Pulmonary pattern with signs of pneumosclerosis. Diffuse pulmonary pneumosclerosis - what is it? Diffuse pulmonary pneumosclerosis: treatment with folk remedies.
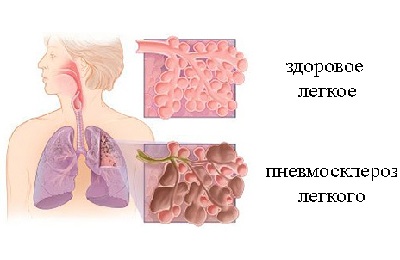
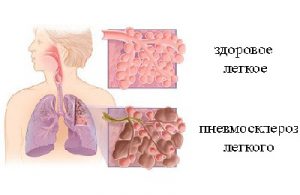
Pneumosclerosis is a pathological change in the human body, characterized by the development of excess pulmonary connective tissue within the bronchopulmonary segments.
The causes of pneumosclerosis most often manifest themselves in lobar or segmental pneumonia, as well as in chronic pneumonia (metapneumonic pneumosclerosis).
Most often, sclerotic changes occur in the basal segments of the left lower lobe. In addition, the disease pneumosclerosis is localized in the ventral pulmonary segments.
One of the most common causes of the development of pneumosclerosis is foreign bodies trapped in bronchial tree. In this case, the speed of clinical development of pneumosclerosis depends on the duration of presence foreign body in the tissues of the bronchi and on the speed of development inflammatory process.
Malformations of the bronchi and lungs also lead to sclerosis.
There are diffuse and limited pulmonary pneumosclerosis.
Diffuse pneumosclerosis lungs is observed in hereditary pathological conditions.
The causes of the onset of pneumosclerosis can be:
- chronic and acute pneumonia;
- Chronical bronchitis;
- congestion in the lungs with some cardiovascular diseases(especially with mitral valve defects);
- tuberculosis of the pleura and lungs;
- lung injury;
- pulmonary atelectasis;
- fibriosing alveolitis;
- connective tissue diseases;
- ionizing radiation;
- chemical warfare agents and toxic substances.
Pneumosclerosis, putting pressure on the heart, can lead to serious complications and severe heart disease.
Symptoms of pneumosclerosis
The main symptoms of pneumosclerosis can be considered signs of a disease leading to pneumosclerosis.
In addition, with diffuse pneumosclerosis, shortness of breath appears after physical exertion, becoming constant over time and continuing even at rest. A loud cough appears with discharge in the form of purulent mucous sputum.
Direct symptoms of pneumosclerosis are clinical symptoms pulmonary cirrhosis:
- shape change chest;
- noticeable atrophy of the muscles of the pectoral girdle;
- wrinkling of the intercostal spaces;
- movement of large vessels, heart, trachea towards the affected area;
- dull sounds during percussion;
- wheezing on auscultation;
- weakening of breathing.
Emphysema and pneumosclerosis have many common features.
Emphysema is characterized by increased air content in the lungs. Emphysema can be diffuse or focal. Chronic and acute bronchitis plays an important role in the development of emphysema and pneumosclerosis.
Sputum accumulated in the bronchi and the lack of ventilation in this part of the lung helps to develop pneumosclerosis and emphysema. Bronchial asthma also contributes to their development.
Prognosis for pneumosclerosis depends on the rate of change in lung tissues and from the progression of cardiac and respiratory failure. The worst case scenario awaits the patient when a secondary infection occurs and a honeycomb lung forms.
In the case of the formation of a honeycomb lung, respiratory failure becomes more complicated, pressure in the pulmonary vessels, cor pulmonale appears. The occurrence of secondary infection, tuberculous and mycotic processes often leads to death.
Treatment of pneumosclerosis
Treatment is carried out by a therapist or pulmonologist.
Inflammatory processes and complications in the lungs are an indication for inpatient treatment in the pulmonology department.
Therapy of pneumosclerosis places the main emphasis on eliminating the etiology of the disease.
Short-term manifestations of pneumosclerosis do not manifest themselves in the clinic of the disease and do not require active therapeutic intervention.
For exacerbations of pneumosclerosis, the following is prescribed:
- expectorants;
- antimicrobial;
- bronchodilators;
- mucolytic agents.
In case of exacerbation of heart failure, the following are prescribed:
- potassium preparations;
- cardiac glycosides.
Treatment for diffuse pneumosclerosis, accompanied by an allergic component, requires the use of glucocorticoids.
A good effect in the treatment of pneumosclerosis has:
- physiotherapy;
- oxygen therapy;
- breast massage;
- medical and physical training complex.
Severe complications of the disease require resection of the affected parts of the lung.
The latest innovation in the treatment of pneumosclerosis is the introduction of stem cells. This technique allows you to resuscitate the gas exchange function of the lungs and restore their healthy structure.
Treatment of pulmonary pneumosclerosis with folk remedies
First of all, learn to calm down and live in happiness and joy. Watch funny movies, listen to good music. Enjoy the birds, the rain and the wind. Don't forget about walks in nature and physical exercise. Let your lungs easily and joyfully fill with fresh air.
