The norm of a blood test at 3 months decoding. Norms and interpretation of the clinical (general) blood test in children
A general blood test in children is an important element of medical monitoring of the child's health. After childbirth, this is the second acquaintance of a newborn baby with doctors. Survey baby necessary to obtain diagnostic data on the state of his health. Further monitoring of the growing generation is carried out until the closing of the children's medical record 026 / y at 16 years old.
Complete blood count (CBC) is the standard, most used clinical study in medicine. Conducting this type of examination is a necessary condition for any outpatient treatment, without which it is impossible to imagine any academic therapy.
The general blood test is also called clinical trial blood, since according to the medical classification it is part of the general clinical examination methods. The study is divided into narrow (1-2 parameters), standard (up to 10 parameters) and extended (more than 10 parameters).
 The research task of the examination includes the study of erythrocytes - red blood cells that contain the hemoglobin polypeptide, which stains the cell in a characteristic scarlet color; leukocytes - white blood cells that do not have pigment (eosinophils, platelets, basophils, monocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes); hemoglobin level and hematocrit (the volume of red blood cells to the total blood volume); erythrocyte sedimentation rate; color index (required if the analysis was done manually).
The research task of the examination includes the study of erythrocytes - red blood cells that contain the hemoglobin polypeptide, which stains the cell in a characteristic scarlet color; leukocytes - white blood cells that do not have pigment (eosinophils, platelets, basophils, monocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes); hemoglobin level and hematocrit (the volume of red blood cells to the total blood volume); erythrocyte sedimentation rate; color index (required if the analysis was done manually).
Attention! The bodies of an adult and a child are significantly different from each other. The child has a different metabolism, different nervous system, other life cycles, another clinic of diseases.
Table of norms for a general blood test in children
Norms general analysis blood samples in children are needed to actually understand where the range of high and low values lies, suggesting possible pathologies in children's health.
| Indicators | Index | Unit. |
Normal values |
||||
| first week of life | up to a year | from 1 to 6 years old | from 6 to 12 years old | 12 to 16 years old | |||
| -MCHC- | % | 0,86-1,16 | 0,74-0,94 | 0,82-1,05 | 0,82-1,05 | 0,82-1,05 | |
| Lymphocytes | -LYM- | % | 22,1-55,1 | 38,1-72,1 | 26,1-60,1 | 24,1-54,1 | 25,1-50,1 |
| Eosinophils | -EOS- | % | 2,1-7,15 | 1,1-6,15 | 1,1-6,15 | 1,1-6,15 | 1,15-5,0 |
| Basophils | -BAS- | % | 0-1 | 0-1 | 0-1 | 0-1 | 0-1 |
| Neutrophils are segmented | – | % | 30,1-50,1 | 15,1-45,1 | 25,1-60,15 | 35,1-65,2 | 40,1-65,2 |
| Neutrophils are stab | – | % | 0,51-4,1 | 1,1-5,0 | 1,1-5,0 | 1,1-5,0 | 1,1-5,0 |
| red blood cells | -RBC- | x1012 cells /l | 4,41-6,61 | 3,61-4,91 | 3,51-4,51 | 3,51-4,71 | 3,61-5,12 |
| Reticulocytes | -RTC- | ppm | 3-15 | 3-12 | 2-12 | 2-11 | 2-11 |
| thrombocrit | -PST- | % | 0,16-0,37 | 0,16-0,37 | 0,16-0,37 | 0,16-0,37 | 0,16-0,37 |
| Leukocytes | -WBC- | 109 cells/l | 7,21-18,51 | 6,15-12,0 | 5,1-12 | 4,4-10 | 4,3-9,5 |
| Hemoglobin | -Hb- | g/l | 138-220 | 99-138 | 109-144 | 114-148 | 114-150 |
| -ESR- | mm/hour | 0,1-2,0 | 2,0-12 | 2,0-10 | 2,0-10 | 2,0-10 | |
| Monocytes | -MON- | % | 2,0-12 | 2,0-12 | 2,0-10 | 2,0-10 | 2,0-10 |
| platelets | -PLT- | 109 cells/l | 180,5-400 | 180,5-400 | 180,5-400 | 157-380 | 157-390 |
Attention! The norms of a clinical blood test for children, the data in this table may differ from those on the Internet. In any case, the information provided is for informational purposes and is not intended to become a reason for parents to self-treat their children.
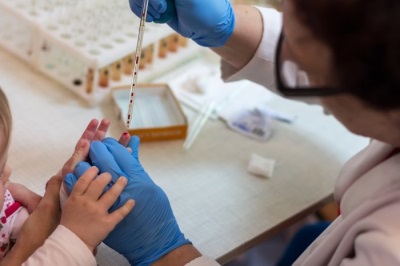
Preparing a child for a general blood test
Before the tests, it is very important to prepare the child not so much physiologically as psychologically - children, especially at a young age, experience stress during the blood sampling procedure, so in this part of the article we will talk not only about physiological, but also psychological measures of influence on a small patient.
