Focal hyperplasia of the integumentary pitted epithelium of the stomach. A complete description of the types of gastric hyperplasia
Hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa is one of the organ diseases digestive system, which are difficult to diagnose early stages. It is expressed in pathology, leading to an increased process of cell division in the body. Their excess leads to the appearance of polyps. Without proper treatment, these tumors become malignant.
Gastric hyperplasia has several forms. They differ from each other in their localization in the digestive organ. Doctors in their practice often encounter foveolar type disease and hyperplasia of the integumentary pitted epithelium of the digestive organ.
Features of foveal hyperplasia

Foveal hyperplasia of the stomach occurs as a result of severe cell proliferation epithelial type in the tissues of the stomach. Usually this phenomenon is observed in the mucous membrane of the organ. It is usually considered as a disease that does not lead to the development of malignant or benign tumors, which cannot be said about other forms of hyperplasia.
The disease usually occurs against the background of:
- Gastritis.
- Ulcers.
- Other inflammatory processes of the stomach.
Foveal hyperplasia in the area of the gastric mucosa in the initial stages does not cause severe discomfort. A person usually learns about this disease during a routine visit to the doctor.
Features of hyperplasia of the integumentary epithelium of the stomach
It is not so easy to detect hyperplasia of the integumentary epithelium of the digestive system. It manifests itself in functional changes that affect the activity of cells in the gastric mucosa. All this can be revealed only during histochemical examination or electron microscopy.
The disease can be detected by the following signs:
- The appearance of small gastric pits.
- Change appearance organ. He takes a corkscrew different shapes.
Hyperplasia of the integumentary pit epithelium of the entire stomach requires the same treatment as foveolar type disease. This is despite the fact that the two diseases have different symptoms.
Reasons for the development of various forms of hyperplasia
Hyperplasia is caused by various reasons. They are almost all the same for different forms of the disease. The disease can be provoked by:
- Hormonal imbalances in the body.
- Presence of untreated infectious diseases such as gastritis and ulcers.
- Inflammation of various stomach tissues.
- Problems in the intrasecretory work of the organ mucosa.
- Long-term impact on gastrointestinal tract toxic carcinogens.
- The presence of microorganisms of the Helicobacter pylori type in the body.
- Disturbed nervous regulation of the digestive system.
- Hereditary factor.
It is very important to correctly determine the cause that provoked gastric hyperplasia. This is what the attending physician will rely on when selecting individual therapy for the patient.
Symptoms of both types of hyperplasia

In the initial stages, the disease does not make itself felt. A person remains in good health, so he does not worry about his health again. Complaints begin to appear only after hyperplasia of the digestive organ begins to progress at an accelerated pace. This happens if a person continues to lead the same lifestyle that led to such an illness.
In later stages, the disease can be recognized by the following signs:
- Severe pain in the upper abdomen, where the stomach is located. Unpleasant sensations are caused by involuntary muscle contraction. The pain can be either temporary or permanent.
- Stomach dysfunction.
- Anemia cannot be ruled out.
When stomach pain occurs, many people try to suppress it with painkillers. But in this case you can’t do that. You should immediately contact a specialist so that he can find the cause of the discomfort and offer suitable treatment. This is especially important in the case of hyperplasia, since pain indicates its rapid development.

Diagnosis of hyperplasia

Hyperplasia is characterized by the proliferation of pathogenic cells in the body. Therefore, it can be identified by examining the problem organ from the inside. Special medical equipment helps doctors cope with this task.
To confirm the diagnosis of hyperplasia, the patient must undergo the following examinations:
- Radiography. With its help, you can see the number of polyps that have formed in the stomach due to the disease. The doctor will also notice a tumor if it has already formed.
- Ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract. Gives a similar result as with radiography.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy. One of the most unpleasant procedures for the patient. But she gives exact result, which helps the doctor see the whole picture of the disease. This examination is carried out by inserting a device into the organ. Thanks to him, the specialist examines existing polyps and other growths in detail.