We should never forget about good nutrition and never overeat. A plant-based and dairy diet is especially valuable and beneficial.
Eat dried fruits containing potassium in the morning on an empty stomach and placed in water in the evening (dried apricots, raisins). This procedure gives a wonderful diuretic and laxative effect, that is, it relieves congestion in the lungs.
Have a good effect homeopathic remedies and honey massage.
Pneumosclerosis is serious illness lungs, in which the affected areas of the respiratory organs lose the ability for normal gas exchange. There is a pathological proliferation of non-functioning connective tissue, which gradually replaces the pulmonary parenchyma; this process contributes to the compaction of the lungs and their shrinkage.
Respiratory diseases are the most common among people of all age groups. Probably every person has encountered one of them at least once in his life (bronchitis, sinusitis, etc.). In most cases, such ailments do not cause much concern and do not seem serious or pose a threat to the normal functioning of the human body. This is fundamentally wrong, since respiratory diseases can provoke dangerous pathology, known as pneumosclerosis. It can occur at any age, but most often it affects men over fifty years of age.
In this case, the development of destructive processes in the vascular system of the respiratory organs, accumulation of mucus and compression are observed. The result of all this is a decrease in lung size, disruption of their ventilation, and deformation of the bronchi. The lungs are unable to contain the required amount of air, as a result of which the entire body suffers from a lack of oxygen. And oxygen deficiency, in turn, leads to many other pathologies.
Due to stagnation that occurs as a result of an excess of secretions, infectious lesions of the body occur.
Such changes in lung tissue are irreversible, and the disease in question tends to progress. Lack of timely treatment can contribute to severe consequences in the form of lifelong disability, and death is not excluded. The development of this disease usually occurs due to inflammatory processes occurring in respiratory organs.
Forms of the disease
Pneumosclerosis is classified depending on the degree of lung damage. There are focal and diffuse forms of pathology.
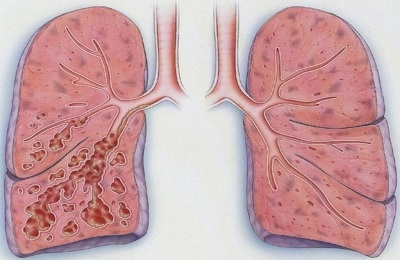
In focal or local forms of pneumosclerosis, disturbances in the elasticity and gas exchange of the pulmonary parenchyma are not observed. There is compaction and the formation of purulent foci on the lung tissues, varying in size. Depending on the size of the affected areas, focal pneumosclerosis is divided into small focal and large focal. With this form, the disease can proceed unnoticed by the patient himself, and manifest itself only in minor signs, characteristic of any other diseases respiratory system, for example, a frequent cough accompanied by the release of a small amount of sputum. Pathology is diagnosed only when the patient is examined using an X-ray machine.
Diffuse or widespread form of pneumosclerosis is characterized by damage to the entire lung tissue. In this case, there is a violation of the structure of the lungs, their compaction and reduction in volume, and a decrease in ventilation functions.
Diffuse moderate pneumosclerosis is not as severe as compared to the main form of the disease, and also poses less danger to the body. But, based on the fact that the disease progresses rapidly, it is very important to identify and eliminate signs of even moderate pneumosclerosis at the very early stages of its development. In this way, it is possible to avoid many unwanted health consequences.
According to the degree of damage, pulmonary pneumosclerosis is divided into fibrous, ordinary sclerosis and cirrhosis.
In the fibrotic stage, the lesions are limited and alternate with healthy areas.
With sclerosis, the respiratory organs lose their original airiness, become denser and smaller.
The cirrhosis degree, as the most severe, is characterized by a complete replacement of the lung parenchyma with connective tissue.
It is worth mentioning separately pneumosclerosis of the basal segments, which develops in the lower parts of the main respiratory organs. The cause of its occurrence in most cases is inflammation of the lower lobes of the lungs.
Pneumosclerosis - contagious or not?
The pathology in question is non-infectious nature, so it is not considered contagious. A patient with pneumosclerosis does not pose a threat to others. But anyone who has suffered any bronchopulmonary disease can get this disease. Especially if appropriate treatment was not carried out, or it turned out to be ineffective or was not completed completely.
Therefore, even with minor symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention in a timely manner. medical care, and also strictly follow all medical instructions, and in no case neglect the prescribed medication.
Reasons for development
There are many reasons why a person gets pneumosclerosis. Most often, this pathology is the result of some past diseases, and it can also be accompanied by the following ailments:
All these diseases lead to serious pathological changes in the respiratory organs, and also contribute to the weakening of respiratory function and the development of respiratory failure.
It is very important to establish the correct diagnosis, despite the fact that it is no longer possible to return the lungs to their previous healthy state. But it is quite possible to stop the progression of the disease with the help of modern medical techniques and using non-traditional remedies. traditional medicine.
Symptoms of the disease
U of this disease there are no specific symptoms, since it often occurs as part of another pathological process, or as a consequence of it. But following signs may indicate the development of this disease, so they must be taken into account and mentioned during the history taking.
