Dark blood on top of stool. Blood in the stool: causes in an adult
Bloody feces are a symptom of a number of intestinal diseases - from benign (hemorrhoids) to very serious (rectal cancer). Only an examination by a proctologist will help determine the cause of the bleeding.
A presumptive diagnosis can be made by independently analyzing your well-being, but you can definitely exclude cancer only after visiting a doctor.
Anal fissures and hemorrhoids
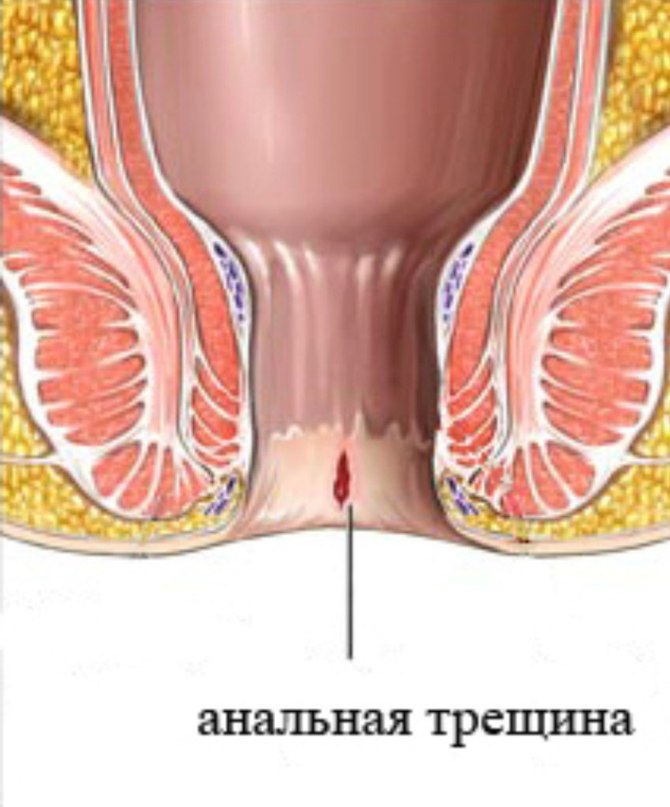
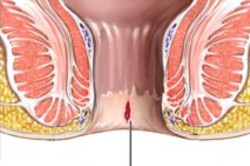 If the integrity of the rectal mucosa is compromised, blood appears after defecation. By what symptoms can one suspect the presence of anal fissures?
If the integrity of the rectal mucosa is compromised, blood appears after defecation. By what symptoms can one suspect the presence of anal fissures?
- painful and unpleasant sensations in the anus, irritation, burning, pain, stinging;
- blood on toilet paper and underwear;
- blood not mixed with feces, liquid;
- bright scarlet;
- when passing feces there is severe discomfort, pain, irritation and pain in the rectum;
- the amount of bleeding may be scanty or heavy, but it increases after physical activity, straining and sphincter tension;
- a feeling of itching in the anus, which is activated by prolonged sitting or walking.
Anal fissures most often occur in adults. In children, constipation with blood can cause tears and cracks in the mucous membrane due to spasm of the rectum and too hard stool.
Even if a child has blood during bowel movements once, you need to consult a doctor. There are 4 main causes of damage to the rectal mucosa in adults:
- functional constipation, prolonged use of laxatives;
- anal sex in violation of safety regulations;
- pathologically increased tone sphincter;
- changes in the tone of the rectum and sphincter as a result of childbirth.
