Stages of the procedure for issuing equity securities. Procedure for issuing securities
On the procedure for issuing securities.
According to Russian legislation, legal entities that have the organizational and legal form of a joint stock company (JSC) carry out an issue - issue and placement of shares. The ownership of these securities (CS), which secure the shareholders' shares in the authorized capital and profits, comes into force after state registration of the issue. The authority to carry out such a procedure is vested in the territorial departments of the Bank of Russia.
A similar procedure for issuing securities exists for bonds, options, etc.
Types and purposes of emissions
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Laws “On Joint-Stock Companies” and “On the Securities Market”, other legal acts comprehensively regulate the purposes of placement of various issues of the Central Bank.
Types of emissions commonly encountered in everyday practice include:
- primary– placement of the first issue of shares upon creation of a joint-stock company;
- additional– issue of an additional issue when increasing the size of the authorized capital;
- reorganization– making changes to the distribution of shares of founders / shareholders in cases of merger / division / affiliation / spin-off of organizations or their transformation (LLC / production cooperative into JSC);
- bond issues carried out to attract additional working capital through a bond issue.
Procedure for issuing securities
The legislation prescribes a certain sequence of actions within a strict time frame for activities aimed at transferring ownership rights from the issuer to the first owners of the securities.
Stage I. Decision on issue.
Performers. Board of directors/supervisory board of a joint stock company.
Stage II. Approval of the decision.
Performers and deadlines. The board of directors/supervisory board approves the decision on the issue no later than 6 months after its adoption.
Stage III. Registration of issue.
2) making a decision on registration by the authorized state body of the Bank of Russia.
Performers and deadlines. The territorial department of the Bank of Russia reviews an application for registration completed in accordance with legal requirements within 30 days from the date of submission by the issuer.
Emission is suspended if violations are detected. 30 days are allotted for elimination; failure to comply with this period may result in refusal of registration.
Stage VI. Placement of issued securities.
Performers. Carried out by the issuer (or an agent authorized by him - a professional participant in the securities market) on the conditions set forth in the “Decision on the issue” (see above).
Stage V. Registration of the results of the issue.
Performers and deadlines. The territorial department of the Bank of Russia reviews and registers the report on conditions similar to state registration of the issue (see above).
Important! The report must be filed within 30 days of the designated posting period.
Note: an organization has the right to delegate the adoption and approval of documents on the issue and placement of securities to other (other than the board of directors) its own governing bodies, if such functions are prescribed for them in the company’s charter.
Special cases
The standard procedure for issuing securities discussed above changes during the initial placement of newly created joint-stock companies or during their complex reorganizations. In this case, actions for state registration are carried out after the issue of securities: the application to the authorized territorial department of the Bank of Russia simultaneously contains information about the issue of shares and a report on their placement.
security right issue
In accordance with Art. 19 of the Federal Law “On the Securities Market”, the procedure for issuing equity securities includes the following stages:
- * adoption by the issuer of a decision on the placement of issue-grade securities;
- * approval of the decision on the issue of issue-grade securities;
- * state registration of the issue of issue-grade securities;
- * placement of issue-grade securities;
- * state registration of a report on the results of the issue of equity securities.
When placing issue-grade securities by open subscription or by closed subscription among a circle of persons whose number exceeds 500, state registration of the issue is accompanied by state registration of the securities prospectus.
All stages of the issue are regulated in detail by law.
There are certain features when issuing shares when establishing joint-stock companies, so the study of the issue procedure should begin with their consideration.
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 99 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, when establishing a joint-stock company, all its shares are distributed among the founders, i.e. among persons who decide to create a joint stock company. The procedure for distributing shares among the founders, the types of shares and the timing of their payment are determined in the agreement on the creation of a joint-stock company, for which the law requires a mandatory written form (Part 2, Clause 1, Article 98 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
This agreement cannot be considered as a constituent agreement. According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the constituent document for joint-stock companies is only the charter. The agreement between the founders is valid until they fully fulfill their obligations, including payment for shares, unless a different period is specified in the agreement itself. The agreement of the founders on the creation of a joint-stock company, by its legal nature, is an agreement on joint activities to establish the company.
In this regard, when considering a dispute about invalidating an agreement on the creation of a joint-stock company, courts must be guided by the relevant norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on the invalidity of transactions. If such an agreement does not comply with the requirements of the law or other legal acts, it is void, regardless of whether it is recognized as such by the court (Article 168 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Since the Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not exclude the possibility of filing a claim to declare a void transaction invalid, any interested party may file such a claim in court. Supreme Court of the Russian Federation and the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation “On some issues of application of the Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies”” dated April 2, 1997 // Russian Air Force. ? 1997. ? No.9..
From the moment of concluding an agreement on the creation of a joint-stock company, the founders have civil obligations to pay for the shares assigned to them. Clause 2 of Art. 99 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation contains a mandatory rule prohibiting the release of a shareholder from the obligation to pay for shares.
Payment for shares can be made in cash or other form. As payment for shares, it is possible to contribute securities, other things or property rights or other rights that have a monetary value. The monetary valuation of the property contributed in payment for shares when establishing a company is made by agreement between the founders.
When paying for shares in kind, an independent appraiser must be involved to determine the market value of such property. The value of the monetary valuation of property made by the founders of the company cannot be higher than the value of the valuation made by an independent appraiser (clause 3 of Article 34 of the Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies”).
In addition, the legislation establishes a dispositive rule, according to which shares paid for in kind are paid for in full upon their acquisition, but the agreement on the creation of a company may provide for a different payment procedure. The shareholder laws of many foreign countries establish more stringent requirements for payment for shares in kind. Thus, in France it is not allowed to pay for shares with intellectual capital.
The company's shares distributed upon its establishment must be fully paid within a year from the date of state registration of the company. At least 50% of the company’s shares distributed upon its establishment must be paid for within three months from the date of state registration of the company (Clause 1, Article 34 of the Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies”).