Physiological measures to prepare the child for analysis
 Blood sampling for analysis is done in the morning on an empty stomach. In the case of a general blood test - not a mandatory rule, as, for example, with a biochemical study - there the requirements are more stringent, but you should still refrain from eating a lot of food before starting the procedure. The volume of blood in a child in relation to the volume of the body is greater than that of an adult, therefore any physiological acts, whether it is sleep, eating or toileting, are important for the result of the study.
Blood sampling for analysis is done in the morning on an empty stomach. In the case of a general blood test - not a mandatory rule, as, for example, with a biochemical study - there the requirements are more stringent, but you should still refrain from eating a lot of food before starting the procedure. The volume of blood in a child in relation to the volume of the body is greater than that of an adult, therefore any physiological acts, whether it is sleep, eating or toileting, are important for the result of the study.
Before the examination, the child should sleep - this is reflected in the behavior of red blood cells; eat a little - slightly sweet tea, unsweetened porridge with a minimum of fat; go to the toilet - the release of the body from toxins affects the quality of the blood. The child should not play sports, experience physical activity before the procedure.
Attention! A general blood test in an infant has its own characteristics of preparation, for example, if a mother feeds a child before the procedure, this may affect the result of the analysis.
Psychological preparation of children before the blood sampling procedure
In this section, we will not talk about very young children, the responsibility for which lies entirely with the mother, we will only note that psychological condition mother is very important for the child. If the mother is irritated and restless, this will definitely be passed on to the baby.
Starting from the moment when the child has realized himself as a person, he begins to oppose himself to the environment, which leads to all sorts of conflicts. Children more strongly than adults experience a sense of fear. It’s good that this feeling is irrational and can be “turned off” by adding positive emotions. Therefore, it is important to keep calm, cordiality and benevolence next to the children during the procedural moments.
Deciphering the values of indicators of the UAC
 Modern laboratories equipped special machines, which reduce the work of laboratory assistants to a minimum - it is enough to fill the material into the device and in a moment the result will be ready. However, in today's medicine there is no unconditional trust in machines - most of the analyzes are rechecked manually. Machine-assisted screening sparks online boom in interest in specific medical terms and designations. Patients, having received a leaflet issued by a laboratory machine, rarely have the opportunity to satisfy their curiosity on the spot, to engage in an independent study of their health status.
Modern laboratories equipped special machines, which reduce the work of laboratory assistants to a minimum - it is enough to fill the material into the device and in a moment the result will be ready. However, in today's medicine there is no unconditional trust in machines - most of the analyzes are rechecked manually. Machine-assisted screening sparks online boom in interest in specific medical terms and designations. Patients, having received a leaflet issued by a laboratory machine, rarely have the opportunity to satisfy their curiosity on the spot, to engage in an independent study of their health status.
Attention! Deciphering the results of a general blood test will only make sense if a table of norms for children is used. The norms given in the table will show where the high and low value is.
Color option
This indicator of a clinical blood test is needed when we are talking about manual research. What does this parameter show? In a simplified explanation, this indicator serves to measure the hemoglobin content in red blood cells. 
The color indicator has three main values:
- hypochromia - there is almost no hemoglobin in the cell, which is why its nucleus is discolored;
- normochromia - hemoglobin is normal, the nucleus is lighter than the circle, does not merge in color with the body of the erythrocyte;
- hyperchromia - the cell is excessively saturated with hemoglobin, the color of the nucleus merges with the color of the erythrocyte body.
Lymphocytes
There are many lymphocytes various kinds and types, which, however, is not of particular importance in a clinical blood test. Lymphocytes are an integral part of human immunity.
Eosinophils
Eosinophils are white blood cells that are susceptible to eosin, a laboratory dye that can show them on instrument glass. They have the ability to phagocytosis.
Basophils
The largest of the granulocytes (a group of white blood cells). Take part in the first phase of the immune response (allergic reaction). They can carry immunoglobulin E granules, like killer lymphocytes. Absorb poisons, preventing them from penetrating the tissues of the body.
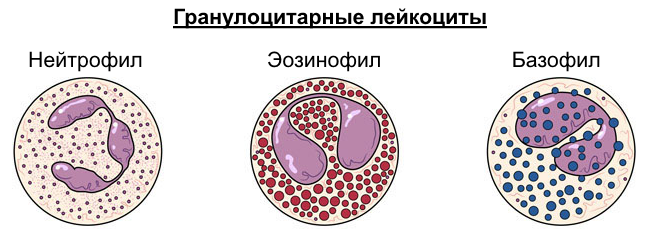
Neutrophils
Neutrophils are white blood cells involved in phagocytosis. After the act of phagocytosis, they die.
red blood cells
Erythrocytes are cells that contain the polypeptide pigment hemoglobin. Erythrocytes play an important role in the body, delivering oxygen to the tissues, taking carbon.
