Benefits in the treatment of cataracts for pensioners. Free cataract surgery
According to the World Health Organization, 51% of cases of blindness in the world (more than 18 million people) are caused by age-related cataracts. Another 53 million people living on the planet today have lost their ability to work for the same reason. At the same time, cataracts are one of the few diseases that can be completely cured by surgery in just a matter of minutes.
After replacing the cloudy lens with artificial vision, 95% of patients return to the same level that they had before the disease. In Russia, more than 375,000 lens replacement operations are performed annually, which is much less than the actual need. Today we will figure out how to treat cataracts and how to choose artificial lenses.
What you need to know about cataract treatment
Vladimir Trubilin, Head of the Ophthalmology Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency
1. Methodology. First you need to understand by what method the doctor intends to remove the patient's own clouded lens, in place of which a new artificial one should be placed. There are two main methods: the old one, when the patient's own lens is removed with a scalpel through an incision (of course, very traumatic). Nevertheless, more than 30% of all lens replacement operations performed in Russia are still performed in this old-fashioned way.
Phacoemulsification is the process of softening the lens with a laser and removing the resulting "emulsion" through a tiny puncture. In addition to the obvious advantage of the second method - a small incision that does not need to be sutured, there is another plus - the less “mature” the cataract, the easier it is to remove it. “Previously, cataract surgery was deliberately delayed until it literally turned to stone (of course, vision deteriorated greatly). Using a laser, it is possible to remove a cataract much earlier, when its consistency is more like a marmalade, ”says Vladimir Trubilin. There are only a few contraindications for photoemulsification: some types of congenital defects of the cornea of the eye, the need to replace the lens as a result of severe trauma (only less than 1% of cataract cases).
2. Lenses. Most ophthalmologists believe that here it is necessary to focus not so much on the country of origin or on the lens manufacturer, but on their own requirements for the quality of vision after surgery. First you need to decide whether you need to completely abandon the wearing of glasses or you are ready to wear them for reading. Are you going to drive a car, shoot, paint. If so, then, of course, you need to choose the so-called complex “premium” lenses with two focuses that correct astigmatism. It is worth noting that the price will immediately increase by 1.5-2 times compared to conventional single-focus lenses.
3. Clinic. The main thing is to decide whether to do the operation in a hospital, spending several days in the hospital, or outpatient in one day. There are many medical institutions in Moscow that practice different approaches. Each of them has its pros and cons. So, if you prefer to “shoot back quickly”, then you should take into account that you will most likely have to appear for the operation early in the morning, just at the time when the city has the biggest traffic jams. It may well happen that you find yourself on the operating table already exhausted, with high blood pressure and not in the best shape at all. In addition, remember that the next day after the operation, the doctor must conduct an examination, that is, you will again have to go to the clinic. Stationary conditions not only allow avoiding unnecessary movements, but also ensure that, if necessary, the patient can count on the help of a general practitioner, cardiologist, and even a resuscitator.
4. The minimum set of equipment. Even a patient who knows nothing about medicine can draw conclusions for himself about the seriousness of a particular medical institution by inquiring about the availability of the following devices in the clinic: a modern phacoemulsifier, a good microscope, a device that calculates the optical power of the lens. “You can find out whether the equipment is good or not in the clinic by the brand name - they must be well-known, and by the name of the models - they must be modern. Do not be too lazy to make inquiries on the Internet,” advises Vladimir Trubilin.
5. Surgeon. He must be known in professional circles. All good specialists, constantly practicing in this field, often participate in various conferences, where they make presentations, and very rarely change jobs, as clinics hold on to them. Accordingly, finding information about a doctor and his qualifications is not difficult. It should be alarming if such information is not available.
6. Price. This is always an important indicator. The cost of a quality operation to replace the lens today in Moscow is 50-60 thousand rubles. When choosing an expensive lens, a well-known clinic and a doctor with a scientific title, it can reach a maximum of 120 thousand rubles. You can have an operation for 25-40 thousand (with an inexpensive lens), but in this case you need to carefully study the technical equipment and qualifications of the doctor.
Does insurance cover the cost?
Cataract surgery is included in the government-guaranteed free minimum medical care and must be paid from the funds of the compulsory health insurance system. In most regions of Russia, the territorial CMI funds annually increase funding for surgical treatment of cataracts as the only way to overcome this disease, the high efficiency of which has been proven by medical statistics.
And in some large cities, the amount of material coverage has already come close to the market value of such operations. So, in May 2012, the TFOMS of St. Petersburg announced an increase in funding for a lens replacement operation from 8 to 39 thousand rubles. This amount will allow not only to carry out the intervention itself using modern equipment, but also to install the lens and pay for several days of postoperative stay in the hospital, without requiring any additional payments from the patient himself. In Belgorod, TFOMS also recently started paying 30,000 for a lens replacement operation. But, alas, this is not the case throughout the country. And patients have to pay extra out of their own pocket for the replacement of the lens.