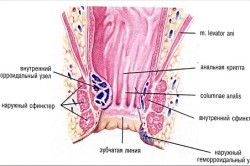 Ruptures of the rectal mucosa can be acute or chronic. Normally, a fresh anal fissure should heal completely in 1-6 weeks. If this does not happen, and cracks occur regularly, do not heal well and cause painful anxiety, the disorder can be considered chronic. Bleeding after bowel movement can occur sporadically and also stop spontaneously. You need to contact a proctologist even if the symptom ceases to appear. Rectal cancer can also cause bleeding for a short period of time, which then stops. A doctor should help with the diagnosis. Hemorrhoids are a very well-known disease, common among adults leading a sedentary lifestyle. For varicose veins rectal veins are characterized by the following symptoms:
Ruptures of the rectal mucosa can be acute or chronic. Normally, a fresh anal fissure should heal completely in 1-6 weeks. If this does not happen, and cracks occur regularly, do not heal well and cause painful anxiety, the disorder can be considered chronic. Bleeding after bowel movement can occur sporadically and also stop spontaneously. You need to contact a proctologist even if the symptom ceases to appear. Rectal cancer can also cause bleeding for a short period of time, which then stops. A doctor should help with the diagnosis. Hemorrhoids are a very well-known disease, common among adults leading a sedentary lifestyle. For varicose veins rectal veins are characterized by the following symptoms:
- With external hemorrhoids, there are nodes, areas of the mucous membrane with enlarged vessels, which can be detected by palpation of the anus. As the disease progresses, the nodes increase in size. At an early stage, they can be retracted by squeezing the sphincter. At the second stage, the nodes are adjusted only manually. At the third stage, it will no longer be possible to return the node inside the rectum. With internal hemorrhoids, this symptom is weakly expressed.
- There is bleeding after or during bowel movements. The blood does not mix with feces, is bright scarlet in color, and liquid.
- There is itching, discomfort and soreness in the anal area. The pain is dull and aching in nature, intensifies with prolonged sitting or walking. With thrombosis of the hemorrhoid, the pain becomes intense, acute to the point of intolerance. Blockage of the vein is accompanied by an increase in the size of the node.
Treatment of hemorrhoids should only be carried out by a proctologist after confirmation of this diagnosis. Timely detection of hemorrhoids in an adult helps stop the progression of the disease and eliminate it with minimal losses unpleasant symptoms. Advanced hemorrhoids are much more difficult to treat. The high mortality rate of patients from colorectal cancer is not caused by the fact that the tumor grows extremely quickly, but by the fact that people do not go to the doctor. Many patients think that any blood during bowel movements indicates hemorrhoids. This opinion is not true.
Diverticula and rectal polyps
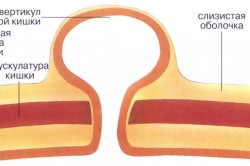 Diverticulosis is the appearance of a small pocket on the surface of the rectal mucosa; if this cavity becomes inflamed, the disease is called diverticulitis. According to statistics, diverticulosis is most common among people over 55 years of age; the disorder does not cause concern until inflammatory process. What are the signs of diverticulitis?
Diverticulosis is the appearance of a small pocket on the surface of the rectal mucosa; if this cavity becomes inflamed, the disease is called diverticulitis. According to statistics, diverticulosis is most common among people over 55 years of age; the disorder does not cause concern until inflammatory process. What are the signs of diverticulitis?
- bloody stools, fresh blood on toilet paper and linen;
- liquid and scarlet blood appears in a particularly large volume after constipation;
- intense pain in the left or right lower abdomen, after bowel movements and removal of gases, the pain does not decrease;
- pain sensations have a constant localization, intensify with pressure on the abdomen, with tension in the press, with bending over and physical activity;
- An increase in temperature up to 38.5 degrees is common;
- Diverticulosis is often accompanied by stool disorder, diarrhea or constipation, and the formation of large amounts of intestinal gas.
If you suspect diverticulitis, you should immediately contact a proctologist or surgeon, since appendicitis and renal colic have similar symptoms. Rupture of an inflamed diverticulum causes the release of intestinal contents into the abdominal cavity, peritonitis, sepsis, death without urgent medical care. Rectal polyps do not manifest themselves in any way in the same way. If tightly compressed feces injure the polyp, bleeding occurs. The blood is fresh, bright, and can stain stool. There is evidence that colon polyps have a tendency to malignant degeneration, so an examination by a proctologist is a must.
Cancer and other causes of bleeding
 It is impossible to diagnose colon cancer on your own; this requires a colonoscopy and other examinations. What are the symptoms of cancer?
It is impossible to diagnose colon cancer on your own; this requires a colonoscopy and other examinations. What are the symptoms of cancer?
