, gastroduodenitis, duodenal ulcer, stomach ulcer, cancer). Be sure to take into account the presence of symptoms. If a person has pain in the hypochondrium, bloating, then an increased protein indicates acute pancreatitis.
Normally, only altered muscle fibers are determined. If the scatological examination showed unchanged muscle fibers, the gastroenterologist will prescribe an additional examination of the pancreas, as this indicator indicates problems with the breakdown of proteins.
Microscopic indicators
Erythrocytes in feces indicate inflammatory processes digestive tract or about the defeat of its tumors. Moving through the intestines, fecal lumps injure the inflamed areas, causing bleeding of varying intensity. Another reason why feces contain blood cells can be helminthic invasion. If occult blood is detected, its amount will be determined as + for a weakly positive reaction, ++ for a positive one.
Mucus is produced by the intestinal epithelium as a defensive reaction to irritants. In the case of the development of inflammation of an infectious or non-infectious nature, the amount of mucus increases. This occurs, for example, in intestinal tuberculosis, cholera, ulcerative colitis, IBS or Crohn's disease. Bacteria that can cause fermentation in the intestines (dyspepsia) form iodophilic flora. Their determination is made using an iodine sample: pathogenic organisms differ in the resulting color.
Extracellular starch indicates a decrease in the function of specific enzymes (amylase) that are responsible for its breakdown. Leukocytes and macrophages indicate the presence of any inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, including those found in large numbers in acute intestinal infection(OKI).
How to prepare for the analysis?
For those who want to have a clinical stool test, a referral is made by a general practitioner at a clinic or hospital. A few days before the sample is taken, the patient is given a special diet that cleanses the intestines, which affects the accuracy of the result. Two nutritional options have been developed: according to Pevzner and according to Schmidt.
In the first case, they eat meat, bread, sauerkraut and potatoes. In the second, they eat five times a day, consuming a lot of dairy products, eggs, potatoes and meat. Considering that both diet options include meat products during preparation, vegetarians need to warn the attending physician about the dietary habits, since due to the exclusion of animal proteins from the diet, some deviations from generally accepted values will be acceptable.
In preparation for the analysis, the use of alcohol should be excluded, it affects the properties of feces. If a person drinks any medical preparations, then it is necessary to cancel them for a while in order to avoid erroneous interpretation of the indicators. Two days before the test, all coloring foods (carrots, beets, asparagus, prunes) are excluded from the diet.

Unlike most blood tests, in this case there is no need to take the biomaterial on an empty stomach. Women should not do coproscopic analysis during menstruation. The implementation of these simple recommendations will allow you to get an objective result of the study, and hence the correct idea of the state of health of the gastrointestinal tract.
How to collect biomaterial?
The morning portion of feces is considered optimal for research. Evening is also allowed, but the sample should be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 10 hours after sampling. There is a certain algorithm for collecting feces for a coprogram. First of all, hygiene procedures are carried out - an external toilet of the genital organs. For defecation, you must use a clean container - a pot or a vessel. If defecation is difficult, you can make a microclyster Microlax or take Duphalac. They do not affect the results of the study. You should not use food cans, boxes or euro toilet bowls as dishes for feces. Feces are collected in a sterile disposable jar or a specialized container with a spoon. It indicates the surname, initials, and the laboratory assistant signs a unique number, date and time of receipt of the biomaterial.
Feces are placed in a test tube. For research in laboratories, a special diachem is used. kit (test strips) and a microscope. When the results are ready, the patient is given a form with a table that shows all the indicators and the limits of the norm for verification. In the case of strange results, which may suggest an error in the study or poor preparation, the analysis is required to be retaken. The execution time is 1-2 days, depending on the chosen laboratory. If the result of the analysis is needed urgently, then the study takes less time. In preparation for surgery, the analyzes are valid for 14 days. If it takes a long time to get to the laboratory, you should clarify the possibility of obtaining results online.
Diagnosis of the body is carried out both in the event of a disease, and for the purpose of prevention, to detect diseases in the early stages. Laboratory analyzes occupy a rather important part in this matter. Analysis of feces for scatology is no exception. It allows you to identify pathological diseases of the digestive system, as various diseases and inflammation of the digestive system will inevitably be accompanied by changes clinical blood picture. Also, this analysis allows you to identify hemorrhoids, determine the level of hemoglobin, and also allows you to see if there is a digestive disorder in children.
How is the analysis given?
