How to check the fallopian tubes. Benefits of conducting research. Types of studies to determine the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Children are an extension of ourselves, so almost every woman dreams of happy and healthy offspring. However, some are faced with the inability to get pregnant after hearing terrible diagnosis"infertility". To find out the reasons and decide on treatment methods, the gynecologist will refer you for testing fallopian tubes. This is one of the first procedures on which reproductive functions body. How do they check the patency of the fallopian tubes, how painful is the procedure? Let's look into these issues.
Postoperative hydrotube should not be performed in this operation or in any of the tubographs. A complete fertility assessment is necessary to determine the cause of the problem and the course of treatment. Usually the doctor starts with the simplest and least invasive tests. If the causes of problems with conception are not determined, further investigations may be indicated. The examination includes a physical examination and laboratory tests.
Diagrams are examined to evaluate the four key elements for a successful concept. Find out if there is a balance in hormonal production that allows egg and sperm development. Determine whether both male and female reproductive systems will allow the fertilizer.
- Find out if there is an abundant ovarian supply and if the woman is ovulating.
- Determine whether there is sufficient sperm quantity and good quality.
Why is the patency of the fallopian tubes disrupted?
The uterus is the most important organ, the health of which determines the possibility of conceiving and bearing a child. The fallopian tubes (popularly called oviducts) are a paired organ connecting the abdominal cavity with the uterus. They are located horizontally on both sides of the uterus, have a cylindrical shape with a diameter of 4 to 6 mm. The inner surface of the fallopian tubes is covered with epithelium with cilia, which help the advancement of the egg.
Medical examinations and general tests to study women
Some studies are likely to be replicated. During this time, it is important not to be disappointed. The goal is to establish a positive course of action for the couple. During a gynecological examination, the doctor will look for any sexual anomaly or other physical signs that may cause difficulty conceiving.
How painful is it to test for poor tubal patency?
The reproductive organs are examined using ultrasound. This is a vaginal exam that takes a closer look at the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus. Hormone levels in the blood are analyzed on certain days menstrual cycle to ensure that the eggs mature.
The fallopian tubes differ slightly in length from each other, which ranges from 10 to 12 cm. The egg and sperm meet in them. The more “correctly” the epithelial cilia function inside the fallopian tubes, the more likely a woman is to become pregnant. The fertilized egg moves along them and enters the uterus for further development.
Fallopian tube test
This is done by injecting contrast into the uterus through the vagina. Using X-rays, check to see if the fallopian tubes are saturated or blocked. A vision instrument is inserted into the uterus through the vagina to look for uterine defects, the presence of fibroids, or damage to the fallopian tubes. If necessary, minor surgery can be performed at the same time.
Under anesthesia, a telescopic vision instrument is inserted into the abdomen through a small incision below the belly button to examine the uterus, ovary, pelvic cavity and fallopian tubes. It is also used to identify endometriosis. If necessary, cysts, uterine fibroids or endometrial tissue are removed at the same time.
According to doctors dealing with infertility problems, from 30% to 40% of all cases of a disappointing diagnosis are associated with obstruction of the fallopian tubes. The causes of the disease may be:
- Organic:
- the presence of inflammatory processes of a nonspecific nature, which are caused by the ingress and active proliferation of bacteria;
- sexually transmitted infections - gonorrhea, chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma infections, trichomoniasis, genital herpes;
- gynecological operations and complications after them;
- abortions;
- surgical interventions in the treatment of diseases abdominal cavity(appendicitis, peritonitis), diseased pelvic organs;
- diseases of the reproductive system - salpingitis, sactosalpinx, endometriosis, uterine fibroids.
- Functional. These reasons are caused by deviations in the structure of the fallopian tubes, congenital complete or partial absence of the latter. In rare cases, they occur due to severe stress or hormonal imbalances.
To identify or refute the diagnosis of “infertility”, to understand the causes of the disease, to prescribe adequate, effective treatment, consultation with a specialist is required, clinical trials. Many women learn about the presence of inflammatory processes, cysts, and fibroids by chance during the diagnostic process. Do not forget about the need to undergo gynecological examinations at least once every six months.