Shares that are not fully paid on time become the property of the joint stock company and must be sold no later than one year from the date of receipt at a price not lower than their par value. If the shares remain unsold, the general meeting of shareholders must decide to reduce the authorized capital of the company by redeeming the unsold shares. Shares, the ownership of which has been transferred to the company, do not provide voting rights, are not taken into account when counting votes, and dividends are not accrued on them.
Founders who improperly fulfill their obligations to pay for shares may be held liable in the form of a penalty, if this is provided for in the agreement on the creation of the company. Founders who have not fully paid for the shares bear joint liability for the obligations of the joint stock company to the extent of the unpaid portion of the value of the shares they own.
After outlining the features of the issue of shares when establishing joint-stock companies, we should dwell in more detail on the consideration of the stages of the issue.
The first stage: the issuer makes a decision to issue equity securities. The decision to issue securities is made by the issuer's management body (board of directors (supervisory board) or other body performing its functions).
From a formal point of view, in accordance with Art. 2 of the Federal Law “On the Securities Market”, a decision on the issue of issue-grade securities is a document containing data sufficient to establish the scope of rights secured by the security. It must contain certain details provided for in Art. 17 of the Federal Law “On the Securities Market”, in particular:
- - full name of the issuer, its location and postal address;
- - the date of the decision to place equity securities;
- - name of the authorized body of the issuer that made the decision on placement;
- - date of approval of the decision on release;
- - name of the authorized body of the issuer that approved the decision on the issue;
- - type, category, type of issue-grade securities;
- - the rights of the owner secured by the issue security;
- - procedure for placement of issue-grade securities;
- - an indication of whether the papers are registered or bearer;
- - nominal value of issue-grade securities.
The decision on the issue may determine the share of shares placed by subscription, if non-placement of which the issue of shares is considered failed. In case of documentary form of issue-grade securities, it is necessary to additionally provide a description or a sample of the certificate.
The decision on release is drawn up in three copies, certified by the registration authority. One copy is kept by the registration authority, the second by the issuer, and the third is transferred to the registrar for storage. In the event of a discrepancy in the text between copies of the decision, the text of the document stored in the registration authority is considered true.
The second stage of the issue procedure is approval of the decision to issue issue-grade securities. The decision to issue securities of business companies is approved by the board of directors (supervisory board). The decision to issue securities of legal entities of other organizational and legal forms is approved by the highest management body.
The third stage of the issue is state registration of the issue of securities.
Russian legislation provides for the need for state registration of all issues of equity securities, regardless of the method of placement, the size of the issue and the number of investors. State registration determines the possibility of advertising, placement (except in certain cases), as well as circulation of issue-grade securities.
For state registration of the issue of issue-grade securities, the issuer is obliged to provide the registration authority with the documents provided for by the Federal Law “On the Securities Market” and the Issue Standards. When placing certified securities, you must also provide a sample security certificate. In addition, the registration authority must be provided with a copy of the agreement with the registrar on maintaining a register of owners of registered securities or a document confirming the circumstances that exempt the issuer from concluding such an agreement.
The legal status of registering bodies is determined by the Regulations on registering bodies carrying out state registration of issues of securities Resolution of the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of March 4, 1997 No. 11 // Bulletin of the Federal Securities Commission of Russia. ? 1997. ? No. 3. (approved by Resolution of the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of March 4, 1997 No. 11, with subsequent amendments).
Registration authority:
- * receives and reviews documents subject to submission for state registration of securities issues;
- * adopts, based on the results of consideration of documents to be submitted for state registration of securities issues, a decision on state registration or refusal of state registration of securities issues;
- * maintains a register of issues of securities registered and canceled by him, as well as issues of securities, the issue of which is suspended or resumed;
- * stores documents related to state registration of securities issues;
- * provides information and reports to the Federal Securities Commission;
- * considers complaints and statements regarding actions related to the issue of securities issues registered by him;
- * cancels the state registration of the issue of securities in the event that the issue of securities is declared invalid or the issue of securities is declared invalid (clause 11 of the Regulations).
To exercise such powers, the registration authority has the right:
- * request from issuers any information related to their issue of securities;
- * send issuers mandatory instructions to eliminate violations related to the issue of securities;
- * suspend the issue of securities and recognize the issue of securities as failed.
The registration authority also exercises other powers granted by laws and other legal acts Russian Federation(Clause 12 of the Regulations).
The registration authority has the right to conduct inspections of issuers of securities.
List of registration bodies carrying out state registration of securities issues on the territory of the Russian Federation Order of the Federal Commission for the Securities Market dated November 15, 2001 No. 1117-r // Bulletin of the Federal Securities Commission of Russia. ? 2001. ? No. 11., establishes that issues of government issued securities of the Russian Federation; issues of government issued securities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation; issues of municipal securities; issues of securities issued by organizations for the purpose of restructuring debt on payments to the federal budget; bond issues of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation; issues of bonds of the state corporation "Agency for Restructuring of Credit Institutions" under guarantees of the Government of the Russian Federation; Issues of securities of state and municipal unitary enterprises or institutions are registered with the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. Issues of issue-grade securities of credit institutions, with the exception of issues of option certificates, are registered in Central Bank RF. All other issues are registered by the Federal Securities Market Commission and its regional branches.
The registration authority is obliged to register the issue of securities or make a reasoned decision to refuse registration within 30 days from the date of receipt of all documents and magnetic media.
The registration authority has the right to refuse to register an issue of equity securities on the grounds provided for in the Federal Law “On the Securities Market”, for example: if the issuer violates the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation on securities; inconsistency of the submitted documents and the information contained therein with the requirements of the law; introducing false or false information into the securities prospectus or the decision to issue securities false information; failure of the financial adviser who signed the securities prospectus to comply with the established requirements.
If state registration of an issue of securities is refused, the registering authority is obliged, no later than three days from the date of the decision to do so, to send the issuer a substantiated notice of the refusal of state registration. The decision to refuse to register an issue of securities may be appealed in court.