- Biopsy. It should not be neglected either. The procedure allows you to determine the malignancy of the tumor in the stomach, which appeared due to hyperplasia.
Biopsy and endoscopy do not always allow correct diagnosis of polyps in the stomach. This is because with these forms of the disease, pseudogrowths often appear, which are not easy to distinguish from real formations.
Nutrition for hyperplasia of the gastrointestinal tract

In order for the treatment to give a positive result, the patient first needs to reconsider his diet. For stomach pathology, it is recommended to use:
- Fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Lean poultry meats.
- Low-fat fermented milk products.
- Various cereals.
The doctor must tell his patient about the dietary habits during the treatment and rehabilitation period. Also, such a diet will be recommended to them for preventive purposes to prevent relapse of the disease.
Treatment of various forms of hyperplasia of the digestive system organ
When treating the disease, it is impossible to do without drug therapy. Merely following a diet will not achieve any special results, since special nutrition is only an auxiliary means.
Treatment directly depends on the severity of hyperplasia:
- In the early stages, for recovery it is enough to take drugs whose action is aimed at eliminating the infection and pathogenic bacteria, settled in the stomach.
- If the disease progresses to a severe form, which is characterized by the appearance malignant tumors, then the patient will have to agree to the operation. After the cancerous tumors in his stomach are removed, he will have to take a course of medications. Diet in this case is mandatory.
Only those whose disease was diagnosed in the early stages can manage without surgical intervention. To avoid serious complications and long-term treatment, it is recommended to regularly visit a doctor to examine the gastrointestinal tract for benign and malignant neoplasms. Taking care of your own health will protect a person from serious problems.
Comments:
- Etiology and pathogenesis of the development of focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa
- Symptoms of focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa
- Diagnosis and treatment of focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa
It is believed that focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa is an early form of polyp formation. As a rule, such damage to the mucous membrane develops in the form benign tumor in one of the sectors of the stomach. The size of the lesion may vary, but upon examination, such a formation looks like a growth with a structure very different from the healthy tissue surrounding it.
When carrying out diagnostics, studies with contrast are indicative, since tissues with a changed structure, when paint gets on them, immediately change their color and differ significantly from the surrounding healthy tissues.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the development of focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa
Hyperplasia is pathological condition, in which an increase in the number of cells and the appearance of a neoplasm are observed. The main reason for the appearance of a neoplasm lies in the pathology of cell division. It is worth noting that cell division during hyperplasia occurs in a normal way, but the number of such divisions sharply increases. Thus, it turns out that in a separate area the number of cells is rapidly increasing. Over time, in addition to the pathological level of cell division, a change in the structure of the cell surface is observed, which is an extremely dangerous phenomenon, since under certain conditions these cells can acquire signs of malignancy. There are quite a few reasons that can provoke the appearance of hyperplasia, including:

- violation of the intrasecretory function of the stomach;
- hormonal imbalances;
- untreated stomach infections;
- pathology of the nervous regulation of the stomach;
- hereditary predisposition to focal hyperplasia;
- exposure to the mucous membrane of carcinogens and other harmful chemicals;
- the presence of certain types of bacteria in the body;
- advanced chronic inflammatory processes with damage to the gastric mucosa;
- chronic gastritis and stomach ulcers.
With hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa, there is an increase in the rate of cell division of the mucous membrane. The gastric mucosa consists of many layers, which is why there are many types of hyperplasia in this area. For example, antral hyperplasia is the most common, since this area occupies a significant part of the stomach. As a rule, hyperplasia in this part leads to the appearance of multiple focal growths of a relatively small size.
Lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the stomach develops due to an increase in cell production in the follicular section of the gastric mucosa. Another common pathology of this type is lymphoid mucosal hyperplasia, which is a pseudolymphomatous formation that develops against the background of a chronic gastric ulcer. Among other things, types of damage to the mucous membrane may include hyperplasia of the integumentary pit epithelium, accompanied by the accumulation of mucin in the cells and the displacement of the nucleus to the base of the cell. This form of hyperplasia is accompanied by the appearance of new pits with a corkscrew shape. In chronic cases, foveal hyperplasia is more often observed, characterized by the proliferation of epithelial cells not only of the mucous membrane, but also of deeper tissues.