We are talking about symptoms such as:
- A recurring cough that early stage may appear only occasionally and not cause much concern. As the disease progresses, the cough usually gets worse and deeper. If the patient coughs up sputum with purulent contents, then this is a reason to suspect he has pneumosclerosis.
- Blueness of the skin and mucous membranes, as a result of insufficient oxygen saturation of the body.
- Shortness of breath, which initially occurs only during physical activity, and then in a calm state.
- Changing the shape of the fingertips, which become like drumsticks.
- A sharp decrease in body weight.
- Pain in the chest area.
- Decreased performance, weakness, deterioration in health.
- Deformation of the chest with displacement of the heart in the direction where the lesion occurred.
Diagnosis of pathology
 The diagnosis of pneumosclerosis can be established using an X-ray examination of the patient, computed tomography of the lungs, bronchography, and spirometry.
The diagnosis of pneumosclerosis can be established using an X-ray examination of the patient, computed tomography of the lungs, bronchography, and spirometry.
A medical examination, listening to the lungs, collecting the patient’s history and complaints, identifying the presence of concomitant diseases or exposure to external adverse factors, such as ionizing radiation, are also necessary.
Drug treatment
Therapy for this pathology directly depends on how pronounced it is, as well as on the characteristics of the course of the disease. In the absence of serious symptoms indicating severe damage to the lung tissue, there is no need for active drug treatment.
When pneumosclerosis develops along with pneumonia, it is necessary to stop the inflammation with the help of antibiotic drugs, expectorants medicines, bronchodilators. When pneumosclerosis is combined with heart failure, treatment is carried out using drugs containing potassium, glucocorticoids, and cardiac glycosides.
In the absence of complications, treatment of the disease occurs on an outpatient basis under the supervision of the attending pulmonologist. But in the case of severe pneumosclerosis, it is advisable to hospitalize the patient, who should be under constant supervision of specialists.
If the presence of deep fibrosis or cirrhosis of the respiratory organ has been established, then it is possible to surgical intervention followed by resection of disease-affected areas.
It is very useful to carry out physiotherapeutic procedures, oxygen therapy to compensate for oxygen deficiency, physical therapy and massages along with medication treatment.
Pneumosclerosis in most cases is a concomitant disease, therefore, in order to recover from it, it is necessary to eliminate the symptoms of the underlying pathology that is its source.
How to treat with stem cells?
This method of therapy is innovative and modern. The uniqueness of stem cells lies in their ability to degenerate into other cells that make up healthy organs and tissues of the human body.
Stem cells are introduced using intravenous injections. Moving through the blood vessels along with the blood, they penetrate diseased organs and help replace tissues damaged by the disease. Cell therapy also results in strengthening the immune system and normalizing metabolism.
If stem cell therapy was started on time, before the onset of the fibrotic process, then positive results can be expected for sure. The more healthy areas of tissue there are in the lungs, the more likely the success of stem cell treatment.
Another indisputable advantage of this therapeutic method– this is absolute safety. As a result of this treatment, the patient’s shortness of breath, periodic cough and other symptoms of pneumosclerosis disappear. And with repeated diagnostics, the absence of pathological processes is confirmed.
Folk remedies for the treatment of pneumosclerosis
 Traditional medicine is a time-tested method of treating many human diseases. The feasibility of using alternative medicine for the treatment of pneumosclerosis lies in the fact that a large number of its recipes are used to eliminate diseases of the respiratory system, which are the source of pneumosclerosis.
Traditional medicine is a time-tested method of treating many human diseases. The feasibility of using alternative medicine for the treatment of pneumosclerosis lies in the fact that a large number of its recipes are used to eliminate diseases of the respiratory system, which are the source of pneumosclerosis.
Usually, decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants are used, which have anti-inflammatory, absorbable, antimicrobial and antiseptic properties.
The most common means:
- aloe;
- eucalyptus;
- oat grains;
- onion;
- dried fruits;
- thyme;
- Birch buds;
- chamomile;
- series;
- sage;
- licorice;
- beet;
- nettle, etc.
Recipes for the treatment of pneumosclerosis:
- Eating onions boiled in milk.
- Alcohol tincture of nettle.
- Finely chopped onions, boiled in sugar syrup.
- Dried fruits soaked in water.
- Decoction of oat grains.
- An infusion of crushed eucalyptus leaves poured with boiling water.
- An infusion of thyme, sage, chamomile and mint.
- Ground aloe leaves combined with honey and homemade wine.
- Infusion of oats, thyme, eucalyptus.
- Inhalations with decoctions based on pine buds, chamomile, sage, yarrow, thyme, licorice, mint, etc.
Treatment folk remedies cannot replace drug therapy. It is important to remember this and use alternative medicine exclusively as an auxiliary therapeutic agent, but only after consultation with your doctor.
Required to comply preventive measures, strengthen the immune system, stop using alcoholic drinks and smoking. A healthy, active lifestyle and proper balanced nutrition, which helps saturate the body, are of great importance. useful substances and vitamins.