- the appearance of feces with mucus and streaks of blood;
- frequent bowel movements, constipation, diarrhea;
- difficulty defecating, sensation incomplete emptying intestines;
- decreased appetite;
- weight loss;
- weakness, fatigue.
Symptoms vary depending on the type and location of the main tumor. If there is blood in the stool, you should not delay your visit to the proctologist, seek help immediately. Some types of cancer metastasize to neighboring organs quite quickly, and the patient may simply not have time to receive treatment while it is still possible. What other reasons can lead to the appearance of blood after bowel movement?
- intestinal infection, for example, salmonellosis, dysentery, amoebiasis;
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- venereal infection, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis.
With intestinal diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease appears. When bleeding from duodenum feces have a characteristic black color and a viscous consistency - like tar or plasticine. Bleeding of the intestinal mucosa is manifested not only by this symptom, but also by others:
- anemia, pale skin;
- muscle weakness;
- rapid fatigue;
- poor concentration, decreased performance;
- discomfort in the abdomen after using the toilet.
Deep black stool does not always mean illness; it may be a reaction to food. In this case, the color of the feces should change to normal within 2-3 days.
Hidden blood cannot always be detected on its own; there is a special device for this purpose. laboratory analysis feces
 If, in addition to blood, there is acute abdominal pain, fever, muscle weakness, vomiting, nausea and headache- you need to immediately call an ambulance and be hospitalized for examination. Especially dangerous symptom is tension and bloating, an intense feeling of throbbing pain and fullness. If such a clinical picture is observed in a child, you need to go to the hospital with him. Blood clots along with feces can also pass out in children due to anal fissures, for example, after prolonged atonic constipation. In this case, there will be no increase in temperature or intoxication.
If, in addition to blood, there is acute abdominal pain, fever, muscle weakness, vomiting, nausea and headache- you need to immediately call an ambulance and be hospitalized for examination. Especially dangerous symptom is tension and bloating, an intense feeling of throbbing pain and fullness. If such a clinical picture is observed in a child, you need to go to the hospital with him. Blood clots along with feces can also pass out in children due to anal fissures, for example, after prolonged atonic constipation. In this case, there will be no increase in temperature or intoxication.
Anal fissures do not require urgent medical attention; just visit a pediatrician. Green or yellow mucus in the stool, as well as foam, indicate an intestinal infection, which can be contagious and transmitted to other people. An intestinal infection causes fever, diarrhea, and dehydration. If a child has diarrhea, be sure to provide him with a sufficient amount of water, and if he vomits, add some water. drinking water a small amount of table salt. Patients with intestinal infection are isolated from healthy people to the infectious diseases department. It is unreasonable to refuse hospitalization; ambulance paramedics simply cannot find out in the field and without equipment what caused the abdominal pain and blood in the child’s stool. In children under 1 year of age, especially those who are on artificial feeding, intestinal volvulus may occur. The violation has the following manifestations:
- the child has a stomach ache, cries, shows restlessness, and actively moves his legs;
- the color of the stool is bright red, raspberry, the consistency of the stool resembles jelly;
- no appetite, sleep disturbed;
- the baby screams until he loses his voice.
With such signs, especially if there is vomiting and fever, hospitalization is vital. The sooner the baby is provided with competent assistance, the less likely it is to die. Therefore, if a child detects mucus and blood in the stool in combination with abdominal pain, you should immediately go to the pediatrician, and if there is a fever, be hospitalized by ambulance.
The appearance of blood in the stool in women
For women during their periods, simply mixing menstrual fluid and stool in the toilet bowl can give the impression of blood in the stool. To confirm or refute your suspicions, you need to examine the discharge separately, and in case of doubt, contact a proctologist after the end of menstruation. In some cases, the simultaneous presence of blood clots in the stool and menstruation can signal endometriosis of the rectum. This is a defect in the structure of tissues in which endometrial cells of the uterus are present in the rectal mucosa, causing monthly bleeding. For diagnosis, you will need to consult a proctologist and gynecologist. Hemorrhoids and anal fissures, especially after childbirth, are a common problem among women.