An additional stage in the issue of securities is the preparation and registration of a securities prospectus. Registration of the prospectus is carried out when placing issue-grade securities by open subscription or by closed subscription among a circle of persons whose number exceeds 500. Federal Law “On the Peculiarities of the Issue and Circulation of State and Municipal Securities” dated July 29, 1998 No. 136-FZ // NW RF. ? 1998. ? No. 31. ? Art. 3814.
The securities prospectus must contain the following information:
- * brief information about the persons included in the management bodies of the issuers, information about bank accounts, about the auditor, appraiser and financial consultant of the issuer, as well as about other persons who signed the prospectus;
- * brief information about the volume, terms, procedure and conditions for the placement of issue-grade securities;
- * basic information about the financial and economic condition of the issuer and risk factors;
- * detailed information about the issuer;
- * information on the financial and economic activities of the issuer;
- * detailed information about the persons included in the issuer's management bodies, the issuer's bodies for control of its financial and economic activities, and brief information about the issuer's employees;
- * information about the participants (shareholders) of the issuer and about transactions carried out by the issuer in which there was an interest;
- * accounting statements of the issuer and other financial information;
- * detailed information on the procedure and conditions for the placement of issue-grade securities;
- * additional information about the issuer and its placement of issue-grade securities.
The securities prospectus is approved by the directors' account and signed by the sole executive body, chief accountant, auditor, and, in cases provided for by law, by an independent appraiser.
In addition, for a public offering and/or public circulation, the prospectus must also be signed by the financial advisor. The persons who signed the prospectus bear joint and several liability with the issuer for damage caused by the issuer to the investor as a result of unreliable, incomplete and (or) misleading information contained in the prospectus.
Registration authorities are responsible only for the completeness of the information contained in the securities prospectus, but not for their accuracy. This means that investors must independently make a decision to purchase or refuse to purchase securities, only based on the fact of registration. In order to avoid misconceptions associated with the fact of state registration, the legislation contains a requirement according to which title page The prospectus must contain the following provision: “The registration authority is not responsible for the accuracy of the information contained in this securities prospectus, and the fact of its registration does not express its attitude towards the securities being placed.” The said phrase must be printed in the largest type used to print the rest of the text on the title page of the Prefect of Securities.
Recent changes to the Federal Law “On the Securities Market” have significantly expanded the list of information indicated in the prospectus, as is customary in practice developed countries. After registering the decision to issue securities and the securities prospectus, the issuer can proceed to the next stage of the issue - placement.
The legal definition of the placement of issue-grade securities is given in Art. 2 Federal Law “On the Securities Market”. Placement means the alienation of issue-grade securities by the issuer to the first owners through the conclusion of civil transactions. Public placement of securities is the placement of securities by open subscription, including the placement of securities at auctions of stock exchanges and/or other organizers of trading on the securities market.
The issuer has the right to begin placing the securities it issues only after registration of their issue. The number of issued issue-grade securities to be placed must not exceed the number specified in the constituent documents and in the decision to issue securities. However, the issuer has the right to place a smaller number of issue-grade securities than specified in the decision on the issue. In this case, the actual number of placed securities is indicated in the report on the results of the issue submitted for registration. In addition, the issuer is obliged to complete the placement of issued securities no later than one year from the date of state registration of the issue, unless other terms for the placement of issued securities are established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with the Standards, the following methods of placing an issue of shares are possible:
- * distribution among the founders of the joint-stock company upon its establishment;
- * distribution of additional shares among shareholders of the joint-stock company;
- * subscription;
- * conversion.
Bonds can be placed only by subscription.
A feature of the distribution of shares when establishing a joint-stock company is that they are placed before the state registration of their issue on the basis of an agreement on the creation of a joint-stock company. Documents for state registration of the issue of shares distributed among the founders of the joint-stock company upon its establishment, as well as a report on the results of their issue, must be submitted to the registration authority no later than a month from the date of state registration of the joint-stock company. It should be noted that violation of the deadline for submitting documents for state registration of the issue and registration of the report on the results of the issue cannot be the basis for the registration authority to make a decision to refuse state registration of the issue.
Distribution of shares among shareholders is one of the ways to capitalize the assets of a joint stock company. The standards establish the rule that additional shares may only be issued from the following sources:
- * additional capital of the joint-stock company;
- * fund balance special purpose based on the results of the previous year;
- * retained earnings of the joint stock company from previous years.
The formation of fractional shares as a result of the distribution of additional shares is not permitted.
The peculiarity of this method of placement is that it does not require the conclusion of any agreements and is carried out by making changes to the data in the system for maintaining the register of shareholders. With this method of placement, payment for shares is made at the expense of the joint-stock company itself, and not at the expense of the shareholders, which, as noted by D.V. Murzin, Murzin D.V. Securities are incorporeal things. ? pp. 142-143. contradicts the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which contains an imperative rule: “it is not permitted to release a shareholder from the obligation to pay for the company’s shares, including releasing him from this obligation by offsetting claims against the company.”
Subscription is the placement of securities on the basis of contracts. Thus, the distinctive feature of this method of placement is the need to conclude contracts. Subscription, unlike other methods of placement, is associated with the attraction of additional capital by the issuer and is carried out as part of an increase in the authorized capital of the joint-stock company.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes two conditions under which joint stock companies have the right to place additional shares:
firstly, an increase in the authorized capital is possible only after it has been fully paid;
secondly, it is not allowed to increase the authorized capital of the company to cover incurred losses (Part 2 of Article 100 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
By general rule The decision to increase the authorized capital by placing additional shares is made by the general meeting of shareholders, but in the charter the decision on this issue may be within the competence of the board of directors.
The Federal Law “On Joint Stock Companies” establishes that additional shares can be placed only within the limits of the number of authorized shares. The category of authorized shares is new to Russian legislation. “It is borrowed,” notes D. Lomakin, “from US corporate law, where a distinction is traditionally made between shares that a corporation has the right to issue (authorized shares) and actually issued shares. A separate group there includes shares paid for by shareholders.” Lomakin D. Legal regulation of the transfer of shares // Economy and Law. ? 1996. ? No. 9. ? P. 146. The number and categories of authorized shares must be indicated in the charter. The par value of authorized shares is not included in the amount of the authorized capital, since the joint stock company is only given the opportunity to issue them.