It is very important to treat existing colds, bronchitis, infectious and viral lesions respiratory tract. If it is necessary to work in hazardous industries, it is recommended to use protective masks and respirators. And if you suspect pneumosclerosis, it is better to change your place of work.
Pneumosclerosis of the lungs- formation of connective tissue in place of the lung. This process can be focal or widespread. With a limited course of the disease, it proceeds unnoticed and is diagnosed only when x-ray examination lungs. This disease, which covers the entire lung or even has bilateral lesions, is manifested by severe respiratory failure and the development of other complications.
In contact with
Origin
In the chronic inflammatory course of the disease in the lung tissue, destruction processes prevail over regeneration (renewal). At the site of the damaged lung, connective tissue is formed that is not able to perform the function of gas exchange. As a result, breathing efficiency is impaired, the respiratory area of the lungs decreases and the level of oxygen saturation in the blood decreases. This causes the development of pulmonary failure. 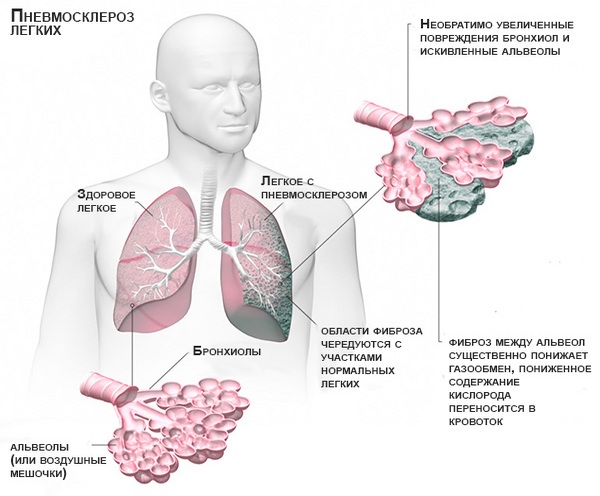
Causes
The reasons for the development are various lung lesions. Most often these are inflammations caused by bacterial infection. Not fully cured, or can cause the development of pneumosclerosis. However, the first place among infections belongs to. In most cases, it is complicated by the development of focal, often deforming pneumosclerosis. A special place is occupied by post-traumatic pneumosclerosis. It occurs as a result of various damage to the pulmonary parenchyma, as well as after. Equally important is the constant inhalation of industrial dust.
The greatest role in the formation of newly formed connective tissue belongs to silicon and beryllium compounds.
Pneumosclerosis also occurs as a result of chronic pathology of the cardiovascular system. These include mitral heart defects and diseases that are accompanied by hypertension in the pulmonary circulation.
A lung disease characterized by the replacement of normal lung tissue with connective tissue. The process is the result of an inflammatory process and degeneration of organ tissue, as a result of which there is a violation of elasticity and gas transport in the affected areas.
- Causes
- Pathogenesis
- Classification of pneumosclerosis
- Symptoms
- Consequences of pneumosclerosis
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
The extracellular matrix grows in the respiratory organs, deforms the branches of the windpipe, and the lung itself shrinks and becomes denser. The lungs lose air and become smaller. The disease is equally common in the population of all ages. Men get sick more often than women.
Pneumosclerosis is divided according to the severity of connective tissue proliferation into:
- fibrosis
- sclerosis
- pulmonary cirrhosis
If pneumosclerosis manifests itself in the form of fibrosis, then cicatricial changes in the organ are moderately pronounced. In the second form, there is a more severe replacement of the lungs with connective tissue. In cirrhosis, the third form, the alveoli are completely replaced, and the bronchi and blood vessels are also partially replaced by disorganized connective tissue. Pneumosclerosis is not only an independent nosological form, but the outcome of other diseases, as well as a symptom.
Causes
Pneumosclerosis quite often accompanies below listed diseases or is formed in their outcome:
- chronic bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, inflammation of the tissue surrounding the bronchi
- diseases provoked by foreign substances in the lungs, infectious in nature, viral pneumonia, mycoses, tuberculous processes in the organ
- allergic and fibrosing alveolitis
- pneumoconicosis, the cause of which is prolonged inhalation of gases and dust, industrial and radiation pneumoconicosis
- genetically transmitted lung diseases
- lung injuries, wound consequences
- Beck's disease in pulmonary form
If acute and chronic processes in the respiratory organs were ineffectively treated or a sufficient course of treatment was not followed, this creates the ground for the development of pneumosclerosis.
Among the provoking factors of the disease in question:
- LV heart failure
- pulmonary circulation defects due to narrowing of the left atrioventricular orifice
- pulmonary thrombosis
- taking toxic pneumotropic drugs
- influence of ionizing radiation on the body
- weakening of general and local immunity
If the pulmonary inflammatory process is not completely resolved, then the inflammation of the lung tissue is also incomplete, connective tissue scars grow, alveolar lumens narrow, which leads to pneumosclerosis. It is noted that the disease often occurs in those who have suffered staphylococcal pneumonia, which was accompanied by the formation of necrotic areas of lung tissue and an abscess. After the abscess healed, fibrous tissue began to grow.