Reticulocytes
Reticulocytes are the medical term for immature red blood cells. Children have more reticulocytes than adults, which is explained by the growth factor of a young organism.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
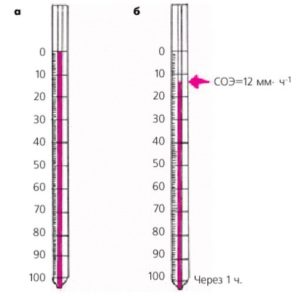 This parameter serves as a non-specific indicator of the definition of many different ailments. An accelerated rate of red blood cell sedimentation may be the result of a starvation diet, dehydration of the body, significant physical activity. If the erythrocyte sedimentation rate significantly exceeds the norm, then this will indicate the development in the patient infectious disease, inflammatory process, poisoning with organic poisons. The exact interpretation of the diagnosis depends on other parameters of the clinical blood test.
This parameter serves as a non-specific indicator of the definition of many different ailments. An accelerated rate of red blood cell sedimentation may be the result of a starvation diet, dehydration of the body, significant physical activity. If the erythrocyte sedimentation rate significantly exceeds the norm, then this will indicate the development in the patient infectious disease, inflammatory process, poisoning with organic poisons. The exact interpretation of the diagnosis depends on other parameters of the clinical blood test.
Leukocytes
Leukocytes is the common name for all white blood cells. Leukocytes are divided into granular (basophilic, neutrophilic, eosinophilic granulocytes) and non-granular (agranulocytes - platelets, monocytes). The presence of leukocytes in the blood above the norm can be a sign of an infectious disease, leukemia, or an inflammatory process. If the leukocyte count is less than normal, this will indicate the possible development of radiation injury, viral infections(rubella, typhoid, AIDS, hepatitis, measles).
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a pigment polypeptide that can retain and release oxygen due to the content of iron atoms.
Monocytes
Monocytes are the most active phagocytes among other white blood cells.
platelets
Platelets are non-nuclear, flattened cell formations that do not have color. Platelets are formed from the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes. Platelets play an important role in the process of blood clotting.
Complete blood count in children: decoding and norms of indicators. In order to reliably assess the state of the child's body, the doctor prescribes a general blood test for each child. Such a study helps a specialist in diagnosing a specific disease. In addition, the UAC gives health worker a lot of information about the health of the child, the effectiveness of the treatment, as well as the patient's risk for certain types of diseases. That is why all children regularly take a general blood test as a preventive measure, as well as during use. drug therapy. Conducting this study involves taking blood, which is carried out quite quickly, and is also not considered too painful for children.
A clinical blood test is the most simple and at the same time understandable diagnostic method which gives a lot useful information showing the general condition of the child's body.
With its help it is possible:- establish the presence of inflammation in the body;
- identify hidden reserves;
- find out the cause of an infection caused by bacteria or viruses that are dangerous to health;
- to establish whether there is enough oxygen supplied to organs and systems - this is easy to do according to hemoglobin readings.
It’s not enough just to donate blood medical research, it is important to correctly decipher the results obtained. Deciphering the results of tests in a child should be performed by the attending physician. He will compare the results obtained with the patient's general health indicators and, based on them, make the final diagnosis. But it is equally important to know about the decoding of the UAC in children to their parents. This must be done so that parents understand the doctor when explaining the results to them, namely about high or low rates.
It is necessary to understand well what a certain indicator, which is indicated in the form, means. It is also worth knowing about the deviations of these indicators from normal, because they indicate the development of diseases in the body.
As mentioned above, KLA is the basis for the diagnosis of many common diseases. If necessary, additional types of hematological examination can be carried out simultaneously with it.
It must be remembered that any hospital may have its own characteristics, which are directly related to the equipment settings and the state of the reagents. Therefore, when deciphering the analyzes, it is necessary to compare the results obtained with the indications of the norm indicated on the form.
When taking a clinical blood test in children, you should know that special preparation for this procedure is not needed. Therefore, it is prescribed not only to determine the type of disease, but also upon admission to the hospital.
But if there is no particular hurry, then in order to get the right and reliable result it is desirable to follow certain rules:- The child does not need to be fed before the study, as this can change normal indicators (to drink half an hour before the analysis is also prohibited).
- It is best to donate blood in the morning, while the child is not very hungry.
- So that children are not afraid of an injection, you need to set them up for this procedure, since severe stress can significantly change the properties of the blood - then the analysis will certainly not be normal.
It is worth knowing that the results of the OAC in childhood are significantly different from those in an adult, because the immune system V children's body functions differently.
In the human blood there is a liquid part and cells responsible for delivering oxygen to systems and organs, as well as protecting the body from all diseases. It is these types of cells (leukocytes, platelets and erythrocytes) that are considered and evaluated by the doctor during the OAC. The quality and appearance of these cells shows the doctor about possible diseases child, as well as the reasons for their development in the body.
 Having received the results of a clinical blood test, it is necessary to evaluate its design, since the results indicated in it may have distinctive features. This is due to the type of study that was assigned by the doctor to the patient, namely, short or detailed.
Having received the results of a clinical blood test, it is necessary to evaluate its design, since the results indicated in it may have distinctive features. This is due to the type of study that was assigned by the doctor to the patient, namely, short or detailed.