It may seem that this event does not require special preparation, but it is not. Coprological analysis of feces to obtain reliable information and a complete picture requires preparation, which will help the doctor. Before passing the analysis, it will be necessary to carry out a number of measures, for example, it is necessary to exclude the use of medicines that affect the functioning of the intestines before passing the material.
For analysis, feces must be collected immediately after emptying into a plastic container with a sealed lid and submitted for laboratory research on the same day.
After about 5-6 days you will get the result. It is very important that additional impurities do not enter the material, for example, there may be soap in the analysis of feces or even impurities. urine. Foreign matter will not allow you to get a reliable picture.


Research results
Let's take a closer look at what the doctor can reveal in the analysis and what this indicates. Deciphering the analysis of feces for scatology:
- Consistency. In this case, there may be several options for deviation from the norm. For example, if the feces are dense and formed, this indicates a lack of gastric digestion. But if it is frothy or mushy, then fermentative dyspepsia is already taking place. The material may also be ointment, which is also not the norm and indicates a violation of pancreatic secretion.
- In the analysis of feces fatty acids. This factor also indicates the presence of certain problems, for example, the absence or insufficient supply of bile, problems with pancreatic secretion, fermentative dyspepsia, accelerated evacuation from the small or large intestine, and there may also be insufficient digestion.
- Color. A grayish-white color may indicate problems with bile, reddish for feces with expressions, and black for bleeding in the stomach or intestines. For example, a light brown color, which may seem normal, indicates an accelerated evacuation from the colon. There are other variants of deviation from the norm, which indicate the presence of problems. Naturally, you can see the color yourself and try to establish a diagnosis, however, only deciphering the coprological analysis of feces will allow you to accurately determine the problem. You should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-treatment, especially when it comes to children, since an analysis of a child’s feces can determine how normal what you perceived as a violation.
- Smell. As nasty as it may be, the smell can also indicate a problem. Putrid, for example, speaks of insufficiency of digestion, which can also be indicated by a faint smell. A sour smell means fermentative dyspepsia. Fetid is usually caused by a malfunction of the pancreas.
- Muscle fibers in stool analysis. This phenomenon is usually observed in violation of the pancreas, as well as in case of insufficient digestion.
- Connective tissue. It is observed with the same problems as described in the paragraph with fibers.
- Neutral fat. The analysis reveals it precisely in violation of pancreatic secretion, but not in similar problems with the rest digestive tract.
- Bilirubin. Its analysis will reveal in case of a violation in the microflora or, in other words, with dysbacteriosis. However, there is one significant nuance in this issue. So, analysis of feces, a coprogram in children will detect it until 6-8 months of age, when the normal intestinal flora is restored.
- Sterkobilin. In children older than 6-8 months and in adults, it should be determined, but its absence, deficiency or even excess will indicate the presence of certain problems.
- iodophilic flora. It will be revealed by analysis in case of problems with secretion, too rapid evacuation, fermentative dyspepsia, and also in case of insufficient digestion.
- Starch, soap. They are found with the same problems as described in the paragraph above.
- Leukocytes. Finding them in the feces indicates a possible calitis.
- Erythrocytes. They can also be found in ulcerative stools, polyps, hemorrhoids, and other cases. Also, their source may be a fissure of the intestine.
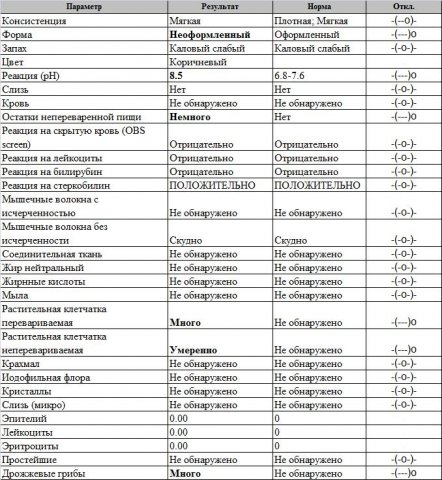
There may be other deviations that the norm of fecal analysis for a coprogram does not contain. As you can see for yourself, most of the problems are caused by a violation of the secretion of the pancreas, and the study of feces will help to identify the problem. Also, do not forget that it is necessary to collect the material following the instructions of the doctor. Preparation for the analysis of feces for a coprogram is a rather important step, as it will help eliminate the possibility of error and get the most accurate results which can even save a life.