If the charter does not contain information about declared shares or their number is less than planned to be issued, then the general meeting must amend the charter; It should be noted that resolving issues related to changes in the number of authorized shares falls within the exclusive competence of the general meeting and cannot be referred to the board of directors. The General Meeting of Shareholders has the right to simultaneously make two decisions: to increase the number of authorized shares and to increase the authorized capital by placing additional shares within the limits of the number of authorized shares.
The decision to increase the authorized capital by placing additional shares determines the number of shares to be placed, their categories, terms and conditions of placement, and form of payment. Additional shares and other issue papers of the company placed by subscription are placed subject to full payment. When paying for additional shares in non-cash, the monetary valuation of the property contributed to pay for the shares is made by the board of directors. Payment for other securities can only be made in cash.
Payment for additional shares of the company placed through subscription is carried out at a price determined by the board of directors of the company, but not lower than their nominal value. The placement price should be determined based on the market value of the shares.
An independent appraiser may be hired to determine the market value. When determining the market value, the board of directors must take into account the printed data on the purchase price or bid and offer prices for the securities being placed, if they are regularly published (in this case, the involvement of an independent appraiser is not necessary); the size of the company's net assets; the price that a buyer who has full information on the aggregate value of all ordinary shares.
To determine the market value of shares, if the owner is the state and (or) a municipal entity, the involvement of an independent appraiser (auditor) is necessary.
In practice, determining the market value of shares is quite difficult, firstly, due to the lack of a constant quotation of shares in most joint-stock companies, and secondly, due to the lack of a generally accepted methodology for determining the market value of shares.
Determination of the market value of shares with significant violations established by Art. 77 of the Federal Law “On Joint Stock Companies” allows you to challenge in court the decision of the board of directors (supervisory board) to determine the market value of shares. The size of the market value of shares determined by the board of directors can be challenged in court only if it is so inconsistent with the actual market value that it indicates that the members of the board of directors acted in bad faith and unreasonably, or if the decision to determine the market value of shares was made with the participation of members of the board of directors who are interested in the company’s placement of shares by L.R. Yuldashbaev. Legal regulation of equity securities (shares, bonds). ? P. 161..
The Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies” provides for two exceptions to the rule that shares should be placed only at their market value. Firstly, a joint stock company has the right to place shares at a price lower than their market value in the case of placing additional shares to shareholders - when they exercise the pre-emptive right to purchase such shares at a price that may be lower than the placement price to other persons, but not more than 10% . Secondly, in the case of placement of additional shares with the participation of an intermediary. The intermediary's remuneration should not exceed 10% of the share placement price.
In cases where a company places issue-grade securities (bonds) convertible into shares, they must also be placed at a price not lower than the par value of the shares into which such securities are converted. This rule was established to prevent circumventing the ban on placing shares at a price below their market value. There are also exceptions to this rule. Firstly, a 10% discount is provided to shareholders who exercise their pre-emptive right to purchase securities over other acquirers. Secondly, the amount of the intermediary's remuneration should not exceed 10% of the placement price of such securities.
The placement price of issue-grade securities that are not convertible into shares is determined by the board of directors of the joint-stock company.
The legislation also imperatively regulates the period of payment for additional shares and other issue-grade securities: placement occurs only if they are paid in full.
Resolution of the Federal Commission for the Securities Market “On improving state registration of bond issues” Resolution of the Federal Commission for the Securities Market “On improving state registration of bond issues” dated June 19, 1999 No. 25. // Bulletin of the Federal Securities Commission of Russia. ? 1998. ? No. 6. provided for the possibility of establishing in the decision on the issue of bonds (except for convertible ones) placed by subscription, their placement in parts over several periods (tranches), but no later than a year from the date of approval of the decision on the issue. Thus, having registered a bond issue for a large amount, the issuer can place them not immediately, but throughout the year, as necessary, in several tranches.
The Federal Law “On Joint Stock Companies” and the Issue Standards distinguish between two types of subscription: open and closed. The classification is based on whether securities are placed among a predetermined circle of persons or not. With an open subscription, shares are distributed among a potentially unlimited number of investors - with a public announcement, an advertising campaign and registration of a securities prospectus. Only open joint stock companies can place shares in this way. A closed company does not have the right to place shares and other securities convertible into shares through open subscription. With a closed subscription, which is carried out among a previously known circle of investors (their number cannot exceed 500), there is no advertising campaign and no public announcements are made about the upcoming issue of additional shares. The company's charter and legal acts of the Russian Federation may limit the possibility of conducting a closed subscription by open joint-stock companies. The decision to place shares and securities convertible into shares through private subscription is made only by the general meeting of shareholders with three-quarters of the votes, unless the need for a larger number of votes to make this decision is provided for by the charter of the joint-stock company.
Conversion of securities is the transformation of one type of securities into another. The procedure for converting equity securities into shares is established:
- * the company's charter - regarding the conversion of preferred shares;
- * the decision on the issue - in relation to the conversion of bonds and other, with the exception of shares, equity securities (Article 37 of the Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies”).
The question of the moment of acquisition of rights to the placed securities is quite complex.