Medical tests and general tests for human studies
The initial examination is carried out by a urologist or andrologist. The doctor will perform palpation, physical examination of the testicles, and epididymal examination to look for abnormalities. You will also inspect prostate gland through the rectum. If a more detailed examination is required, ultrasound of the testicles and prostate can be used.
Sperm obtained through masturbation are examined under a microscope, looking for regularity in shape and motility. Because sperm quality varies greatly, the test can be repeated after three months. If sufficient sperm are found, a test tissue sample can be taken to assess sperm production.
Effective methods for determining tubal patency
How is the patency of the fallopian tubes checked? Methods that have been proven over the years are painful, require lengthy clinical studies, and are performed under general anesthesia. Newer, modern diagnostic methods are relatively painless and do not require general anesthesia. To choose the most suitable method:
Excessively low sperm production can be caused by hormonal imbalance. To rule out this possibility, blood hormone levels are examined. Hormonal disorders more common in men than in women. If a very low sperm count is observed, a blood sample may be ordered to look for genetic abnormalities.
Hysterosalpingography is a non-invasive x-ray test used to examine the uterus and the permeability of the fallopian tubes. This study determines whether there is any problem that impairs women's fertility. It is also used to examine abnormalities within the uterus and determine the presence and severity of tumor masses, adhesions, and uterine fibroids. Sometimes a hysterosalpingogram can open the fallopian tubes so that the patient can become pregnant later.
- Consult a gynecologist for advice.
- The doctor should take a gynecological history.
- Depending on the results, diagnosis/treatment is prescribed or surgery to restore patency of the fallopian tubes.
HSG (Hysterosalpingography)
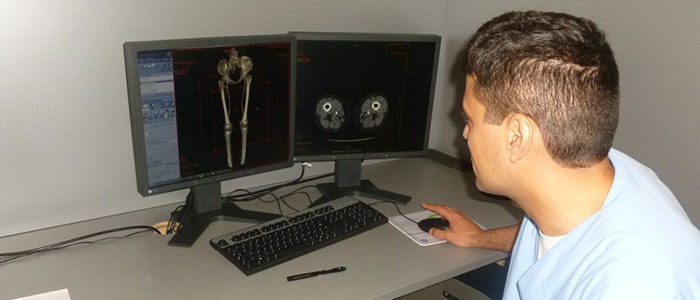
If this test is carried out during a fertility study, it will provide the correct diagnosis and, from there, allow the most appropriate infertility treatment to be applied. This is an x-ray examination taken inside the uterus and fallopian tubes, filled with a water-soluble contrast medium, to evaluate the anatomy and function of these organs using fluoroscopy.
When to perform hysterosalpingography?
This non-invasive medical test helps doctors diagnose and treat certain diseases because they can see internal organs in move. This gynecological test is performed when a full examination of the female genital tract is required due to one of these problems.
This procedure involves examining the patency of the fallopian tubes using x-rays. Hysterosalpingography helps determine whether the fallopian tubes are patent; the presence of deformation changes in the uterus and appendages; learn about the condition of the endometrium and the presence of pathologies. The essence of the diagnosis is the introduction of a special substance into the cervix through the cervical canal, visible on X-ray photographs.
Fallopian tube obstruction
Hysterosalpingography evaluates the morphology of the uterus to verify the absence of pathologies that prevent the natural occurrence of pregnancy due to complete or partial blockage of the fallopian tubes. During normal ovulation, once the oocytes mature, the egg is released. Once released, the egg waits in the fallopian tube for the arrival of the sperm, which will be fertilized with its union, and hence it will occur with the gestation of the embryo, which will move from the fallopian tube to the uterine cavity and will be implanted in the endometrium of the uterus, starting pregnancy.
The specialist sees in the picture the condition of the uterus and appendages: the presence of dilations, constrictions, adhesions, tumors. On average, about 13 mg of liquid is administered. If the fallopian tubes are patent, the fluid flows behind the uterus, around the ovaries. The procedure is carried out 7-12 days after ovulation. It is important that any inflammatory processes. The reliability of the method is 80% and above.