Return to contents
Symptoms of focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa
 Like many other diseases, hyperplasia can long time be asymptomatic, which is why this disease is so dangerous. The thing is that most people ignore routine examinations and try not to visit doctors unless they have obvious signs of pathology in the functioning of certain organs. Thus, many people are not even aware of the presence of the disease until it becomes advanced or chronic.
Like many other diseases, hyperplasia can long time be asymptomatic, which is why this disease is so dangerous. The thing is that most people ignore routine examinations and try not to visit doctors unless they have obvious signs of pathology in the functioning of certain organs. Thus, many people are not even aware of the presence of the disease until it becomes advanced or chronic.
After a certain time, characteristic signs of the development of the disease may appear. Most characteristic feature the onset of the disease is severe pain. Considering that focal hyperplasia develops against the background of erosive processes affecting the gastric mucosa, the pain syndrome can manifest itself especially clearly. Often painful attacks can be accompanied by involuntary muscle contractions. Pain syndrome with focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa can be expressed by short-term attacks or be chronic.
Among other things, the development of focal hyperplasia may be accompanied by digestive disorders. Signs of anemia, which may occur from time to time, are also indicative.
If such symptoms appear, you should not self-medicate, as this can accelerate pathological process and an increase in the number of outbreaks of disease.
Return to contents
Diagnosis and treatment of focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa
 The existing symptomatic manifestations may not be sufficient to make a diagnosis and identify all characteristic features lesions of the gastric mucosa.
The existing symptomatic manifestations may not be sufficient to make a diagnosis and identify all characteristic features lesions of the gastric mucosa.
At the first meeting, doctors, as a rule, interview patients, recreating the medical history.
In order to confirm the diagnosis, a number of tests and studies are required. First of all, radiography is performed, which allows you to quickly identify polyps and the outlines of existing tumors. If hyperplasia is suspected, fibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed.
This research method is perhaps the most productive. During fibrogastroduodenoscopy, a camera is inserted using a special instrument, which allows you to very accurately examine all the walls of the stomach and identify possible deviations.
If an area of obvious pathology is identified, a biopsy may be ordered. A biopsy is an invasive research method that involves taking tissues that differ in pathological structure to identify its morphological composition, as well as the degree of malignancy.
 The basis of treatment and prevention of the appearance of focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa is to establish control over the diet. Poor quality food should be completely eliminated from high content fat In addition, you should learn to eat on time and in small quantities. To create a diet, you should consult a nutritionist.
The basis of treatment and prevention of the appearance of focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa is to establish control over the diet. Poor quality food should be completely eliminated from high content fat In addition, you should learn to eat on time and in small quantities. To create a diet, you should consult a nutritionist.
To prescribe drug treatment, it is very important to identify the root cause of the development of hyperplasia. In most cases, hormonal drugs are prescribed to quickly restore normal speed cell division. In cases where a strict diet and drug treatment do not give the desired effect, a repeated course of treatment may be prescribed.
Hyperplasia is a disease that can affect any internal organ of the body, but most often in practice it is gastric hyperplasia that can be encountered. The disease is quite complex and requires a quick solution to the problem, and self-medication in a particular case is simply impossible!
Hyperplasia is an accelerated intensive growth of cells of the stomach and adjacent tissues. Reproduction occurs by cell division, that is, naturally. Gastric hyperplasia is a pathology of the mucous membranes of the stomach, the result of which is a sharp increase in the number of cells of mucous tissue. As a result of such rapid cell growth, the walls of the stomach thicken and polyps (small tumors) appear.
At more serious stages of the development of the disease, changes occur in the structure of the cells themselves, and this is direct evidence of the beginning of the development of a malignant tumor. Hyperplasia is not a clinical diagnosis, but only states histological changes in the gastric mucosa. There are many forms of hyperplasia.