- hemoglobin level;
- the level of leukocytes;
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
This blood test allows you to assess the condition of the child, but maximum information can only be obtained when the patient is assigned a detailed analysis.
It includes determining the number of shaped elements and other equally important indicators.- Hemoglobin (Hb). This complex protein and the main component of red blood cells, is involved in the transfer of oxygen from the lungs throughout the body. Hemoglobin also helps to remove carbon dioxide and keep the acid balance in a normal state.
- Red blood cells (RBCs). Most of the substances in the blood are erythrocytes containing hemoglobin.
- Average volume (CV). This is an erythrocyte index, of a relative nature, which indicates the volume of erythrocytes in the blood.
- Color index (MSN). Indicates the amount of hemoglobin present in an erythrocyte.
- Reticulocytes (RTC). These substances are new red blood cells that are able to express the body's need for the formation of new red cells. For example, such a condition appears as a result of severe blood loss or the development of certain diseases.
- Platelets (PLT). These are transparent small blood cells that have a spherical shape and are distinguished by the absence of a nucleus. Such elements are responsible for normal blood clotting, therefore they are of great importance in the healing of damaged organs and tissues.
- Thrombocrit (PCT). This is an important indicator that helps to assess the risk of possible thrombosis and bleeding. It is reflected by the ratio of platelet mass to the total blood volume.
- ESR (ESR). This is an abbreviated name for the time of erythrocyte sedimentation in the blood. It is worth noting that this study It is considered the most important indicator of KLA, since thanks to it it is possible to determine the course of a certain disease.
- Leukocytes (WBC). This is a group of cells that does not have a nucleus and is characterized by the absence of color. These elements successfully protect the body from the penetration of various dangerous viruses and other compounds.
- Lymphocytes (LYM). These are elements of the blood that are part of the immune system. These substances circulate circulatory system and tissues of the body and protect it from foreign cells that have got inside.
- Monocytes (MON). These elements are large white blood cells that are responsible for cleansing the blood of cells and other substances. These monocytes are capable of destroying not only the elements of microorganisms, but also them entirely.
 Important: deciphering the general blood test in children is carried out only by a doctor.
Important: deciphering the general blood test in children is carried out only by a doctor.
As mentioned above, the rate of KLA in children will depend on their age. It depends on the fact that as children grow, the composition of their blood will constantly change. Therefore, in order to make it easier to decipher the blood test, the doctors compiled a special table where the main groups of children are distinguished depending on age.
These groups are:- a newborn child whose age is 1 day;
- the age of the baby is a month, then six months and a year;
- 1-6 years;
- from 7 to 12 years;
- from 13 to 15 years old.
An interesting fact is that about 1000 people live in the country, who are called kyanetics, because they have a blue blood color. This is due to the fact that iron is absent in their blood stream, and instead copper is located. Due to this, the blood is characterized by better clotting, and it is also less susceptible to infection. Even as a result of serious injuries, a person will not bleed heavily.
Blood test forms have 2 columns: one indicates the result obtained for a particular patient, and the other indicates the norm for his age category. The interpretation of the obtained results will help to establish the presence of pathologies in the child in a timely manner and take measures to eliminate them. prompt elimination. Important: only a doctor is able to correctly read the result of a general blood test in a child!
Leukocytes are the most important elements in human blood, they help protect against the harmful effects of harmful microorganisms and substances. They are able to disarm all foreign particles that have entered the body. Based on this, we can say for sure that the behavior and condition of these cells can indicate an inflammatory process, a blood test can indicate in sufficient detail the existing pathologies in the body. That is why during the diagnosis of the patient it is simply necessary to find out the number of leukocytes, for this a special study is prescribed, in which the leukocyte blood count is studied. The interpretation of children and adults can be very different, so everyone needs to know exactly how to read the analysis data. They will help to find out the nature of the disease, the cause and prevent the consequences.
Leukocyte formula: what does it consist of?
The leukocyte blood formula (decoding in children and adults has its own differences) is not just some leukocytes, but several of their varieties, each of which is responsible for the operation of a particular system.
Leukocytes are responsible for protecting the body. Their goal is to create a certain boundary that should not be crossed by toxic substances and foreign bodies. As soon as bacteria get into the body, they signal this by an increase in indicators, you can see them on a blood test. Leukocytes are divided into several varieties: basophils, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils and lymphocytes. And they all perform a specific task. But what are their functions?
Neutrophils are responsible for security, they must recognize the virus, capture it and destroy it. They come in several varieties:
- myelocytes and metamyelocytes - these cells are found in the body healthy person it is impossible, they appear only if a leukocyte blood formula was taken for research, the norm in which is violated, and bacteria have already appeared in the blood, causing a serious pathology;
- stab appear if there is a bacterial infection in the body, their number begins to grow if the segmented ones cannot neutralize the microorganisms that caused the infection;
- segmented are in the body in the largest number, since it is they who are assigned the role of defenders of the body.