Why is the fallopian tube obstructed?
An obstruction in the fallopian tubes prevents contact between the egg and the sperm, making it impossible to conceive a pregnancy naturally or through artificial insemination, since with this method fertilization will occur through the fallopian tubes.
When is the procedure necessary?
In the case of tube obstruction, the method of assisted reproduction recommended to achieve pregnancy should be. However, an obstruction in just one of the tubes does not prevent fertilization and natural pregnancy, although this may be more difficult or time consuming.
Ultrasound (hydrosonography)
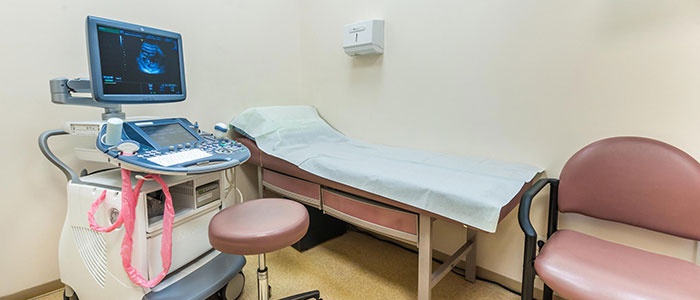
It is possible to check the patency of the fallopian tubes with a reliability of at least 90% without high dose irradiation using ultrasound in 2D, 3D or 4D dimensions. This method is called hydrosonography or echosalpingography (echohydrotubation). To visually confirm/refute the diagnosis, a special vaginal sensor is inserted into the uterine cavity. The main disadvantage of the procedure is the high dependence of the results on the qualifications of the operator servicing the device and his ability to correctly and competently decipher the images.
Hysterosalpingography can also be used to investigate the causes of spontaneous abortions and determine whether they were the result of congenital or acquired uterine abnormalities. On the other hand, hysterosalpingography is used when you have undergone tubal ligation surgery to ensure that the fallopian tubes have become completely opaque.
Preparation for hysterosalpingography
Before performing the test, a complete gynecological examination is necessary.
Medicines to take before the test
This will depend on the doctor and center where this test is performed. Some centers recommend performing an evacuation enema the night before the test. Your doctor may order an anti-spasmodic test to relieve discomfort. In women who suffer from anxiety or have low pain threshold, it is recommended to prescribe some local anesthetics or sedative for a more relaxed test. Sometimes the doctor will also prescribe an antibiotic to prevent possible infections. . This is a simple test that takes no more than 30 minutes and does not require anesthesia or previous hospitalization.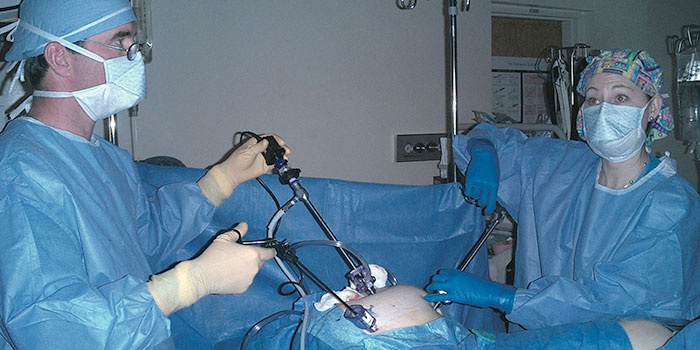
This expensive operation requires a hospital stay of one to two days. It is a surgical procedure in which a laparoscope is inserted into the fallopian tubes through a small incision in the abdomen. The accuracy of diagnosis is 99.9%. The procedure is used to diagnose patency of the oviducts, possible complications (cysts, tumors) after infectious, inflammatory processes, and treatment of the pelvic organs (uterus, ovaries, appendages).