In Art. 29 of the Federal Law “On the Securities Market” establishes a rule on the moment of emergence of rights to issue-grade securities traded on the secondary market. The moment of acquisition of rights to placed securities is not established by law. It seems that in this case we should agree with the opinion of L.R. Yuldashbaeva about the possibility of applying the analogy of the law, and the moment of acquisition of rights to the placed securities and to the securities traded on the secondary market should be determined similarly to Yuldashbaeva L.R. Legal regulation of equity securities (shares, bonds). ? P. 151.. At the same time, as an exception to general rule on the simultaneous transfer of the rights secured by issue-grade securities and the rights to this security; the rights secured by the share pass to the acquirer only after full payment. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 34 of the Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies”, a share owned by the founder does not provide voting rights until it is fully paid for, unless otherwise provided by the company’s charter. Unpaid shares also do not give the right to receive a dividend, since there is an imperative rule that the company does not have the right to decide to pay dividends until the authorized capital is fully paid. Thus, it should be recognized that only full payment of shares is a condition for the transfer of all rights from the share to the shareholder. In addition, a shareholder who has not fully paid for the shares does not have the right to dispose of them. It is also prohibited to carry out any transactions with securities before registering a report on the results of their issue. Article 27 of the Federal Law “On the Securities Market” establishes a ban on the circulation of all issue-grade securities until they have been fully paid for and the state registration of a report on the results of their issue. This rule is established in Art. 5 of the Federal Law “On the Protection of the Rights and Legitimate Interests of Investors in the Securities Market”: the execution by the owner of securities of any transactions with the securities he owns before they are fully paid for and a report on the results of their issue is registered is prohibited.
Before the adoption of the Federal Law “On the Protection of the Rights and Legitimate Interests of Investors in the Securities Market,” transactions with placed securities were allowed until they were fully paid for and before the report on the results of their issue was registered. The possibility of making transactions was associated solely with the need for state registration of the issue of securities. Thus, in the information letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation “Review of the practice of resolving disputes on transactions related to the placement and circulation of shares” it was emphasized that only shares whose issue is registered in the prescribed manner are allowed for circulation on the secondary market Information letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated April 21, 1998 No. 33 // Bulletin of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation. ? 1998. ? No. 6. ? P. 82.. The introduction of restrictions on the circulation of incompletely paid securities, as well as securities the release report of which has not passed state registration, seems completely justified, since these restrictions are designed to protect the rights of acquirers in the secondary securities market.
It should be taken into account that current legislation does not link the entry of a credit entry into a shareholder’s personal account with the fact of full payment for the acquired shares. The opening of personal accounts and the transfer of shares to them are carried out on the basis of a decision on the issue of securities in the case of placement of shares upon the establishment of a company or on the basis of civil contracts concluded between the issuer and the acquirer in the case of the placement of additional shares. Resolution of the Federal Commission for the Securities Market "On approval of the Regulations on licensing activities for maintaining a register of owners of registered securities" dated June 19, 1998 No. 24 // Bulletin of the Federal Securities Commission. ? 1998. ? No. 5., i.e. a person is recognized as the owner of shares until they are paid for. However, failure to pay for shares on time entails such consequences as their withdrawal from the shareholder and transfer to the ownership of the company, about which a corresponding entry must be made in the register of shareholders. The ban on transactions with equity securities before registration of a report on the results of their issue can be explained by the desire of the legislator to ensure the rights of investors. Before registering the report, the FCSM and its regional branches may recognize the issue as invalid on the grounds specified in the law.
Recognition of an issue as invalid entails the withdrawal of securities of this issue from circulation and the return of funds transferred by investors as payment for such securities. But if we allow the alienation of such securities by the first investors, then the problem of protecting the rights of subsequent acquirers of these securities on the secondary market immediately arises. It will be much more difficult to protect the rights of such acquirers, therefore the ban on the alienation of issue-grade securities before registration of a report on the results of the issue effectively protects the rights of subsequent investors in the secondary market.
To summarize, it is appropriate to recall what was said back in 1878 by I.T. Tarasov’s opinion that “there cannot be unpaid shares in the exact sense of the word, because shares are issued or should be issued only when their nominal price is paid in full” Tarasov I.T. Teaching about joint stock companies. ? M., 2000. ? P. 374.. And although, in accordance with current legislation, a person who acquired shares by way of placement is recognized as a shareholder, the right to shares and rights arising from shares are transferred to him, as more than a hundred years ago, in full only after their full payment, as well as registration of a report on the results of their release.
As practice shows, the greatest number of violations of shareholders' rights occur in the process of closed subscription to shares, therefore, in order to protect the rights of small investors, the legislation has established that only a general meeting of shareholders can make a decision on a closed subscription. Such a decision, in particular, must contain an indication of the circle or category of persons among whom it is intended to place the securities, the placement period, the price (the procedure for determining the price). The Federal Law “On Joint Stock Companies” established (Article 40) that shareholders of the company who voted against or did not take part in voting on the issue of placing shares and issue-grade securities convertible into shares through private subscription have a preemptive right to acquire additional shares and issue-grade securities securities convertible into shares, placed through private subscription, in an amount proportional to the number of shares of this category (type) owned by them.
The final stage of the issuance process is the registration of a report on the results of the issue of securities. In accordance with the law, the issuer is obliged to submit a report on the results of the issue to the registration authority no later than 30 days after the completion of the placement of securities. At the same time, documents are submitted confirming the issuer's compliance with legal requirements. The registration authority, within two weeks from the date of receipt of the report on the results of the issue and other necessary documents, is obliged to register the report or refuse to register it. The grounds for refusal to register a report on the results of the issue of securities are the grounds for recognizing the issue as invalid.
Securities are placed on the market and purchased by individuals or legal entities. The funds received are used in accordance with the declared purpose.
Options for issuing securities
The issue and placement of securities is carried out in accordance with the requirements of current legislation and is carried out under the control of government bodies. Such measures are taken to eliminate cases of fraud on the part of unscrupulous firms and companies. The release or issue can have several implementation options:- Primary release is used at the initial stage of development of a company or enterprise. A legal entity starting a commercial activity places shares or bonds on the market in order to attract borrowed funds.
- In the process of operation, the company may re-place securities on the market. Such an issue is called subsequent.
- The distribution of shares also refers to the concept of issue. Executed after registration legal entity and in the process of its activities.
- Closed or open subscription is the placement of securities between a limited number of persons or in the public domain.
Stages of issuing securities
In accordance with the generally accepted scheme for working with securities, the underwriter performs several tasks. A specialist can buy a batch of shares and bonds at a fixed price and place the securities on the market, taking on all the risks. The second option involves repurchasing part of the securities that the company was unable to place on its own. The third way is that the underwriter takes on the function of an intermediary.The technology for issuing securities includes several stages:
- The business owner decides on the need for an issue.