Eosinophils are a kind of protective barrier against all types of bacteria, and they appear most often if an allergy, oncology or autoimmune pathology progresses in the human body.
Lymphocytes help create antiviral immunity, because it is they who have the ability to fix antigens in their memory and are directly involved in the production of antibodies.
Monocytes are similar in purpose to neutrophils, but differ in that they have the ability not only to capture and destroy pathogenic bacteria, but also absorb dead cells, so they purify the blood, allowing tissues to recover.
Basophils appear at the moment when in the body occur allergic reactions They keep harmful bacteria and toxins from spreading.
The leukocyte blood count (decoding in children 2 years old and any other age is slightly different) allows you to assess the patient's condition, identify the severity of the disease, what causes it and what the consequences may be.
Why know the blood formula and when is it considered?
Doctors for any complaints of the patient immediately prescribe a blood test. Leukocyte formula (decoding of children different ages different) will reveal infection, inflammation or foreign body in organism.
The analysis is prescribed for such conditions:
With symptoms such as diarrhea, increased night sweats, swollen lymph nodes, weight loss, difficulty breathing, is the leukocyte blood count elevated? Then you can immediately determine what provoked the symptoms. It is also recommended to conduct this study if the patient has heat chills, headache and body aches.
Analysis technique
To calculate the leukocyte formula with a blood smear, it is necessary to carry out several specific manipulations, dry it, process it with a special dye and examine the material under a microscope. The laboratory assistant counts only those cells that he sees under a microscope until, in the end, he collects one hundred, and sometimes two hundred cells.
The count of leukocytes is carried out by a laboratory assistant visually, using a microscope to help. Leukocytes are distributed unevenly on the surface of the smear: eosinophils, basophils and monocytes can be seen closer to the edges, but lymphocytes are in the center. 
Laboratory assistants can count in two known ways:
- the Schilling method, which allows you to determine the number of leukocytes in 4 areas of the smear;
- the Filipchenko method, which involves dividing the smear into three parts and alternately counting.
On the form, in certain columns, the total number of cells is noted, and after that each of the types of leukocytes is counted separately.
It should also be said that such a cell count is not an entirely accurate method, and all because there are a large number of hard-to-remove factors that introduce their own errors: an error during sampling, preparation and staining of a smear, the individuality of the organism, the human factor in interpreting the results. A feature of several types of cells in a smear is an uneven distribution, which makes counting difficult.
If you need more exact result, then the leukocyte indices are calculated, which are the ratio of different types of leukocytes, and sometimes the ESR indicator is also taken into account in the analysis.
Indices of this kind make it possible to determine the severity of intoxication and characterize the body's ability to adapt, that is, the ability to adapt to the effects of toxins and cope with them without harm to health. In addition, they provide the opportunity to:
- get all the necessary data about the patient's condition;
- evaluate how the immune system works;
- determine the body's resistance;
- determine the level of immunological reactivity.
The norm of the leukocyte formula in the adult population
The leukocyte blood count, which should be deciphered in adults and children only by a specialist who can immediately detect even the slightest change and prescribe the appropriate treatment complex, contains important parameters. But everyone will be able to independently compare the analysis indicators with the norm, for this you need to have an idea what values \u200b\u200bcan be seen in it and what their changes in any direction indicate:
As already mentioned, leukocytes in a blood test are presented in several forms.
- Neutrophils are: segmented or stab, it is this most numerous of the types of cells that the leukocyte blood count contains. Decoding in adults is in the range of 50-70%, and stab - 1-3%. Their number may be higher than normal in oncology, inflammation internal organs and failures in metabolic processes. But a decrease in their number indicates infection, blood pathologies and thyrotoxicosis.
- Eosinophils are white blood cells that fight cancer cells, they help cleanse the body of infection and toxins. The norm in the blood in adults is 1-5%. Their elevated level indicates infections, tumors and blood diseases, and a decrease indicates intoxication or purulent processes.
- Monocytes are one of the largest types of white blood cells that recognize foreign substances in the body. The leukocyte blood formula (decoding in adults) says that monocytes should normally be 3-9%. Exceeding the norm indicates the presence of a viral or fungal infection, and a decrease in aplastic anemia or purulent pathologies.
- Basophils are involved in the formation of delayed-type inflammatory reactions. Their norm is 0.0-0.5%. Exceeding it may indicate the presence of allergic reactions, pathologies thyroid gland, myeloid leukemia, chickenpox, hemolytic anemia.
- Lymphocytes are a type of leukocytes that take part in cellular and humoral immunity due to antibodies. Their norm in the blood of an adult is 20-40%.
From the foregoing, it is clear what normal indicators the leukocyte blood formula gives (decoding in adults). The normage in children is a little different and you need to know what it shows.
What will tell the children's blood formula
It differs significantly from that of adults. So, from 1 year to 3 years, the ratio of segmented nuclear should be within 32-50%, and stab no more than 1%, as well as basophils. Eosinophils should be from 1 to 4%, and lymphocytes - 38-58%, monocytes - 10-12%.