Fasting is also not required. Hysterosalpingography is completely contraindicated in case of pregnancy and lactation. This is done between 5 and 12 days monthly cycle before ovulation begins. In some cases, the doctor will perform a pregnancy test. It also should not be performed if the patient has an active inflammatory process, a chronic pelvic infection, or an untreated sexually transmitted disease.
Does hysterosalpingography hurt?
The patient is placed on her back on the gynecological table, and her legs are placed in stirrups. It is normal to feel mild discomfort and cramping during placement of the contrast medium management catheter, however the duration is short.
Fertiloscopy
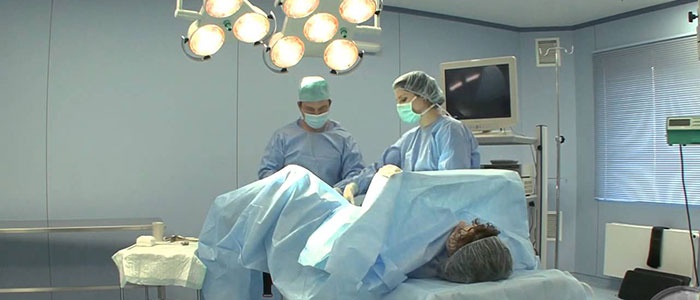
The difference between fertiloscopy and laparoscopy is the insertion of an endoscope through the cervical canal. This relatively new method helps to monitor the condition of the uterus and its appendages with high precision. The lower the chances of detecting obstruction of the fallopian tubes, the preferable it is to perform fertiloscopy. Unlike GHA, this method gives more accurate results for uterine spasms that negatively affect the reliability of hysterosalpingography.
There may also be some minor irritation of the peritoneum, which is the lining of the abdominal cavity, as well as some general pain in the lower abdomen, but these discomforts may only be present for a short time. Additionally, it is normal to feel the presence of certain contractions. For this discomfort, it is best to use an analgesic.
There may be episodes of fever strong pain in the abdomen, the onset of discharge with an unpleasant odor or severe blood loss. It is important to emphasize that if such severe symptoms occur, it is advisable to immediately seek medical advice regarding appropriate treatment for such symptoms.
What tests need to be taken before the examination?
Before sending you to check the patency of the fallopian tubes, the gynecologist will ask you to take tests:
- Urogenital discharge ( gynecological smear).
- Cytological studies of cervical scrapings and cervical canal using a PAP test.
- For sexually transmitted infections, HIV, TORCH infections using polymer chain reaction (PCR).
Where to do and how much does research cost in Moscow?
Public and private clinics and hospitals offer a wide range of services for women who need to check the patency of their fallopian tubes. If several decades ago such a diagnosis put an end to a woman’s desire to become a mother, modern achievements of scientists help restore the functionality of the fallopian tubes, giving the joy and happiness of motherhood.
Price of hysterosalpingography
Prices vary depending on centers specializing in fertility procedures, and in some cases may offer custom prices or rates. In general, the price is usually between 180 and 250 euros.
Does this analysis take social security into account?
In most cases, the hysterosalpingography procedure is included in infertility treatment programs. Although it is important to consider that there are long waiting lists that can last up to several months.Fallopian tube Fallopian tube Uterine tympanic tube Papilloplasmas Fallopian tubes Fallopian tube Cervical canal Cervical canal Link: Link: Water-soluble iodine: Water-soluble iodine: Presentation: Presentation: Contents 20 ml. And it is almost always the direct result of a sexually transmitted disease such as gonorrhea or chlamydia, and is responsible for approximately 000 cases per year.