- The issue of securities is registered with the relevant government agencies.
- Shares or bonds are issued in the initially approved form.
- Securities are placed on the market by the issuer or with the help of underwriters.
- Based on the results of the issue, a report is generated and registered.
- When issuing shares, appropriate changes are made to the company's authorized capital.
Today, NSD has an established technology, proven by many years of practice, for servicing and providing services to issuers of corporate bonds, government bonds of the Russian Federation and constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities in the process of placement and secondary circulation:
- registration of rights and mandatory centralized storage of the certificate of issue of documentary bearer bonds;
- maintaining the issuer's emission account;
- maintaining a treasury securities account;
- making transfers of bonds to depositor accounts based on the results of transactions concluded on the exchange or over-the-counter market, including during the placement and circulation of bonds;
- ensuring the preparation and execution of coupon payments and redemption of the par value of bonds;
- comprehensive support for the process of early repurchase and redemption of bonds by the issuer.
In the process of providing the above services, NSD exchanges documents with the issuer in electronic form(under the agreement on the exchange of electronic documents).
Transfers of bonds across accounts can be carried out under the following conditions:
- transfer on the terms of “delivery versus payment” (DVP) during exchange placement and circulation;
- transfer on delivery versus payment (DVP) terms for over-the-counter placement and circulation;
NSD, as a depository that carries out mandatory centralized storage of certificates for issues of documentary bearer bonds, ensures the transfer to NSD depositors cash received from the issuer to fulfill its obligations to bondholders (for bonds whose state registration or assignment of an identification number was carried out after 01/01/2012).
The procedure for NSD providing the issuer with services for storing securities certificates and recording rights to securities by opening and maintaining the issuer's issue account/treasury securities account, carrying out transactions on these accounts related to the placement, circulation, repurchase, redemption of securities, transfer of payments on securities securities, etc., in accordance with the terms of issue and circulation of securities is established.
Stages of bond issue
At the initial stage, the issuer accepts decision to issue bonds, after which the issuer, together with the financial advisor or underwriter, begins preparation for registration of terms of bond issue (prospectus, decision on issue). The stage of preparing the terms of the bond issue is one of the most significant, since the placement and circulation of bonds on the stock exchange, as well as the servicing of the bond issue at NSD are subsequently carried out in accordance with the registered terms of the issue.
Documents containing the terms of the bond issue, prepared by the issuer for registration of the issue, are necessarily agreed upon with NSD regarding the procedure for servicing the issue by the depository, which carries out the mandatory centralized storage of the securities issue certificate.
The second stage is conclusion of an issue account agreement between the issuer and NSD. A copy of the agreement is provided to the registration authority during state registration of the issue of securities or to the exchange that assigns an identification number to the issue of exchange-traded bonds.
The next stage is state registration issue of bonds by the registering authority with assignment of a state registration number or assigning an identification number to the issue of exchange-traded or commercial bonds.
After state registration of a bond issue or assignment of an identification number to the bond issue, the issuer forms and submits a package of documents to NSD necessary to ensure the placement, circulation and redemption of the bond issue, in accordance with the Regulations on the interaction between NPO JSC NSD and the issuer.
Issuer before the placement start date transfers for storage to NSD bond certificate issued for the entire volume of the issue. The certificate must be issued in accordance with the requirements of Federal Law dated April 22, 1996 No. 39-FZ “On the Securities Market”. An example of filling out and the form of the Certificate is presented in the section “Documents regulating interaction with issuers”. This section presents the documents that the issuer must prepare when interacting with NSD.
Procedure for the initial placement of bonds on the MB
- The issuer submits to NSD a set of documents for the placement of bonds (issue documents (prospectus, resolution), etc.):
- NSD deposits the certificate;
- NSD, on the instructions of the issuer (instruction MF020), transfers bonds to the trading section of the issue account.
- The issuer authorizes the underwriter to place orders for the sale of bonds in the Trading System of the Moscow Exchange on behalf of the issuer.
- Reservation of funds by trading participants in accounts with NSD.
- NSD transmits to NCC information about the number of bonds in the issuer's issue account and to the Moscow Exchange Trading System about funds reserved in the settlement accounts of trading participants.
- The underwriter places orders for the sale of bonds in the Trading System of the Moscow Exchange.
- Trading participants who have reserved funds in a current account with NSD submit orders to purchase bonds in the Trading System of the Moscow Exchange.
- Based on the results of trading, NCC transmits to NSD information on the number of bonds to be written off from the Issuer's emission account to the depositor's account or. Also, information is sent to NSD about the debiting of funds from the settlement accounts of trading participants whose purchase applications were satisfied, and the crediting of funds to the underwriter’s settlement account.
- NSD makes settlements on transactions according to information received from NCC.
- NSD debits funds from the settlement accounts of trading participants and credits them to the underwriter's settlement account in accordance with the information received from NCC.
- The underwriter transfers the funds received as a result of the placement of bonds to the issuer's bank account.
Procedure for the initial placement of bonds through closed subscription
Free delivery on counter orders:
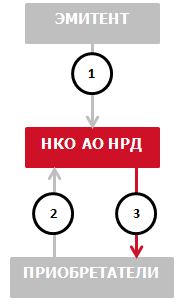
- The Issuer submits to NSD a set of documents for placement and deposits the certificate, and also submits a custody order (in the MF010 form) to transfer bonds from the Issuer's issue account to the acquirer's custody account.
- The acquirer submits to NSD:
- custody order (in form MF010) to credit bonds from the Issuer's issue account to the acquirer's securities account;
- verifies the custody orders of the Issuer and the Acquirer;
- transfers bonds from the Issuer's issue account to the Acquirer's securities account;
With control of cash settlements:
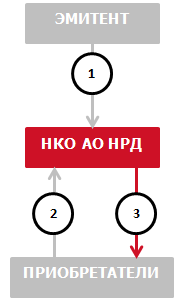
- The issuer submits to NSD a set of documents for the placement of bonds (issue documents (prospectus, resolution), etc.):
- The Issuer enters into an Issue Account Agreement with NSD;
- NSD opens an issuing account;
- NSD accepts bond issues for servicing;
- NSD deposits the certificate;
- The issuer submits an order to transfer bonds to the depositor's securities accounts (instruction MF170).