If the disease in question is a consequence of pulmonary tuberculosis, then connective tissue may appear in the organ, which leads to the development of peri-scar emphysema. A complication of chronic inflammation in the bronchi, such as bronchitis and bronchiolitis, is the occurrence of perilobular and peribronchial pneumosclerosis. Pleurogenic pneumosclerosis can begin after repeated inflammation of the pleura, in which the superficial layers of the lung join the inflammatory process, its parenchyma is compressed by exudate.
Radiation and Hamman-Rich syndrome in frequent cases are provoking factors for the development of pulmonary sclerosis of diffuse origin. A lung is formed that looks like a shoulder honeycomb. Mitral valve stenosis and left heart failure may cause fluid to leak from blood vessels, which leads to pneumosclerosis of a cardiogenic nature. P. can be caused by bronchial, vascular, or pulmonary pathologies when the flow of lymph and blood is disrupted.
Among other causes of pathology
highlight:- chronic bronchitis accompanied by peribronchitis
- chronic pneumonia, untreated acute pneumonia, bronchiectasis
- congestion in the lungs in some heart diseases, mainly with mitral valve defects
- pneumoconiosis of various origins
- prolonged and severe exudative pleurisy
- pulmonary atelectasis
- tuberculosis of the lungs and pleura
- traumatic injury to the chest and lungs
- systemic connective tissue diseases
- treatment with drugs such as apressin or cordarone
- effects of chemical warfare agents on the lungs
- effects of ionizing radiation on the human body
- idiopathic fibrosing alveolitis
Pathogenesis
The development of the disease in pathogenetic terms depends very much on the causes (provoking factor). But still, in the pathogenesis of any form of pneumosclerosis, disruption of pulmonary ventilation, drainage function of the bronchi, blood and lymph circulation is important. The proliferation of connective tissue causes disruption of the structure and destruction of specialized morphofunctional elements of the lung parenchyma. Arising from pathological processes in the bronchopulmonary and vascular systems, disturbances in blood and lymph circulation contribute to the development of pneumosclerosis.
Pneumosclerosis, according to the characteristics of its pathogenesis, is divided into diffuse and focal (or local). And focal can be large- and small-focal.
Classification of pneumosclerosis
Classification according to the degree of replacement of lung tissue with Pischinger's space:
- fibrosis with alternation of limited affected areas in the form of cords with healthy air-filled tissue
- pneumosclerosis itself (connective tissue replaces pulmonary tissue, tissues of a denser consistency than normal lung tissue are noted)
- complete replacement of pulmonary connective tissue, compaction of the alveoli and pleura, as well as blood vessels; displacement of the mediastinal organs to the affected side. This is the stage of cirrhosis.
There is a special form of focal pneumosclerosis - carnification, in which the pulmonary parenchyma in the inflamed area resembles raw meat in consistency and appearance. Microscopically, areas of fibrinous exudate, sclerosis and suppuration, fibroatelectasis, etc. are detected. Limited pneumosclerosis differs from diffuse pneumosclerosis in that gas exchange does not deteriorate, the lung is as elastic as before the disease. In the diffuse form, ventilation is reduced and the affected lung is rigid.
Pneumosclerosis, based on the predominance of affected structures, is divided into the following forms:
- peribronchial
- alveolar
- perilobular
- interstitial
- perivascular
Classification according to the reasons for the formation of the disease:
- postnecrotic
- discirculatory
- dystrophic
- post-inflammatory
Symptoms
Signs of the underlying disease causing pneumosclerosis:
- chronic pneumonia
- Chronical bronchitis
- bronchiectasis
Dyspnea with diffuse pneumosclerosis, which at the beginning of the disease is observed only during exertion, but then appears when the person is at rest. A productive cough is characterized by the production of mucopurulent sputum. Severe diffuse cyanosis is typical.
Auscultatory and percussion signs
:- shortening of percussion sound
- limited mobility of the pulmonary edge
- fine wheezing
- weakened vesicular breathing with a hard tint
- dry scattered wheezing
Along with the symptoms of pneumosclerosis, the clinic of emphysema and chronic bronchitis often appears. Diffuse forms of pneumosclerosis are accompanied by precapillary hypertension of the pulmonary circulation and manifestations pulmonary heart.
The following symptoms indicate lung cirrhosis:
:- partial atrophy of the pectoral muscles
- severe deformation of the chest
- tracheal displacement
- shrinkage of intercostal spaces
- displacement of large vessels and heart to the affected side
- sudden decrease in breathing
- dull sound when percussing
- dry and moist rales detected by auscultation
With a limited form of pneumosclerosis
the patient does not complain about anything. Only a slight cough with minimal phlegm may bother you. When examining the affected side, it is discovered that the thorax in this place has a kind of depression.Pneumosclerosis of diffuse origin
has a symptom such as shortness of breath. At later stages it is present, even if the person is not taking any action at the moment (sitting or lying). Alveolar tissue it is poorly ventilated, which is why the skin has a bluish tint. The Hippocrates finger sign is recorded, which indicates increasing respiratory failure. The patient complains of cough. At first it appears rarely, but then it becomes intrusive, purulent sputum is released. The course of pneumosclerosis aggravates the underlying disease.In some cases it is noted aching pain in the thoracic region, patients may lose weight, appear weakened, and causeless fatigue is likely. Symptoms of pulmonary cirrhosis may develop:
- atrophy of intercostal muscles
- gross deformity of the thorax
- displacement of the throat, large vessels and heart to the affected side
With diffuse pneumosclerosis, the cause of which is a violation of the hemodynamics of the small bloodstream, clinical symptoms of cor pulmonale sometimes appear. The severity of any form of pneumosclerosis correlates with the size of the affected areas.