Gastric hyperplasia is the body's reaction to unexpected damage to the walls of the stomach (both physical and pathological), which can be caused by a number of reasons. The most common causes of such damage are:
- Gastritis and other acute inflammations of mucous tissues. Inflammation is one of the main causes of active cell division, leading to the formation of polyps. Everyone has probably heard about such a bacterium as Helicobacter pillory, which is the cause diffuse changes epigastric region;
- General hormonal imbalances. For example, an excess of estrogen in the body can cause the development of hyperplasia;
- Heredity. One of the possible hereditary diseases in the female line is adenomatous polyposis. This is a very rare disease that is inherited. If it is present, polyps begin to form at the bottom of the stomach;
- Long-term use medicines. Very often when increased acetone, people are prescribed special inhibitor drugs that help reduce acidity. With their long-term use, the walls of the stomach suffer, and accordingly, damage is formed that provokes this disease;
- Disturbed hormonal balance of the stomach. In the presence of functional disorders in the functioning of the duodenum, the body actively produces gastrin, a substance that irritates mucous tissues.
These are direct causes that lead directly to the development of the disease itself. But there are a number of other factors that can provoke this disease or accelerate the process of its development, namely:
- Gastric ulcer of any type;
- Disorders of the nervous system;
- Various infectious diseases of the stomach (Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and others);
- Negative effects of carcinogens and other chemicals. Typically occurs when frequent use sweet carbonated drinks;
- Dysfunction of internal secretion.
Very often, hyperplasia occurs as a result of incomplete treatment of any stomach diseases.
Types of hyperplasia
Today, there are a large number of types of hyperplasia. They all differ in that each of them has its own individual pathogenesis and affects a specific area of the stomach. The main types include:
- Focal hyperplasia of the stomach. It is generally accepted that focal hyperplasia is the beginning of the development of all subsequent types and the formation of polyps. In this case, a specific, clearly limited area of the mucous membrane is affected. Lesions can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes. Such changes are very noticeable, as they have a completely different color and stand out noticeably against the background of healthy tissue. Focal hyperplasia begins with the formation of one lesion and during development forms polyps in each gastric section, for which reason it is often called wart;
- Lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the stomach is one of the most common types of disease, which is diagnosed in both men and women of various age categories. The cause of this type of disease is various inflammatory processes in the gastric mucosa, as well as food additives containing substances marked with the symbol E (carcinogenic group);
- Lymphoid hyperplasia. Due to amplification inflammatory process, the number of lymphocytes in mucous tissues increases, which leads to inflammation lymph nodes;
- Hyperplasia cover epithelium stomach. The walls of the stomach are covered with a thin layer of epithelium, which begins to grow rapidly during development of this disease. This causes changes in the tissue structure of the epithelium itself and often leads to the development of malignant tumors. Hyperplasia of the integumentary pit epithelium is considered the most dangerous type of disease;
- Glandular hyperplasia. This type is characterized by a structural change in the internal glands, as a result of which growths are formed in their place, the bodies of which consist of glandular cells;
- Polypoid is one of the most dangerous and common forms. This is a benign neoplasm containing many immune response cells (leukocytes, macrophages). These growths can be up to 2 centimeters in diameter and, with the slightest structural changes, can degenerate into malignant ones;
- Antral. The antrum is a kind of closing valve that transfers processed food from the stomach directly to the intestines. The cause of damage to this section is an ulcer;
- Foveal hyperplasia of the stomach is a curvature of the folds of the mucous membranes of the stomach, an increase in their length and density. It is provoked by taking various anti-inflammatory drugs non-steroidal drugs. It is this form that is characterized by the most severe symptoms.

Scientists do not yet fully understand the reasons for the formation of such changes, since very often there are cases when damage to the stomach by polyps occurs in absolute health of the body, in particular, the mucous membranes of the stomach.