- The depositor submits to NSD:
- securities instruction in form MF170 to credit bonds from the issuer's issue account to the depositor's securities account;
- payment order for the transfer of funds from your current account at NSD to the issuer's current account at NSD.
- NSD performs the following actions:
- verifies the securities orders of the issuer and the depositor and the payment order of the depositor;
- transfers bonds from the issuer's issue account to the depositor's securities account;
- transfers funds from the depositor's current account to the issuer's current account.
NSD performs the functions of a paying agent
According to Federal Law No. 39-FZ “On the Securities Market” and Articles 214.1 and 310 of Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Law):
- Income for all securities with mandatory centralized storage (hereinafter referred to as Securities) are transferred by the issuer through the depository which carries out mandatory centralized storage of securities (hereinafter referred to as the Central Depository). The Central Depository transfers income to its depositors, including depositors - nominal holders, who transfer income to their depositors, etc., to the final owner;
- Depositories are tax agents when making income payments for Securities in relation to individuals and non-residents who have an owner's securities account in this depository.
- Lists of owners for payments on Securities are not collected. Income is transferred to the depositor in whose securities account the securities were recorded on the date determined in accordance with the decision to issue securities to the current legislation.
- The right of the issuer is provided once a year to receive from the depository, which carries out the mandatory centralized storage of issue-grade securities, a list of owners for a fee not exceeding the cost of its production, and in other cases - for the fee specified in the agreement with the depositary, which carries out the centralized storage of securities .
Thus, the function of transferring payments is an integral part of the depository services that depositories provide to their depositors. The law applies to bond issues that are registered/identification number assigned after 01/01/2012 and to all federal government issued securities with mandatory centralized storage, regardless of the date of registration of their issue.
For bond issues that were registered/identification number assigned before 01/01/2012, the procedure for collecting a list of owners and/or nominee holders, its transfer to the issuer and paying agent, as well as the procedure for paying income remains the same, in accordance with the issue documents of the securities issue.
For bond issues that were registered/identification number assigned before 01/01/2012, the performance of NSD’s functions as a paying agent involves a full range of payment servicing services, including:
- carrying out calculations and transfers of funds on behalf of the issuer;
- providing the issuer with reports on payments made;
- informing about the terms and conditions of coupon payments and bond redemptions interested parties; provision of reports to persons authorized to receive coupon payments and amounts from the redemption of the par value of bonds.
Advantages of NSD when providing payment agent services for bond issues that are registered/identification number assigned before 01/01/2012
NSD generates information about recipients of payments on bonds. Transfer of such information to the issuer and then to a third party (another paying agent) may result in distortion or loss of data about payment recipients, which is excluded in the case where NSD is the paying agent.
The increase in the actual period of circulation of bonds on the market is achieved by excluding third parties from the payment scheme, which reduces transaction costs for the formation and transmission of the list of recipients of payments on bonds and allows for the maximum proximity of the fixation date to the date of payment of the coupon income.
The procedure for NSD to provide services to the issuer to perform the functions of a paying agent is determined by the agreement on the provision of services for servicing payments of the nominal value of bonds upon their redemption and payments of coupon income (paying agent agreement).
The cost of NSD's services has remained at a competitive level for many years and does not exceed the prevailing market rates of other paying agents. You can familiarize yourself with the tariffs for payment of NSD services under payment agent agreements when servicing bond issuers in the “Tariffs” section.
Scheme of interaction between the Issuer and NSD when accepting for servicing an issue of exchange-traded bonds with a certificate and issue documents in electronic form
- The issuer submits to the Moscow Exchange a set of documents necessary to assign an identification number to the bond issue (contact telephone number of the Moscow Exchange for interaction: +7 495 363-32-32).
- The issuer submits to NSD a set of documents for the placement of bonds:
- The issuer sends to NSD a certificate in electronic form (in PDF format), signed by the digital signature of the first person or the digital signature of an authorized employee (in the case of placing an issue under the exchange-traded bond program).
To sign an electronic signature certificate, you need to right-click on the certificate in PDF format at the workplace where the Luch software and the Certificate Directory are installed and select the “Sign” option.
The certificate is sent through Luch software in the form of an untyped document (the size of the file/files should not exceed 10 MB) to the address NDC000IAD000.
Table of deadlines for sending certificates:
* where R is the start date of placement, the period is calculated in working days
- The issuer sends to NSD the forms of documents for the placement of bonds, provided for by the Regulations on the interaction between NSO JSC NSD and the issuer.
Form Z1.1 is sent through Luch software in the form of an untyped document to the address NDC000IAD000.
When listing on an exchange:
An order to open a trading section on an emission account (AF090) is sent through the Luch software in the form of an order with the transaction code “90” (if the section has not been opened previously).
An order for the transfer of securities within one account (MF020) is sent through Luch software in the form of an order with the transaction code “20”.
When placing bonds outside the exchange:
Instructions to transfer bonds to the securities accounts of NSD participants are sent using Luch software with transaction code 16 or 16/2. To execute a transfer, you must submit a counter instruction with transaction code 16/1 or 16/3.
- The issuer sends to NSD a certificate in electronic form (in PDF format), signed by the digital signature of the first person or the digital signature of an authorized employee (in the case of placing an issue under the exchange-traded bond program).
Servicing share issuers
NSD provides the following services to share issuers:
- Depository services for public offering of securities
- Maintaining a treasury securities account
Provision of depository services during the initial placement of an additional issue of shares of the Issuer on the stock exchange (carried out within the framework of the Agreement on the provision of depository services through open subscription)
Stages of interaction between the Issuer and NSD during the initial placement of an additional issue of shares on the stock exchange:
- Approval of the draft decision on the issue of shares in terms of provision of depository services (before state registration);
- Concluding an agreement on the provision of depository services during a public offering of shares (after state registration);
- Agreeing on a time schedule for interaction on the placement date with authorized employees of NSD, the registrar, the underwriter, the trading system (exchange) and NCC.