Moscow is no exception, where the amount of financial compensation from compulsory medical insurance is only 6,700 rubles. for one operation. With this money, you can, of course, perform an operation, but only with an artificial lens Russian production. “Usually such a lens does not allow for surgery through a puncture, an incision is required. Therefore, the majority of Muscovites who come to us through compulsory medical insurance prefer to pay extra for a more modern lens from 12 to 15 thousand rubles, ”explained the operating surgeon of the Moscow Eye Microsurgery Center named after S.N. Fedorov Professor Boris Malyugin.
In this regard, residents of the Moscow region were much more fortunate: the TFOMS of this region pays from 24 to 30 thousand rubles for the replacement of the lens. depending on the complexity of the operation, which not only allows the operation itself to be carried out using modern technologies, but also includes the cost of a good imported lens. And this is not the only advantage of the residents of the Moscow region in terms of surgical treatment of cataracts. All residents of the Moscow region can relatively easily get a referral from a district ophthalmologist for a consultation and subsequent operation in the MNTK, one of the most popular clinics in the city.
Residents of the capital are rigidly assigned to different clinics according to the territorial principle. Thus, according to the compulsory medical insurance policy, only residents of the Northern Administrative District are sent to the Fedorov clinic, the south and south-west of the city are assigned to hospital No. 83, the Western District - to city hospitals No. 67 and No. 36, the North-West - to city hospital No. 15.
Where in Moscow you can operate a cataract according to compulsory medical insurance
Vostochny AO
City Clinical Hospital No. 15 im. O.M. Filatov
City Clinical Hospital No. 36
City Clinical Hospital No. 70
FGU NMHTS im. Pirogov
DKB MPS im. ON THE. Semashko
Western AO
KB No. 86
TsKB UDP RF
City Clinical Hospital No. 67
Northern AO
FGU MNTK Moscow
Federal State Institution Research Institute of Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery
Northeast Autonomous Okrug
Central Design Bureau of the MPS im. Semashko
MONIKI
Northwestern AD
City Clinical Hospital No. 52
Central Design Bureau of Civil Aviation
Central JSC
MOKB
City Clinical Hospital No. 1 im. N.I. Pirogov
CDC №9 MO RF
Morozov Children's Hospital
NII GB them. Helmholtz
Research Institute GB RAMS
Southern AO
GKB FMBA №85
GKB FMBA №83
City Clinical Hospital No. 12
Central Design Bureau of the Russian Academy of Sciences
Southwestern AD
Endocrinological NC
Botkin Central City Hospital
Useful site
There is a practice in which district specialists give a referral to only one that is close to them due to some individual reasons. medical Center, although in fact the choice of clinics offered under compulsory medical insurance is much wider. The department of social protection of the population of Moscow promised to solve this problem the other day. Already from the beginning of November, a resource called "People's Map" will appear on the Internet. Here, on an interactive map of the city, you can not only see with your own eyes clinics of all levels and specializations that serve your particular street and home, but also read the opinions of patients who have already visited these medical institutions. The new network service, as conceived by the creators, should become an environment for the exchange of information between consumers of various social services, including medical ones. According to the creators of the "People's Card", the site will contain information about 50 health centers that provide free primary medical examinations. Over time, there will be diagnostic centers, and specialized hospitals. Visitors to the site - presumably mostly middle-aged and older - will be able not only to find information about the clinic, but also to get the opinion of individual specialists from those patients who have already visited this institution. And of course, leave your own review.
Free cataract surgery
Free cataract surgery
One of the reasons why many patients are in no hurry to have cataract surgery is the high cost. It includes the payment for the services of a surgeon, the cost of the artificial lens itself, the cost of staying in a hospital, etc. On average, a cataract operation will cost 30-80 thousand rubles. Therefore, some patients delay treatment as much as possible, hoping that conservative methods will be effective or the cataract will resolve itself. But such an outcome is unlikely. Therefore, the question of whether free cataract treatment is possible today is more relevant than ever.
How to save on treatment?
There are several ways:
- Apply with compulsory medical insurance policy to any state ophthalmological clinic. The patient is given a free diagnosis and, if a cataract is detected, they are prescribed surgery. You will be allocated a place in the hospital, and the time of the operation will be scheduled. In this case, the classical method of surgery is used, which is fraught with high trauma and a high risk of complications. A Russian-made implant is installed. If the patient expresses a desire to install an imported artificial lens, then he will have to pay for the materials.