Symptoms
Quite often, in the initial stages of the development of the disease, a person does not feel any obvious symptoms, and, accordingly, has no idea about the progression of the disease. This is precisely where the danger of bottom pathology lies. But after a certain period of time, during the active stage of development, the disease gradually makes itself felt, accompanied by symptoms such as:
- Severe and prolonged pain inside the abdomen, especially in the upper part. These pains can be different, there is a burning sensation, sharp tingling, pressing aching pain;
- A belch appears, which is accompanied by a long and sour taste;
- At more progressive stages, nausea and vomiting appear;
- Severe bloating occurs;
- Hiccups appear;
- Lost appetite.

Against the background of all these phenomena, accompanying symptoms appear:
- Increase in temperature;
- General weakness;
- Body aches;
- Possible dizziness;
- Frequent bowel movements;
- Low blood pressure;
- Belching may release blood;
- The skin becomes paler.
If you begin to feel several symptoms at once that worry you quite for a long time, you should consult a doctor immediately. Only he will, if necessary, appoint correct treatment. The process of recovery and rehabilitation of the body with this disease directly depends on the time when the disease was identified. The earlier the diagnosis was made, the easier and faster the body will recover.
Diagnosis of the disease
There are several methods for diagnosing this disease, which, as a rule, are used in combination to obtain the most accurate result and further confirm or exclude it. These methods include:
- General and biochemical analysis blood;
- Radiography;
- Endoscopy. These include colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy;
- FGDS – fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This method allows you to examine the walls of the stomach and recognize polyps and tumors.
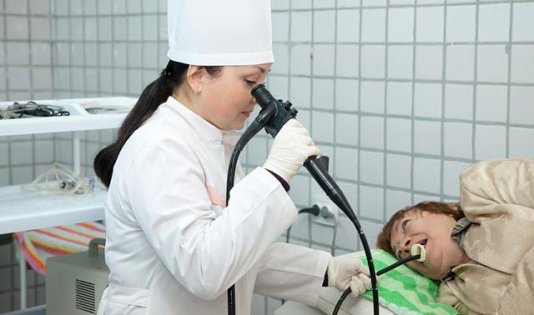
It is absolutely not advisable to carry out computed tomography and MRI for this disease, since this technique does not show all the changes that occur in the stomach. If necessary, the doctor can take gastric juice for examination. Naturally, before the doctor prescribes certain tests, he must analyze all the symptoms that the patient experiences.
Treatment
The treatment method directly depends on the cause of the disease. But, for all types of hyperplasia, there is a standard treatment regimen:
- Antibiotics that should relieve inflammation, eliminate pain symptoms, and also overcome infection and bacteria that provoked the development of the disease (Metronidazole, Clarithromycin, Levofloxacin, Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin, Tetracycline);
- Inhibitory drugs that prevent acid secretion in the stomach (Omeprazole, Vasonat, Pantoprazole);
- Bismuth preparations. These are special products that restore the mucous membranes of the stomach, normalize the secretion, properties and structure of the mucous tissue, and also create unfavorable conditions for the development of the bacterium Helicobacter pillory.
Only the attending physician should select drugs for drug therapy, based on the clinical picture according to all studies conducted. Treatment will take a total of 7 to 14 days.
Very often, as a concomitant treatment, doctors recommend to patients old folk remedies, namely:
- Tea with ginger. Ginger root is a powerful antibacterial and antiseptic, which kills all harmful bacteria, including Helicobacter pillory;
- Chamomile. Chamomile tea perfectly relieves inflammation, eliminates pain and relieves tension. muscle tissue stomach;
- Peppermint. Adding a few mint leaves to your tea can help relieve nausea and heartburn during treatment.
In the presence of malignant tumors, inflammation of the gastric lymph or oncology, treatment includes biopsy, surgery and chemotherapy.