During anal sex, injuries, cracks and ruptures of the rectum are possible, so you need to follow safety precautions and avoid anatomically incorrect actions on the part of your partner. During pregnancy, the weight of the baby and amniotic fluid puts significant pressure on the pelvic floor, causing many women to experience internal hemorrhoids. A hemorrhoidal node is not always visible upon palpation, so the absence of tangible signs does not mean that there are no hemorrhoids. After childbirth, weakened pelvic floor muscles cannot ensure normal vascular function, and hemorrhoids progress. Treat hemorrhoids folk remedies– useless and naive. A timely visit to a proctologist will help you find out whether there is reason to worry about your life and health.
The discharge of black feces with blood indicates the need to find out the cause of two symptoms at once:
- Black feces;
- Blood in stool.
- Blood sausage and meat products with blood;
- Liver of animals and birds;
- Chokeberry;
- Red and black grape varieties;
- Prunes;
- Red beets;
- Natural juices from the listed vegetables and fruits;
- Red wine;
- Taking activated carbon;
- Taking iron supplements (Totema, Sorbifer, Ferrum-Lek, etc.);
- Taking multivitamin complexes with iron (Vitrum, Centrum, Multi-Tabs, etc.);
- Taking medications containing bismuth (De-Nol, Novbismol, etc.).
The second variant of black feces is called pathological and is caused by bleeding from the upper sections digestive tract. So, black feces is a sign gastrointestinal bleeding. Most often, such bleeding develops with cirrhosis of the liver, as well as with cancer or peptic ulcer stomach or duodenum. Usually in such situations, in addition to black stool, a person also experiences other symptoms of blood loss, such as pallor, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, fainting and abdominal pain. Moreover, the severity of symptoms depends on the amount of blood loss. If black stool appears in combination with the indicated symptoms, you should immediately seek medical help.
Thus, black stool may be a sign of pathology or may be caused by certain foods or medications. If you pass black stool with blood, you should first evaluate the most probable cause This is the color of feces. However, even if the black color of stool is due to the consumption of certain foods or medications, that is, it is physiological, then blood impurities clearly indicate pathological processes, occurring in the organs of the digestive tract.
Blood in stool can vary. The type of blood in the stool is very important to determine the specific pathological condition, which caused its appearance. A person can distinguish two types of blood in stool with the naked eye:
- Fresh blood, colored bright red;
- Blood in the form of dark red clots or streaks.
If blood in the stool is found in the form of dark red streaks or clots, then we're talking about about chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. Blood in this form is often present in the stool in Crohn's disease, nonspecific ulcerative colitis or dysbacteriosis.
Thus, black feces with blood may indicate the presence of the following variants of pathology of the digestive tract:
- The combination of gastrointestinal bleeding (black feces) with pathology of the lower intestines (red fresh blood);
- Combination of gastrointestinal bleeding (black stool) with inflammatory diseases intestines (streaks and clots of dark red blood);
- Pathology of the lower intestine (red fresh blood) in combination with physiological black feces, caused by the consumption of a number of foods or medications;
- Inflammatory bowel disease (streaks and clots of dark red blood) in combination with physiological black feces, caused by the consumption of a number of foods or medications.
Blood in stool is difficult to detect because most people simply don’t pay attention. Discharge of blood from the anus is not always accompanied by painful sensations or other symptoms. This causes certain difficulties - a person does not see a doctor, does not have a colonoscopy, and in the meantime the pathology can develop. The causes of blood in the stool of an adult are serious in 70% and may be associated with the appearance of tumors in the intestine and other serious illnesses gastrointestinal tract.
Droplets of blood in the stool appear in two ways: rectally through damage to the colon, rectum or microcracks in the anus.
Possible causes of blood in stool in men
Discharge with residual blood is provoked different types diseases. Some of them are not life-threatening and are easily treatable. And others require special attention.
When figuring out the exact etymology of the appearance of blood drops in stool, one should also rely on the patient’s lifestyle, his diet, and the presence of secondary diseases.