- Treatment under the policy of VHI. Here, only part of the services (diagnostics, recovery) is provided free of charge. But the materials and work of the surgeon will need to be paid. The fact is that the implant itself, which is installed in place of the affected lens, costs a lot of money. Therefore, the cost in this case will be about 10-15 thousand. Which is much cheaper than if you had to pay for the treatment in full.
- Quota for VMP. Some private and public clinics provide patients with quotas for free treatment of eye cataracts. The patient is provided with a full range of medical services: diagnostics, preparation for surgery, and the operation itself. However, you have to pay the cost of food and stay in the hospital itself. Free cataract surgery according to the quota is carried out in a special direction, which is issued by an ophthalmologist. With this referral and a package of other documents, you need to contact the local health authority, where a decision will be made within 10 days on issuing a quota. If the answer is positive, the documents are sent to the selected clinic, where the application is considered within 10 days and the date of surgical treatment is set.
Which clinics in Moscow treat cataracts for free?
There are a number of clinics in the capital, where any Russian citizen, upon providing a compulsory medical insurance policy, can receive free services for the treatment of cataracts with the provision of a quota. It's about not only about conservative methods, but also about surgical treatment.
- First eye clinic- a full range of examinations of the organs of vision is carried out here, which makes it possible to detect common and rare eye pathologies. Surgical treatment cataracts are performed using the phacoemulsification method - a modern and safe surgical intervention, after which there are no sutures left.
- Konovalov Ophthalmology Center - European level medical education and equipment allows the clinic to provide highly qualified services. A full examination and IOL with the installation of imported materials are carried out here.
- MNTK "Eye Microsurgery" named after S.N. Fedorova - anyone here can sign up for a free appointment to consult about the disease and clarify the diagnosis. The clinic provides comprehensive treatment for most eye diseases, including cataracts.
- Ophthalmological clinic "Excimer" - ultrasonic cataract phacoemulsification is performed. Patients are offered a preliminary examination and monitoring of recovery in the postoperative period. Promotions are regularly held here and impressive discounts are made for diagnostics and surgical treatment.
16/04/2010
Cataract is the most common eye disease leading to blindness. At the age of 40, every fifth person has it, at the age of 60 - to a greater or lesser extent, it is diagnosed in everyone. According to statistics, in a city of 5 million, from 20 to 40 thousand cataract operations should be performed annually. But they are made much less.
AT
looking through cloudy glass
If a the world begins to fade, objects lose their clarity, the eyes seem to be covered with a film, and when reading and writing, the letters blur and acquire double contours - this is clouding of the lens of the eye, a cataract. On the one hand, it is called a disease, on the other - the natural aging of the lens of the eye. Indeed, age-related clouding of the lens occurs most often, but it can also be congenital, developed against the background of metabolic disorders, diabetes. The cause of cataracts can be beriberi, excessive ultraviolet radiation, any serious injury.
Doctors can name many reasons for the appearance of cataracts and even describe the mechanisms of its development. But by and large, they cannot explain its origin. That is why there are still no drugs that can not only cure, but even stop the process of clouding of the lens. The only way to save or restore vision is surgery.
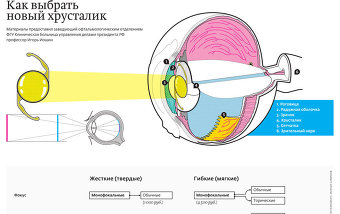
The human eye is a complex optical system, and the lens is its natural transparent lens that transmits and refracts light rays. A healthy lens quickly reacts to light, "focuses", so that a person sees objects at different distances - both near and far. When a cataract develops, the lens becomes cloudy, like old glass, and since it loses transparency, it means that only part of the light rays enter the optical system of the eye, vision becomes fuzzy and blurry. Over time, it can completely lose transparency (doctors in such cases say: “Cataract is ripening”), and the person goes blind.
R ride without waiting for maturity
Perhaps the surgical treatment that was used 20 or even 10 years ago is one of the reasons why people do not go to the doctor when early signs the appearance of the disease. Indeed, many, having heard the phrase “surgical replacement of the lens”, immediately recall grandparents, parents who, seeing almost nothing, could not receive medical care until “the cataract matures”, that is, the pupil turns from black into white. Only then could ophthalmologists proceed with the operation to replace the lens. It was a rather serious surgical intervention: during the operation, a large (8 - 15 mm) incision was made, and in its place a scar was formed that changed the shape of the cornea. This inevitably led to the development of astigmatism, and glasses had to be worn.
With the development of microsurgery, it is possible to restore vision, which a cataract has just begun to spoil, quickly and practically without a scalpel, more precisely, without large incisions. All modern ophthalmological centers in St. Petersburg use a seamless and bloodless technology called phacoemulsification. Through a minimal incision (puncture) in the cornea with a size of 2 - 3 mm, a special ultrasonic tip is inserted into the lens area, which destroys and removes the clouded lens. An artificial lens is inserted into the space formed in its place (capsular bag) - a folding elastic intraocular lens (IOL), which the surgeon sets in the correct position. The operation takes an average of 20 minutes. The incision does not even need to be sewn up, it heals on its own.