Diet
As with any other severe form of pathology of the stomach or intestines, it is necessary to reduce the load on the digestive organs to an absolute minimum. Just sticking dietary nutrition, the disease will disappear quickly and forever. As a rule, they use diet No. 5 according to Pevzner, the rules of which are:
- Meals should be fractional (small portions, but 5-6 times a day);
- Food should not contain any spices, should not be sour, spicy or salty;
- During the treatment period, it is necessary to completely eliminate vegetable fats;
- It is forbidden to eat fried foods;
- Carbonated drinks, juices, and alcohol are strictly prohibited;
- Meat and fish only of low-fat varieties and only boiled or steamed;
- To quickly restore damaged tissues, you need to consume more complex fiber (porridge).
Remember that hyperplasia is not a diagnosed disease, but occurs as a result of chronic pathologies of the mucous membranes of the stomach, which most often lead to gastritis and gastric ulcers. Treatment depends entirely on the cause that caused these disorders. If you follow all the recommendations of your doctor and follow a dietary diet during treatment and during the rehabilitation period, full recovery occurs as soon as possible.
Causes of development of hyperplasia of mucous membranes and muscle tissue internal organs– sudden acceleration of cell division. This is mainly due to poor nutrition, changes in hormonal levels and poor heredity.
In cases of advanced gastritis and ulcers, doctors most often encounter focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa. Most types of cell regeneration pathology do not have symptoms or serious complications at the initial stage of development. Over time, they become the basis for the formation of polyps, fibroids, cysts and malignant tumors.
Causes of focal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa
Doctors call hyperplasia an endoscopic disease. In most cases, there are no symptoms of pathology; thickening of the epithelium as a result of a high rate of cell division is detected when examining the stomach with an endoscope. The exact type of disease can only be determined after a tissue biopsy.
The causes of the disease and the characteristics of its course are varied:
- For chronic inflammation due to the presence of the pathogen Helicobacter Pylori in the mucosa, take regularly non-steroidal drugs. Anti-inflammatory medications, when used over a long period of time, can cause cell division to accelerate. Acidity-reducing inhibitors also produce a similar result. proton pump. The oxygen released when consumed accelerates tissue regeneration. Long-term use will provoke cell division accelerated several times.
- Presence of gastritis and regular intake hormonal drugs creates conditions for the formation of thickenings in mucous and glandular tissues.
- A rare hereditary disease such as adenomatous polyposis manifests itself in the form of glandular hyperplasia in the antrum. Hyperplastic polyps grow in the lower part of the stomach, near the exit of food into the intestines.
- Hormonal imbalance. The cause of hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa is an excess of the female hormone estrogen. In some cases, tissue thickening begins in women in the uterus and gradually affects neighboring organs. When affected by a tumor duodenum The hormone gastrin is released, which also provokes the formation of thickening of the mucous membrane and its scarring.
- With catarrhal chronic gastritis with high acidity, hyperplasia occurs. As a result of inflammation and constant irritation of the mucous membrane at the site of tissue damage, accelerated cell regeneration may begin with scarring and the formation of excess tissue.
Types and symptoms of focal hyperplasia
Based on the etiology and pathogenesis - the characteristics of the course of diseases and the form of formations, several types of gastric hyperplasia are distinguished:
- Focal.
- Foveolar.
- Antral.
- Glandular.
- Covering epithelium.
- Lymphofolicular.
- Polypoid.
- Lymphoid.
On initial stage During their development, all types of hyperplasia do not have symptoms. They are discovered by chance during examination of a patient with gastritis or a stomach ulcer. The type of growth formation can be determined only by the results of chemical and biological studies of a sample of damaged tissue. Progressive cell division at the initial stage of the disease cannot be determined. Only with endoscopy of the stomach can the doctor notice already formed thickenings in the mucous membrane. By taking a tissue sample for analysis, a decision is finally made about the development of hyperplasia and its type is determined.
Subsequently, symptoms similar to those of advanced disease appear in most types of gastritis:
- Indigestion.
- Nausea.
- Pain with muscle tension.
- Poor digestion of food.
- Anemia.