Providing services to the Issuer for the transfer of shares issued by this Issuer from a treasury personal account opened with the registrar to a treasury securities account at NSD
Stages of interaction:
- Conclusion/updating of a treasury securities account agreement, opening (maintaining) a treasury securities account within the framework of the concluded agreement;
- NSD opens a personal account for ND/ND CD with the Issuer's registrar (if such an account has not been opened previously) and accepts the issue(s) of shares for depository services. To accept for servicing issues of shares of issuers issued in accordance with the requirements of the current legislation of the Russian Federation, the Issuer must provide the necessary documents to NSD.
- The issuer submits a transfer order to the registrar for the transfer of securities from the treasury personal account to the personal account of NSD's nominee holder in the register or an order to conduct a transaction on the personal account of the nominee holder of NSD's central depository. The issuer submits an order (operation code 35) to accept securities for storage/accounting.
- Shares accounted for in the treasury deposit account with NSD can be issued for circulation by the Issuer both on the exchange (if listed) and outside the exchange.
Scheme for transferring shares from a treasury personal account opened with the registrar to a treasury securities account at NSD:
- The Issuer submits to the Registrar a Transfer Order to write off the Issuer's shares from the treasury personal account;
1*.The issuer submits an order to NSD to accept securities for storage/accounting
In the case of a NDDC personal account, NSD, on the basis of the above instructions, generates an Instruction for the registrar to carry out an operation on the NDDC personal account
- The registrar informs NSD by sending a certificate of transaction on the personal account of ND NSD or sends a reconciliation request for the transaction on the personal account of NDDC NSD.;
2*. In the case of a personal account, NDDC - NSD confirms the transaction to the registrar or refuses to carry out the transaction.
Issue of purchased securities on the stock exchange:
- Acquirers submit applications to purchase shares of the Issuer in the Trading System;
- Exchange of information between the Clearing Organization, NSD, Trading System (Exchange):
- about the number of shares in the accounts;
- about the results of the auction.
- NSD credits shares to the Acquirers' securities accounts, according to information received from the Clearing Organization.
Issue of purchased securities outside the exchange:
3*. The issuer submits an order to transfer shares from the treasury securities account to the acquirer's securities account. The acquirer submits a counter instruction to credit the shares.
Bond issue
In accordance with Bank of Russia Instruction No. 128-I, a credit institution has the right to place bonds subject to the decision of the board of directors (supervisory board), unless otherwise provided by the charter. In this case, the issue of bonds is allowed only after full payment of the authorized capital. The amount of the issue (nominal value) should not exceed the amount of the authorized capital or the amount of security provided to the credit organization by third parties for this purpose.
The Bank has the right to issue registered and bearer bonds, secured by a pledge of its own property or provided by third parties, as well as without collateral. According to the method of generating income for investors, they can be interest-bearing and discount (placed at a price below par value), convertible into shares; with a one-time repayment period or with a repayment period in series at certain periods.
The nominal value of the bank's bonds can be expressed in the currency of the Russian Federation or in foreign currency, subject to compliance with the norms of the currency legislation of the Russian Federation and regulations of the Bank of Russia.
By decision of the bank's board of directors, bonds and other issue-grade securities convertible into shares may be placed. If the bank is an open joint-stock company, it has the right to place issue-grade securities convertible into shares through open and closed subscription, although closed subscription may be limited by the bank’s charter and legal acts of the Russian Federation. If the bank is a closed joint stock company, then it does not have the right to place securities convertible into shares through open subscription or otherwise offer them for purchase to an unlimited number of persons.
The bank's shareholders have a pre-emptive right to purchase equity securities, convertible into shares, placed by open subscription, in an amount proportional to the number of assets of shares of the corresponding category they own. Payment for convertible securities is carried out at a price determined by the board of directors based on their market value, but not lower than the par value of the shares into which the securities placed by subscription are converted.
Procedure for issuing securities
The issue of chain securities by banks is subject to registration. Moreover, if registration of the issue of chain securities is carried out without registration of the issue prospectus, then the issue procedure consists of the following stages:
- 1) the issuer makes a decision on the issue;
- 2) registration of the issue of securities;
- 3) production of securities certificates (for the documentary form of issue);
- 4) placement of securities;
- 5) registration of a report on the results of the release.
If the registration of an issue of securities is accompanied by the registration of a prospectus, then the issue procedure includes the following stages:
- 1) making a decision on the issue of securities;
- 2) preparation of the issue prospectus;
- 3) registration of the issue of securities and the issue prospectus;
- 4) disclosure of information contained in the prospectus;
- 5) production of securities certificates (for the documentary form of issue);
- 6) placement of securities;
- 7) registration of a report on the results of the issue;
- 8) disclosure of all information contained in the report on the results of the issue.
Registration of an issue of securities must be accompanied by registration of a prospectus for the issue of securities if at least one of the following conditions occurs:
- placement of securities is carried out among an unlimited number of persons or a previously known circle of persons, the number of which exceeds 500;
- if the total volume of emissions exceeds 50,000 minimum wages.
The issue prospectus is prepared and approved by the board
bank or other authorized body. It must be certified by an independent auditing firm in following cases:
- when issuing shares associated with an increase in the authorized capital (including during the reorganization of a credit organization by merging with it another credit organization);
- when issuing shares carried out in the process of transforming a credit organization from a limited liability company into a joint-stock company;
- when issuing bonds.
Practice shows that long-term restrictions in Russian legislation regarding the issue of bonds by banks have reduced the interest of issuers in this instrument for raising funds.
Practice shows that banks are constantly increasing the issue of bonds as one of the main sources of raising funds, especially in conditions of the financial crisis and liquidity problems (Table 9.2).