The leukocyte blood count, decoding in children of 5 years old, does not change, all indicators remain the same. The only difference is an increase in segmented neutrophils from 36 to 52% and a decrease in lymphocytes to 33-50 percent. 
There are no exact rules for changing a blood test for leukocytes. With various pathologies, the indicator can change in the same way, but at the same time, with one disease, it can differ significantly in different patients, and this is due to the individual characteristics of the body.
what can they point to?
When the doctor recommends a blood test, the leukocyte blood formula will be considered at the same time. Deciphering in children and adults may indicate an increase in the number of neutrophils, in medicine this is called neutrophilia, and overestimated indicators can indicate:
- the presence of an infection caused by bacteria, fungi, certain viruses or protozoa;
- the beginning of the inflammatory process, for example, it can be rheumatism, pancreatitis, peritonitis, dermatitis and others;
- the appearance of a tumor on one of the organs;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- endogenous intoxication;
- ischemic tissue necrosis;
- taking certain drugs that can change the composition of the blood;
- the presence of stressful situations in the life of the patient or physical overstrain, also this condition is often observed after surgical treatment.
An increased number of lymphocytes - lymphocytosis, may indicate:
An elevated level of eosinophils - eosinophelia, may indicate:
An increased number of monocytes is a sign of monocytic leukemia or pulmonary tuberculosis.
An increased number of basophils, which make up the smallest part of white blood cells, may indicate chronic ulcerative colitis or advanced blood diseases.
As is clear from the foregoing, the leukocyte blood count, decoding in children and adults, is very important, because it is thanks to it that you can quickly identify health problems and begin treatment.
what do they indicate?
A reduced number of neutrophils may indicate the presence of such pathologies in the patient's body:
- influenza, chickenpox, hepatitis, rubella;
- typhoid fever and brucellosis;
- typhus and malaria;
- weak immunity in the elderly;
- blood diseases: leukemia, Iron-deficiency anemia and others;
- taking anticancer drugs;
- anaphylactic shock;
- congenital neutropenia.
And if the leukocyte blood count (decoding) was checked, the lymphocytes are below normal according to its results, then this may indicate such diseases:
- acute form of infection;
- immunodeficiency;
- miliary tuberculosis;
- aplastic anemia;
- lupus erythematosus;
- kidney pathology.
A decrease in the rate of eosinophils, which occur in rare cases, may indicate:
- stress or shock;
- the onset of inflammation;
- purulent infection of the most severe form.
Blood formula in newborns
The leukocyte blood count, decoding in children after birth, is somewhat different and depends on age. In the first months after birth, the leukocyte formula is only formed in children, it will persist until about one year of age. Indicators in infants are unstable, they can be greatly disturbed in diseases caused by climate change and anxiety. By the age of six, the content of neutrophils and lymphocytes becomes greater, and by the age of 15, the formula is more and more like that of adults. 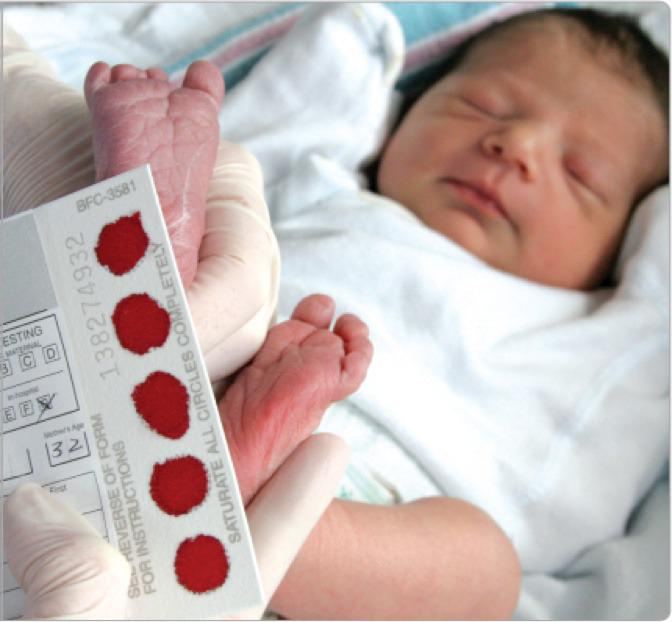
So, as the child grows, so does his leukocyte blood count. Decoding in children of 6 years old becomes more stable and does not change much with mood swings, as in infants. In newborns, neutrophils are in the range of 51-71%, in the first days after birth, the number increases, and then gradually decreases. The number of lymphocytes is also unstable and is 15-35%, and by the 14th day of life the level reaches 55%, but when the child is a week old, the curves of lymphocytes and neutrophils converge, such an intersection in medicine is called the first cross, but more on that later .
As for basophils, newborns do not have them, monocytes in the blood account for 6.5-11%, and after a week their number increases to 14.1%, the lower limit is 8.4%. The minimum number of plasma cells is 6.4-11.2%. In infants from the first day to the seventh, there is a visible shift to the left according to Schilling, which is established by the end of the first week.