Stages of the disease:
- compensated
- subcompensated
- decompensated
Emphysema and pneumosclerosis
A sign of pulmonary emphysema is the accumulation of increased amounts of air in the lung tissues. Pneumosclerosis, which is the result of chronic pneumonia, has very similar symptoms. The development of emphysema and pneumosclerosis is affected by infection of the bronchial wall, the influence of inflammation of the branches of the windpipe, and obstructions to the patency of the bronchi. Sputum accumulates in the small bronchi. Ventilation in this area of the lung can cause emphysema or pneumosclerosis. Diseases that are accompanied by bronchospasm, for example, bronchial asthma, can accelerate the development of these diseases.
Hilar pneumosclerosis
Connective tissue can grow in the hilar regions of the lung, then hilar pneumosclerosis is diagnosed. It is preceded by processes of inflammation or dystrophy, when the elasticity of the affected area is lost and gas exchange disturbances occur in it.
Local pneumosclerosis
Local pneumosclerosis, as already indicated, can be called limited by some authors. Symptomatically, it can be hidden for a long period, but upon auscultation, hard breathing and fine rales can be heard. It is detected by x-ray methods. The image shows an area of compacted lung tissue. Local pneumosclerosis may not cause pulmonary failure.
Focal pneumosclerosis
Focal pneumosclerosis can be a consequence of the destruction of the lung parenchyma, and the cause of the latter, in turn, is a lung abscess or cavities. The proliferation of connective tissue can be observed both at the site of existing and at the site of healed cavities and lesions.
Apical pneumosclerosis
In the apex of the lung in the apical form of the disease there is a lesion. As is typical for pneumosclerosis, the lung tissue at the apex is replaced by connective tissue. At first, the process is similar to bronchitis, and most often bronchitis precedes and becomes the cause of apical pneumosclerosis. It can be detected by x-ray.
Age-related pneumosclerosis
Age-related pneumosclerosis becomes the result of changes associated with the aging process of the human body. This form develops, as the name implies, only in elderly people if they have congestion during pulmonary hypertension. The disease mainly affects men; smokers are at increased risk. If an x-ray reveals pneumosclerosis in an 80-year-old (or older) person, but the patient has no complaints, this is the norm.
Reticular pneumosclerosis
As the amount of connective reticular tissue increases, the lungs become less clean and clear, and the tissue acquires a mesh-like structure, reminiscent of a spider's web. For this reason, the normal pattern is almost not visible; it looks weakened. CT scan clearly shows compaction of connective tissue.
Basal pneumosclerosis
When connective tissue begins to grow in the basal parts of the lung, then pneumosclerosis is classified as basal. It is often preceded by lower lobe pneumonia. The radiograph shows increased clarity of the lung tissue in the basal regions, enhancing the pattern.
Moderate pneumosclerosis
At the onset of the disease, the proliferation of connective tissue replacing the pulmonary tissue is moderate. Changed lung tissue alternates with healthy parenchyma. An x-ray reveals this picture, but the patient has no complaints, nothing bothers him.
Postpneumonic pneumosclerosis
This form of the disease is a complication of pneumonia. The inflamed area looks like raw meat. Macroscopically, the affected area is more compacted; this area of the lung is smaller in size than normal.
Interstitial pneumosclerosis
In this form, the connective tissue mainly covers the interalveolar septa, tissues, surrounding vessels and bronchi. Interstitial pneumosclerosis is a consequence of interstitial pneumonia.
Peribronchial pneumosclerosis
Connective tissue grows, surrounding the bronchi. The cause of this form of pneumosclerosis is the transfer of bronchitis in a chronic form. For a long period of time, the patient does not feel any changes in the body; he may only be slightly bothered by a cough. Over time, sputum appears.
Post-tuberculosis pneumosclerosis
In post-tuberculosis pneumosclerosis, the proliferation of connective tissue occurs after recovery from pulmonary tuberculosis. This condition can develop into “post-tuberculosis disease,” in which there may be different nosological forms of nonspecific diseases, for example, COLD.
Consequences of pneumosclerosis
With this disease, the alveoli, bronchi and blood vessels of the lungs change morphologically, therefore among the complications of the lungs the following are likely:
- reduction of the vascular bed
- impaired ventilation
- chronic respiratory failure
- arterial hypoxemia
- addition of pulmonary emphysema
- association with inflammatory lung diseases
- cor pulmonale
Diagnostics
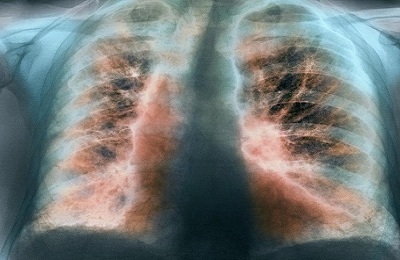
The X-ray picture is polymorphic, because it shows manifestations not only of pneumosclerosis itself, but also of associated diseases: emphysema, bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis, etc. Typical looping, enhancement and deformation of the pulmonary pattern along the bronchial branches, as the bronchial walls become denser, sclerosis and infiltration of peribronchial tissue occur.