The price of services differs depending on the type of diagnosis, the degree of reliability of the final results, possible consequences And side effects:
| Clinic name | Type of analysis | |
| Clinic InVitro All of these conditions can cause adhesive obstruction, scar tissue, tumor formation, or a polyp in the tube. If the damage to the fallopian tubes is partial, they may remain open enough for them to occur, but partial blockage increases the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. To begin with, they are very thin, so there is not much to block them, making it impossible for eggs to pass through. Research has shown that low progesterone levels, smoking and use medicines for fertility may affect women's performance, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy. | Taking gynecological material | |
| Comprehensive analysis of “Sex and the City”: 12 infections + smear | ||
| Cytological examination of scrapings of the cervix and cervical canal PAP test | ||
| Polyclinic "Otradnoe" | Cytology | |
| From 180 to 2780 |
||
| Center women's health | Complex analyzes to identify hidden infections+ PAP test | |
| Infection research PCR method from 1 to 18 infections | From 350 to 2950 |
|
| Flora smear | ||
| Taking biomaterial (smear) | ||
| Comprehensive services (tests to detect pipe patency) | From 5500 to 15000 |
|
| OnMed Gynecology | Taking biomaterial (smear) | |
| Study of infections using PCR method from 1 to 20 infections | From 300 rub. |
|
| Cytology |
Types of diagnostics and prices for them in various clinics:
| Type of clinical/diagnostic study | Approximate cost, rub. | Clinic name |
| On Clinic (international medical Center) |
||
| Description of the image by the doctor | ||
| Echosalpingography (ultrasound) | Clinic "Lama" (center for operative gynecology) |
|
| Anesthesia (intravenous) | ||
| Appointment and examination by a gynecologist | for free |
|
| Clinic InVitro |
||
| Clinic "Family Doctor" Moscow, St. Petersburg |
||
| Injection into the cervix | ||
| Polyclinic "Otradnoe" |
||
| Hydrosonography | ||
| Consultation with a gynecologist + ultrasound (echosalpingography) | Center for Reproduction and Family Planning |
|
| Operative laparoscopy + hysteroscopy | ||
| Sonohysterosalpingography | Traditional Midwifery Center |
|
| Hydrotubation |
Video: how to check the fallopian tubes for patency
Checking the fallopian tubes for patency begins with preparation:
- Treatment of inflammatory processes of the genital organs.
- Thorough hygienic toilet.
- Taking antispasmodics medicines in the dosage recommended by the gynecologist.
When choosing research methods, consult a gynecologist: find out which one is suitable for your case, ask them to justify why. If you're afraid painful sensations, unpleasant symptoms, discuss in advance the possibility of pain-relieving injections into the cervical area. Try to calm down as much as possible before the procedure: spasms caused by nervous tension, may negatively affect diagnostic results. You can learn more about the benefits of certain methods of checking the patency of the fallopian tubes by watching the video below.
Preparing for the examination
Diagnosis of fallopian tube patency
Advantages of methods for studying tubal patency
The ability to conceive, bear and give birth to a healthy child is the main feature, value and joy in a woman’s life. It is no coincidence that in ancient times even the very meaning of a woman’s life was assessed by her ability to bear children. We live in much more enlightened and freedom-loving times, when women can afford to plan a family, the number of children and the time of their birth at their own discretion. But motherhood still remains the most important and happiest period of life, without which it is difficult to fully experience all its facets. An important condition for the implementation of this function is the health of the body as a whole and reproductive system in particular. A particularly important role is played by the fallopian tubes and their ability to pass through an egg ready for fertilization.
Violations of this function, that is, the patency of the fallopian tubes, are fraught not only with diseases of the female genital organs, but also with a complete loss of the ability to have children. That is why it is so important to diagnose developing abnormalities in a timely manner and take all possible measures to prevent the problem from worsening. Moreover, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, complete or partial, is far from a death sentence and not a guarantee of infertility. With timely and high-quality treatment, you can get rid of it and give birth to a healthy child, even more than one. That is why modern medicine has developed and actively uses methods for checking the patency of the fallopian tubes. Effective and safe, they allow you to identify deviations even further early stages and prevent possible complications. But to do this, you need to know about these methods and understand their importance, and also not neglect regular examinations by a specialist.