For the first month of a newborn's life, a clear leukocyte blood formula is drawn, the decoding in children up to a year varies in a wide range, but by the age of 6 the formula is established and does not jump at the slightest stressful situations.
Formula shift
Thanks to modern technologies, today automatic blood analyzers allow you to very quickly, and most importantly accurately, calculate the leukocyte form, which has greatly facilitated the diagnosis and establishment of accurate diagnosis. During the decoding of the analysis, changes in the ratio of mature and immature neutrophils are taken into account, because they are present in the blood formula in different forms and are listed in order from young to mature, the count goes from left to right.
Laboratory assistants can fix several types of shifts that indicate various pathologies.
If there is a shift to the left, then myelocytes and metamyelocytes are present in the blood. Such changes may indicate such processes:
- acute inflammatory processes: prostatitis, orchitis;
- purulent infections;
- acute bleeding;
- acidosis;
- poisoning with toxins;
- high loads.
If the leukocyte blood count was checked (decoding in adults), the norm in this case is violated, shows a left shift with rejuvenation, then this may indicate the presence of such pathologies:
- leukemia;
- erythroleukemia;
- spread of metastases;
- myelofibrosis;
- coma.
Crossover of the leukocyte formula
This wording occurs when the leukocyte blood count is considered, the norm in children 3 years old or any other age. In this case, it is unstable. If in an adult any changes in the analysis indicate a pathology or the presence of harmful organisms, then in children these changes may be associated with the formation of immunity. Such a phenomenon is considered not a pathology, but a normal phenomenon, but the main thing is not to miss the disease behind such changes.
The first crossover occurs in the first 7 days of life, when the number of neutrophils and lymphocytes equalizes, after which the content of lymphocytes increases, and neutrophils, on the contrary, decreases. Such changes are considered normal and do not cause concern.
The second crossover occurs at 5-6 years, and only at 10 the indicators can approach those that are the norm in adults.
A blood test is a very serious analysis that should not be ignored. Just a few grams of blood - and the whole picture is obvious. You can see any changes that will allow you to assess the health of the patient, and even those pathologies that have not yet manifested themselves in the form of symptoms can be seen.
Helps the doctor find out if the baby is healthy or has any pathologies. In addition to calculating the total number of blood cells, hemoglobin levels, hematocrit and ESR, the leukocyte formula is also determined in the clinical analysis. What is hidden under this name, why define it and how to decipher it correctly?
A clinical blood test of a baby helps the doctor to identify existing pathologies
What is this
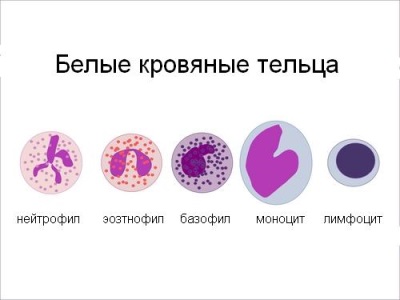
Leukoformula(blood formula or leukogram) called the number of different forms of leukocytes calculated as a percentage. Unlike platelets and erythrocytes, white blood cells are different types. In some of them there are granules, therefore such leukocytes are called granulocytes (they include basophils, neutrophils and eosinophils), in others there are no granules, therefore they are called agranulocytes (their representatives are monocytes and leukocytes).
Having counted their number under a microscope, the laboratory assistant expresses it as a percentage. Looking at the result of the analysis, the doctor sees how many percent of certain leukocytes of their total number are contained in the child's blood.
Why and when determined
Although all white bodies protect the child from factors unfavorable to his health, each type of leukocyte plays a specific role. That is why the leukocyte formula helps to clarify the diagnosis, find out the severity of the patient's condition, and also see if the prescribed treatment is working.
This is also emphasized by the popular pediatrician Komarovsky. He emphasizes that leukocytosis (an increase in the number of all white blood cells) or leukopenia (a decrease in the number of all white blood cells) will only help to find out that the child has a disease, and using the leukocyte formula, the doctor can understand which one pathological process takes place in the baby's body.
Recording of Komarovsky's program dedicated to clinical analysis baby's blood, see below:
The leukogram is prescribed:
- Scheduled for preventive examination of children of a certain age (at 1 year, and then annually).
- Before vaccination.
- With complaints and suspicion of an infection, for example, if the baby is losing weight, his lymph nodes have enlarged, diarrhea has appeared, body temperature has risen, joints are aching, and so on.
- If an exacerbation of a chronic disease has begun.
- If the child is preparing for surgery.
Note that the appearance of the leukocyte formula is influenced by various factors, and the main one is age. The picture in the analysis form of a newly born child, a baby at the age of 2 or 3 years, or in a teenager at 15 years old will be different. That is why the age of a small patient should always be indicated on the referral. This will help the laboratory assistant to note exceeding the norm or too low indicators.
Norm indicators and the role of different forms of leukocytes
Eosinophils
|
In newborns |
|
|
From the 10th day of life in children up to a year |
|
|
In children older than one year |
Neutrophils
These most numerous white blood cells are needed to fight pathogenic microbes. They are represented in the blood of the child in several forms, distinguished by their maturity:
- young neutrophils. They are also called myelocytes and metamyelocytes. Normally, they are absent in the leukocyte formula.