By palpating the patient's abdomen, the doctor determines the presence of thickenings or tumors. Polyps in the antrum cause severe constant pain.
Focal mucosal hyperplasia
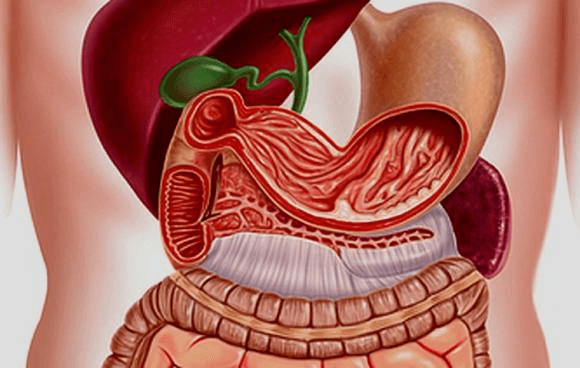
According to the localization of formations, mucosal hyperplasia is divided:
- Focal.
- Foveolar.
Focal hyperplasia of the stomach is characterized by a single formation in the form of a tubercle at the site of inflammation. In addition to single ones, several small tubercles may form, usually located in one area of the stomach. Upon examination, the thickening usually has a round or oval shape, protruding above the underlying tissues. Subsequently, they can rise above the surface on a stalk. The focal form of hyperplasia is considered the initial stage of the disease. At the site of the formation of thickenings in the mucous membrane, there are accumulations of Helicobacter pylori bacteria.
When examined with an X-ray with a contrast composition, such tissue damage stands out on the surface of the mucous membrane as a wart. Experts have given a second name to the disease – wart hyperplasia. At the initial stage of development, there are no symptoms. The disease is detected when endoscopic examination patient with gastritis or ulcer. In its development, the focal form of mucosal hyperplasia turns into a more complex form - polypoid. Does not form malignant tumors.
Focal mucosal hyperplasia often develops against the background of atrophic gastritis. Thickenings of rapidly regenerating cells are surrounded by dead tissue. The thickenings themselves do not turn into cancerous tumors. The process of food absorption is disrupted, and the concentration of hydrochloric acid increases. When the disease is advanced, polyps form at the site of hyperplasia. Appear severe pain in the stomach. Growths with legs are cut off without dissection abdominal cavity using an endoscope. Polyps that are not amenable to therapeutic treatment and have grown into the walls are excised.
Foveal hyperplasia of the stomach is characterized by damage to large areas of the mucosa and can spread to the entire inner surface of the stomach. It has a complex branched structure, identified by the increased protrusion of the folds. Often occurs against the background of advanced catarrhal, diffuse and erosive gastritis, as a more severe form of the disease in the absence of treatment.
Polypoid hyperplasia and its consequences
Pathological neoplasms differ from ordinary polyps:
- Rapid growth.
- They have an uneven shape, an accumulation of cells of various origins.
- The erosive surface may bleed.
- When the size reaches 2 cm, the process of malignization begins - the degeneration of cells into cancerous ones.
Polyps can grow from the mucosa and have a stalk. Contain a large number of autoimmune and glandular cells. When polypoid hyperplasia is diagnosed, surgery is prescribed to remove them. Under the epithelium of the mucous membrane there are a large number of lymph nodes and vessels. As a result of infectious diseases, the number of lymphatic cells increases sharply. Growths form on the capillaries and enlargement of the lymph nodes due to their proliferation. Experts cannot accurately name the causes of lymphoid hyperplasia of the mucous membrane.
The pathology can be focal in any area of the stomach and affect the entire surface. It develops at the site of a chronic ulcer or inflammation in the absence of treatment. Symptoms at the initial stage are limited to hunger pains at night. Lymphoid polyps are removed surgically.