Fallopian tubes: structure, functions, health
The fallopian tubes in science and medicine are called fallopian tubes or, more simply, oviducts. The second name itself quite clearly describes their role in the female body. Indeed, the fallopian tubes are a paired organ that connects the ovaries with the uterine cavity and creates a kind of “corridors” through which the egg enters the uterus. Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tubes when the ovulated egg is captured by the cilia of the epithelium and moves into the fallopian tube, where it can remain from 8 to 24 hours. All this time, she remains viable thanks to the special environment inside the oviduct and waits for a meeting with the sperm. If that meeting occurs and the egg is fertilized, then the cilia on the surface of the tubal epithelium propel it further into the uterus. If the egg remains unfertilized, then through the same oviducts it is still sent to the uterus, where it gradually dies.
Thus, it is these small tubes located on both sides of the uterus that directly determine whether the female and male reproductive cells will unite, whether conception will occur, and whether the zygote (fertilized egg) will enter the uterine cavity. This is the role of the fallopian tubes in the implementation of the function of childbirth, and it is ensured by their specific structure. The walls of the oviducts are similar in composition to the walls of the uterus and, like it, have several layers of mucous and epithelial tissue. This fabric forms tubes ranging from 8 to 20 cm in length (on average about 12 cm). The main difference between the mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes and the mucous membrane of the uterus is the presence of mobile cilia, designed to transport elements entering the tubes: eggs, sperm and zygotes. Moreover, each of the two pipes is quite mobile and flexible. Healthy, developed oviducts consist of: 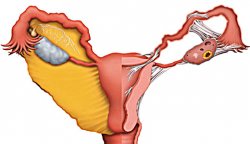
- A funnel located on the side of the abdominal cavity, that is, the ovaries, and having a diameter of about 20 cm. With the help of many fimbriae, the funnel covers the ovary and ensures that the egg enters the tube and then moves along it.
- The ampullary area, narrower than the infundibulum, but still wide enough for the egg to pass through.
- An isthmic area that narrows as it approaches the uterus. This narrowed part of the oviduct forms a kind of isthmus.
- The uterine section is the place where the fallopian tube passes directly into the uterine cavity.
Even medical procedures performed without directly touching the uterus and/or oviducts can cause damage and obstruction of the fallopian tubes. For example, previous operations on other pelvic organs - even widespread removal of appendicitis - can lead to obstruction. The “soldered” place of the tube can be located along its length, or between the tube and the ovary. Such places are called commissures and are essentially sticky walls of the oviduct and the ovary itself. Treatment in this case can be either medicinal or surgical. Of course, no doctor can give a 100% guarantee of a complete cure. But removal of the fallopian tubes in case of adhesions is an extreme measure, which is taken extremely rarely. In most cases, conservative and surgical treatment together lead to a favorable resolution of the problem.
Checking the patency of the fallopian tubes
Today medicine has a whole range of methods for diagnosing the condition of the fallopian tubes. 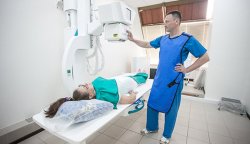
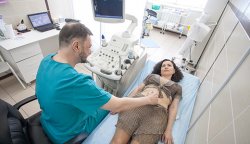 Thus, you can check the patency of the fallopian tubes in one or more different ways, each of which has its own pros and cons, indications and warnings. In any case, the study is necessary for women who cannot get pregnant for the first time, who have had an ectopic pregnancy, inflammation of the pelvic organs and/or suffering from endocrine diseases. And even if the test results are disappointing and show obstruction of the fallopian tubes, there are also several medicinal and surgical methods restoration of patency. And in vitro fertilization always remains a backup option. This means that the main thing is not to despair, undergo timely diagnosis, take care of your health and strive to become a healthy and happy mother of a beautiful baby.
Thus, you can check the patency of the fallopian tubes in one or more different ways, each of which has its own pros and cons, indications and warnings. In any case, the study is necessary for women who cannot get pregnant for the first time, who have had an ectopic pregnancy, inflammation of the pelvic organs and/or suffering from endocrine diseases. And even if the test results are disappointing and show obstruction of the fallopian tubes, there are also several medicinal and surgical methods restoration of patency. And in vitro fertilization always remains a backup option. This means that the main thing is not to despair, undergo timely diagnosis, take care of your health and strive to become a healthy and happy mother of a beautiful baby.