- stab- young neutrophil cells. Doctors call them "sticks" for short.
- Segmented. Such neutrophils are fully mature cells and normally they should predominate among all neutrophilic leukocytes.
The normal content of stab cells immediately after birth is called 5-12%, but by the fifth day after birth, their number decreases to 1-5% and remains so until the age of 5. In children older than 5 years, 1-4% of stab neutrophils is considered the norm.
The norm of segmented cells is presented in the table:
Basophils
Such leukocytes contain granules with biogenic amines, releasing them into the blood during immune reactions. The presence of 0-1% of basophils in the blood of a child at any age is considered the norm.
Monocytes
These cells transform into macrophages and ingest microbes, dead cells and other substances, removing them from the child's body. Normally, the number of monocytes from the total number of leukocytes is represented by the following percentage:
A video about what monocytes are can be viewed here:
Lymphocytes
This type of leukocytes is quite numerous and, like neutrophils, is represented by different forms, but in the general blood test, individual types of lymphocytes are not determined. The main task of these cells is to participate in immune responses. They actively protect children from viruses. The norm of lymphocytes in children of different ages is considered:
How to decipher the results
The doctor should evaluate the leukogram, comparing its data with the child's symptoms and other examinations.
Minor deviations
The ratio of leukocytes may vary slightly due to:
- Psycho-emotional load.
- Physical activity.
- Eating before donating blood.
- Taking certain medications.
 The mental work of a child can significantly affect the leukocyte count
The mental work of a child can significantly affect the leukocyte count
Change in the number of neutrophils
If neutrophils are increased compared to other white blood cells, this is called neutrophilia, and a decrease in the number of such cells is called neutropenia. The main reasons for these changes are:
|
Above normal |
Below normal |
|
Rubella, hepatitis, chickenpox, influenza |
|
|
Infection with fungi, protozoa and some viruses |
Defeat bone marrow with chemotherapy or radiotherapy |
|
Inflammatory process (dermatitis, arthritis, rheumatism, pancreatitis, etc.) |
Hyperfunction of the spleen |
|
Poisoning |
Leukemia and other neoplasms |
|
Cytostatics and others medications |
|
|
Some medicines |
Anaphylaxis |
|
Postoperative period |
Congenital pathologies |
|
Thyrotoxicosis |
|
|
blood loss |
B12 deficiency anemia |
Shift left
This phrase describes an increase in the number of stab neutrophils in the leukogram, as well as the appearance of young forms. A similar picture is found in purulent processes, burns, intoxication, leukemia, extensive bleeding or hemolytic anemia. A slight shift to the left occurs with stress and high physical activity.
shift right
This is the name for a decrease in the number of "rods" in the blood and an increased percentage segmented forms. Similar test results are less common than left shift and may indicate polycythemia, anemia, leukemia, blood transfusion, acute bleeding and other pathologies.

Change in the number of basophils
An increased number of such leukocytes is observed with chronic diseases, for example, ulcerative colitis, hypothyroidism, nephrosis, chronic leukemia. Also, elevated basophils are characteristic of allergies, chicken pox, hemolytic anemia, conditions after removal of the spleen or after treatment with hormonal agents.
A decrease in basophils in the blood is observed very rarely and is not a diagnostically important sign.
Change in the number of lymphocytes
If such cells are determined in excess of the norm, this is called lymphocytosis. The lack of this type of leukocytes in the blood is called lymphocytopenia. Most often, such conditions are caused by such problems:
Change in the number of eosinophils
An increased number of such cells is called eosinophilia and is diagnosed with:
- Worm infestations.
- Infection with protozoa.
- Allergic reactions.
- Leukemia.
- Scarlet fever and rheumatism.
- Malaria.
- Mononucleosis.
- extensive burns.
- Acute bacterial infections.
A decrease in the percentage of eosinophils, which is called "eosinopenia", is very rare in children and may be due to inflammatory process V initial stage or severe purulent infection. Also, the number of these white cells decreases due to treatment with glucocorticoids or heavy metal poisoning.
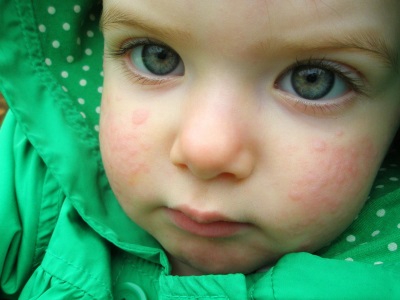 Severe allergic reactions are accompanied by eosinophilia
Severe allergic reactions are accompanied by eosinophilia
Change in the number of monocytes
Exceeding the norm of such cells is called monocytosis and is determined when:
A decrease in the level of monocytes (monocytopenia) is characteristic of the postoperative period, exhaustion of the body, sepsis, or steroid use. Also, the number of monocytes is reduced after chemotherapy or exposure to radiation.