Bronchography shows deviation or convergence of the bronchi, narrowing and absence of small bronchi, and deformation of the walls. Spirography is effective diagnostic method if pneumosclerosis is suspected, it detects a decrease in VC, FVC, and Tiffno index.
Over the affected area, physical examinations reveal decreased breathing, dry or moist rales, and dullness of percussion sound. Lung examination is also a reliable diagnostic method. Even if there are no symptoms, x-rays help to detect changes if they are present, their nature, prevalence, and how pronounced they are. Magnetic resonance imaging, bronchography, and CT scan of the lungs can more accurately assess the condition of unhealthy areas of lung tissue.
An x-ray shows the following changes in the affected lung:
- reducing it in size
- increased pulmonary pattern along the branches of the bronchi
- the pulmonary pattern is reticulated and looped due to deformation of the bronchial walls
- "honeycomb lung" in the lower regions
Fluorography for pneumosclerosis
If you have any complaints of cough or any respiratory symptoms, you must undergo a fluorographic examination of the chest organs. Every year, in order to prevent and early detect pneumosclerosis, tuberculosis and other similar diseases, all persons over 14 years of age must undergo medical checkup. With pneumosclerosis, the vital capacity of the lungs decreases, and the Tiffno index (which is an indicator of bronchial patency) is low.
Treatment
The main thing in treatment is to defeat the infection in the respiratory organs, restore breathing and normal blood circulation in the lungs, and strengthen the immune system.
At high temperature patients with pneumosclerosis should adhere to bed rest; after improvement of the condition, semi-bed rest is recommended. The diet should be aimed at accelerating repair in the lungs, stimulating oxidative processes, improving hematopoiesis, etc. Taking into account the patient's condition, diet 11 or 15 should be prescribed. Meals are fractional. There is no specific treatment for pneumosclerosis.
Experts recommend small doses of glucocorticoids for six months to a year. In the acute period, the daily dose is 20-30 mg. And maintenance therapy involves a dose of 5-10 mg. The dosage should be reduced gradually. For bronchitis, pneumonia, bronchiectasis, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial treatment. As for the choice of antibiotics, macrolides are most often effective, among which azithromycin is often prescribed.
For the treatment of pulmonary pneumosclerosis, the doctor may prescribe II-III generation cephalosporins. A proven antimicrobial drug is metronidazole, which is administered intravenously. Sulfonamide drugs also have an antimicrobial effect, of which sulfapyridazine is widely used. Therapy also includes taking the following medications:
- expectorants and thinners
- bronchospasmolytic
- cardiac glycosides (for circulatory failure)
- vitamins (retinol, tocopherol acetate, etc.)
Non-drug methods
treatment of pulmonary pneumosclerosis:- physiotherapy
- oxygen therapy
- surgery
- folk remedies
Read more about the treatment of pneumosclerosis here.
Health means not only indicators of physical activity, endurance, and good tests. Often diseases occur unnoticed by a person. One of them is hilar pneumosclerosis or the process of replacing lung tissue with connective tissue.
In order to be able to quickly begin the treatment process, you need to know the basic characteristics of the disease.
Features of pneumosclerosis
The development of the disease occurs against the background of an already existing inflammatory process that accumulates in the tissues of the lungs. They gradually change, deform, for this reason, elasticity in the affected areas is disrupted, and gas transport also changes.
 In the future, if measures are not taken to prevent the development of pathology, extracellular matrix deforms the branches of the windpipe. As a result, the damaged lung becomes denser and shrinks, as airlessness is formed.
In the future, if measures are not taken to prevent the development of pathology, extracellular matrix deforms the branches of the windpipe. As a result, the damaged lung becomes denser and shrinks, as airlessness is formed.
During the development of pneumosclerosis, respiratory function is impaired, since the size of the respiratory surface necessary to ensure it is significantly reduced.
Many of our readers for the treatment of cough and improvement of bronchitis, pneumonia, bronchial asthma, tuberculosis is actively used by the Monastic collection of Father George. It consists of 16 medicinal plants, which are extremely effective in the treatment of chronic COUGH, bronchitis and cough caused by smoking.
According to medical research conducted in different countries, the percentage of the disease is the same among people of all age groups. A slight advantage is observed among men aged 35-50 years.
Causes
The main reason for the development of pathogenic processes in lung tissue is the presence of inflammation. It should also be taken into account that the development of the disease can be triggered by:
The hereditary factor is also one of the main reasons for the development of the disease. That is why it is important to closely monitor your health and undergo routine medical examinations in a timely manner. There are also other reasons that can become the basis for triggering processes of change in lung tissue:
- (caused by heart defects and vascular problems);
- long-term treatment with medications ( by-effect row medicines);
- damage to tissues by special damaging substances (for military purposes).