Thickening in the tissues of the antrum
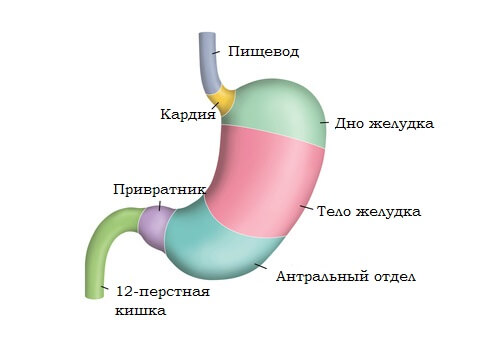
Changes in hormonal levels associated with an imbalance of intrasecretory work. There is an increase in the production of some enzymes by reducing the number of others. Tissue decomposition is disrupted, decay products are not excreted in the usual way and accumulate in the follicular tissue. This leads to the formation of lymphofolicular hyperplasia of the mucosa. Another reason is the accumulation of carcinogenic substances on the walls of the stomach and tissue intoxication. Lymphofolicular hyperplasia often develops into cancer.
The antrum of the stomach constantly experiences heavy loads associated with its functions. It is where the final processing of food occurs, its neutralization with alkali, and pushing into the intestines. This area of the organ is most susceptible to the formation of hyperplasia of all types. Symptoms include heaviness in the stomach and belching. When reflux occurs, a burning sensation and pain appear in the navel area.
Treatment is carried out with antibiotics, since the main causative agent of the disease is Helicobacter Pylori. At the same time, drugs that reduce acidity and diet are prescribed. When the stomach tissue is deeply damaged by bacteria, accelerated division of glandular cells occurs. They rise above the mucous surface in the form of warty growths. As a result, additional release of hydrochloric acid occurs, its concentration in gastric juice increases.
Thickening of the mucous layer and diagnosis of pathology
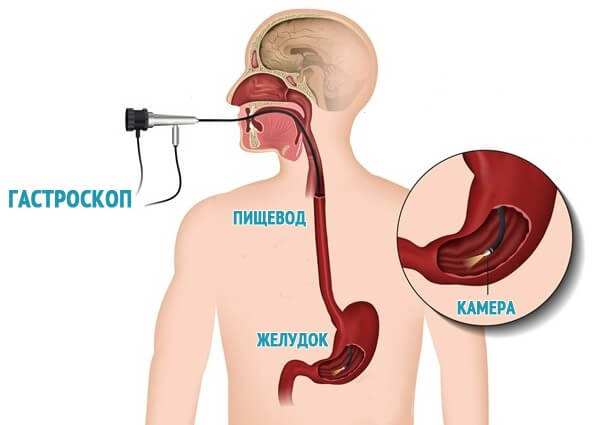
Mild and common forms include hyperplasia of the epithelium - the upper layer of the mucous membrane. As a result of inflammation, the number of glandular cells that produce mucus increases. The inner protective layer begins to thicken in places or over the entire surface. New holes form between the branched growths and old ones deepen. The amount of mucin in the cells increases and the nucleus shifts.
This thickening enhances the protective functions of the mucosa from the effects of hydrochloric acid. The epithelium does not degenerate into malignant formations. At the same time, the stomach walls absorb nutrients less well. A thick layer of mucus reduces muscle flexibility and the movement of food to the intestines is inhibited. At the initial stage there are no symptoms. Then appear:
- Heaviness in the stomach.
- Belching sour.
- Nausea.
- Weakness.
- Lack of appetite.
- Weight loss.
It is impossible to diagnose hyperplasia of the integumentary layer based on symptoms. It is necessary to carry out a full cycle of studies, including a biopsy of mucosal tissue. Standard blood and urine tests for gastrointestinal diseases are taken from the patient. They are examined for traces of bacterial activity. Contrast x-rays show changes in tissue. At the site of formation of thickenings, polyps and other growths, it changes the color of the tissue in the picture.
Ultrasound indicates the localization of formations, their size and the degree of tissue damage. Using ultrasound, the doctor makes sure that there are no malignant tumors or metastases. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy allows the doctor to visually examine the inner surface of the stomach wall and take a tissue sample for examination. After this, the type of mucosal hyperplasia is determined and prescribed drug therapy or surgery.