The most common reasons:
What does black stool mixed with blood indicate: 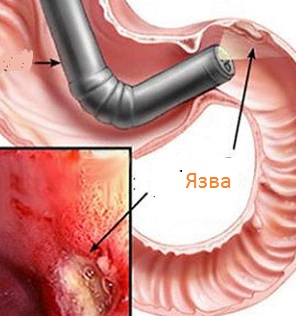
- For duodenal ulcer. The ulcers bleed and burst; in addition, one feels nausea, suffers from heartburn and sour belching with an unpleasant odor;
- On pathology of the esophagus - tumors, peptic ulcers, diverticulum. In most cases, the blood comes out with vomit, but sometimes it reaches the rectum;
- For mechanical damage - impacts, injuries, bruises abdominal cavity. Bloody stool is often accompanied by damage to the rectum;
- A long course of anticoagulants, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs reduce the level of prothrombin in the blood serum, it becomes very thin. Any minor blow to the stomach, bruise, or intestinal disease in this condition can lead to internal bleeding;
- Diseases of the bile and bile ducts - cholecystitis, tumors. Obstructive jaundice appears with changes in the color of the skin and whites of the eyes, and attacks of sharp pain in the right hypochondrium are bothersome. Helps diagnose gallbladder pathologies laboratory tests, Ultrasound;
- Malignant tumor, pancreatic cyst, as well as pancreatic necrosis (death of pancreatic tissue). The clinical picture is complemented by abdominal pain, indigestion, and decreased appetite. There is a large amount of undigested protein in the stool.
If, in addition to blood, corn, meat streaks, and tomato skin are found in the stool, this does not indicate an enzyme deficiency; everything is fine with your intestines.
Also remember if you have recently eaten dishes with beets or tomatoes. Often, beet juice may change the color of the stool towards a reddish tint or red blotches are observed - this is normal.
Why does blood come out of the anus with feces in women?
Women, having discovered traces of blood on toilet paper and in stool, immediately begin to sound the alarm. Selection bloody stool, bruises can appear against the background of various diseases or accompany a certain condition.
During pregnancy and after the birth of a child, the possibility of seeing drops of blood in the stool is high. This is due to heavy loads on the vascular system and the intestines.
Determining the cause at home is difficult, and the risk of misdiagnosis is high. It is better to go to the hospital and undergo a proper examination.
Which doctor should I contact if I have blood in my stool?
If you are suffering from abdominal pain, and after defecation you notice blood, you need urgent help from a specialist. A proctologist will help diagnose, prevent, and cure diseases of the large intestine, rectum, and anus.
Proctology is a popular branch of medicine, so you can find a proctologist at your place of residence.
In addition to the proctologist, depending on the problem, you may need a consultation: 
- Surgeon. Some gastrointestinal pathologies require surgical intervention;
- Hematologist. Blood in the stool sometimes occurs due to poor coagulation, hematological diseases;
- Oncologist. A doctor in this branch of medicine will help you choose correct treatment against cancer of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Infectious disease specialist. Dysentery, salmonellosis and other diseases require the supervision of an experienced infectious disease specialist; he will help you cope with the disease quickly and without consequences.
How to treat the problem of blood in stool?
You can only fight the cause of blood in the stool at home if the diagnosis has already been made and you have discussed the treatment regimen with the proctologist.
Self-medication with internal bleeding of the intestines and stomach can lead to not only serious complications, but also death. Urgent hospitalization is required. If blood is released from the intestines due to acute infection- dysentery, you should urgently call an ambulance. The longer dysentery lasts without treatment in a hospital setting, the greater the risk of developing secondary pathologies in other organs.
To treat hemorrhoids, you should use ointments:
You can cure hemorrhoidal disease with the help of suppositories:
Products with an antibacterial effect for healing anal fissures:
- “Mepakrine”, “Albendazole”, “Niclosamide” - help against cestodes;
- “Chloxyl”, “Bithionol”, “Perchlorethylene” - cope with trematodes;
- "Levamisole", "Piperazine", "Mebendazole", "Albendazole" - destroy nematodes.
If biochemical analysis blood serum showed that you have low coagulability. This means you need to take a course of coagulants (drugs that thicken the blood), refuse or reduce the dosage of antibiotics, antiviral agents, as well as drugs for the cardiac vascular system.
Peptic ulcers, thrombosis, oncology, and chemical poisoning cannot be treated at home. Only hospitalization and therapy under the supervision of experienced medical professionals will help you.