Classification of the disease
Pneumosclerosis, which develops in the tissues of the lungs, is classified according to several criteria, on the basis of which the main factors influencing the course and development of the disease are identified. So the classification is carried out according to the degree of prevalence. In this case, experts highlight:
Doctors also developed a classification based on the location of the greatest damage to the lung tissue:
Doctors distinguish between focal and diffuse degrees, which are also characteristic of the basal form of the disease. If it spreads to both lungs, then this is a diffuse stage. It is characterized by the formation of cysts in the lung tissues. As a result, the process of nourishing cells and supplying them with oxygen is disrupted, resulting in a decrease in volume.
If only one lung is affected, a focal degree of the disease is diagnosed.
 Also, this stage can be large or small focal, depending on the area that has undergone changes.
Also, this stage can be large or small focal, depending on the area that has undergone changes.
In addition, there are 3 stages of the disease:
- Compensation stage;
- Subcompensation stage;
- Stage of decompensation.
Only diagnostic measures can establish changes.
Symptoms of the disease
Diagnostic measures
In order to identify hilar or any other type of pneumosclerosis in lung tissues, when it appears characteristic symptoms undergo diagnostics.
![]() The risk group, which must be constantly examined, includes enterprise workers, construction workers, and athletes.
The risk group, which must be constantly examined, includes enterprise workers, construction workers, and athletes.
The main method for diagnosing the hilar form of pneumosclerosis is X-ray. If changes take place, they will appear on it in the form of characteristic zones. IN initial stages As the disease progresses, changes are visible only in one root area, then their number increases.
Another method of diagnostic testing is pulmonary function tests. They allow us to determine the degree of development of the disease - pathogenesis. In the case of focal development, its treatment subsequently shows satisfactory results.
If diffuse, therapeutic correction will not be effective. Tests can also reveal the type of disease, the intensity of changes in tissues, and the degree of reduction of the damaged lung.
Additionally, during diagnostics the following are used:
- visual inspection;
- bronchography is performed.
To confirm the results obtained, the doctor may order an MRI or CT scan.
 The process of making a diagnosis is not complete without testing:
The process of making a diagnosis is not complete without testing:
- general blood analysis;
- examination of sputum (if it is released).
A comprehensive study will determine the extent of damage in the root region and prescribe effective treatment.
Treatment of the disease
After undergoing the examination, the patient receives a list of medications and procedures that form the treatment. It is important to remember that a special method that can completely rid a person of the disease has not been developed. All measures are aimed at eliminating the cause, which has become a catalyst for negative processes in the lung tissue.
So, if a mild form of hilar pneumosclerosis is diagnosed, the basis of treatment will be therapy aimed at maintaining the body. Loads are excluded, the main rule is caution. Treatment in this case is aimed at eliminating the emergence of new areas of inflammation.
Radical diffuse type therapy includes:
In the event that pulmonary insufficiency is not noted, physiotherapeutic procedures are included in the therapy. Surgery is required in advanced cases or when complications occur.
Treatment also includes:
- establishing a special daily routine;
- diet;
- strengthening immune system(taking vitamins, hardening);
- oxygen treatment (oxygen therapy).
It is necessary to maintain a special microclimate in the room. The optimal temperature is +20 degrees. Walks and airing are required.
ethnoscience
An additional element of treatment and prevention is traditional medicine. It is permitted to be used in mild form course of the disease and in unadvanced cases that respond well to treatment. The bulk of recipes and methods of treatment are aimed at treating bronchitis.

Important! It is prohibited to use traditional medicine recipes without the consent of a doctor. Self-medication can do more harm to health than good.
Possible consequences and complications of the disease
If you pay insufficient attention to the recovery process or start the disease, then the person may face consequences and complications. The danger of pneumosclerosis is that it affects the cardiovascular system.
 Pulmonary insufficiency also develops - gradually the lower part becomes loose in its structure, similar to a soft sponge. As a result, serious breathing difficulties that require immediate correction arise, and a secondary, sometimes severe infection appears, which minimizes the treatment provided. General state the person deteriorates noticeably.
Pulmonary insufficiency also develops - gradually the lower part becomes loose in its structure, similar to a soft sponge. As a result, serious breathing difficulties that require immediate correction arise, and a secondary, sometimes severe infection appears, which minimizes the treatment provided. General state the person deteriorates noticeably.
It must be remembered that life expectancy directly depends on timely treatment. If you follow the recommendations and do not start the disease, the likelihood of a favorable prognosis and a positive outcome of therapeutic intervention increases.
All appointments must be carried out, and the stages of therapy must be completed. Sometimes it is recommended to refuse the work you are doing if it is the work that caused the development of the disease.
Thus, it is necessary to know the features of the disease called hilar pneumosclerosis, understand what it is and what consequences can occur if you do not pay due attention to the treatment process. For effective therapy you need to contact a specialist (pulmonologist). The prognosis with timely treatment and the absence of secondary infection is positive.