Contraindications to this operation - a minimum. Since it is performed under local anesthesia, it is made both 80-year-old and 90-year-old. But she has one big minus, which becomes an obstacle to timely treatment - the price. It consists of the cost of the lens and consumables, the cost of the surgeon and medical staff, the patient's stay in the clinic and the depreciation of equipment. In St. Petersburg, the replacement of the lens in one eye costs from 20 thousand rubles - with a domestic lens and domestic consumables, up to 44,750 - with a folding acrylic IOL. However, there are several ways to reduce the cost of this procedure.
4
how to replace the lens, or How to save on surgery
The first, and most difficult, is to get a referral from an ophthalmologist at a district clinic and perform an operation under a compulsory medical insurance policy. It involves free preoperative diagnostics, surgery with a domestic hard lens, consumables and anesthesia in the same traditional way - with a large incision and a corneal suture. Stay and meals in the city hospital are free of charge. But modern ophthalmologists do not like to do these traumatic operations, which actually return them 20 years ago. Therefore, a patient with a compulsory medical insurance policy will be explained that if he wants to restore his vision with better drugs, a more physiological lens, non-traumatic and without a rehabilitation period, it is better to pay for a normal lens, and it costs from 3 (domestic) to 12 thousand (imported), and expendable materials(in ophthalmology, even disposable knives). Everything else, as required by the policy, is free ...
The second way, a compromise, is to try to cure cataracts under the VHI policy. In this case, if the policy program provides for planned treatment in a hospital, the patient receives everything free of charge in comfortable conditions. Except... the intraocular lens. In this case, you will have to pay.
The third method, the most laborious one, is to call the medical institutions of the city (city, regional, federal) and find out which of them have quotas for the provision of high-tech medical care (HTMC) in ophthalmology. The quota for lens replacement surgery is the cheapest of all ophthalmic quotas that are distributed under the state and city programs for the provision of high-tech medical care. The state allocates about 18 thousand rubles for it and has not increased it over the past five years, although prices have risen, the same lenses have risen in price. And just a week ago, a government decree was issued, according to which IOLs (lenses) are now subject to VAT, which inevitably leads to an even greater rise in price. It would seem that it is unprofitable for clinics to work according to quotas, because the cost of the actual operation for almost everyone is about 20 thousand rubles, not counting the IOL. Nevertheless, several clinics in the city receive them, which means they must work them out. And since people from the regions come to us infrequently, they easily get to St. Petersburg residents. True, the quota is a quota, but it’s completely free, and in this case, the operation will not work - you will have to pay the cost of staying in the hospital and food. As a rule, this is 1 - 2 days (one day, depending on the level of comfort of the ward, costs from 1.5 to 5 thousand rubles). It is important to find out in which clinic which lenses are installed. Because attempts to meet the amount limited by the quota turn into the use of far from the best IOLs of domestic or Indian production.
The fourth way, the easiest and most uneconomical, is to sign up at a clinic where lens replacement operations are performed and pay for everything medical services, from which the price of the operation is formed. But if the patient chooses it and at the same time suffers not only from cataracts, but also from myopia, farsightedness or presbyopia (age-related farsightedness), then you can think about implanting other lenses - multifocal ones. The cost of such an operation, of course, will not please many, for example, in the Moscow Scientific and Technical Center for Eye Microsurgery it costs up to 68 thousand rubles, in the ophthalmological clinic of St. Petersburg Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education - 58 thousand rubles, in Excimer - up to 85 thousand rubles. Moreover, these lenses must be put on both eyes, which means we multiply the price by two. Unlike conventional folding IOLs, which return only clarity of vision to a person, these artificial lenses allow their owner to see well at any distance, and he refuses both glasses for nearsightedness and farsighted glasses. That is, it completely restores vision so that there is no need to use any additional means to correct it. The disadvantage of these lenses is the so-called halo effects. The fact is that these artificial lenses consist of peculiar optical rings, each of which is designed for a certain distance: if you look into the distance, one ring works, if you look closer, another. The transition from one ring to another is felt by the patient. But, they say, you can get used to it.
To
ataract and glaucoma - two in one
When a cataract develops with age - after 40 years, it is often accompanied by another age-related disease - glaucoma. But if the treatment of cataracts is called the "pearl" in surgical ophthalmology, since it completely restores a person's vision, then it is still impossible to achieve this in the treatment of glaucoma. It refers to vascular pathologies: against the background of an increase in intraocular pressure, the outflow of intraocular fluid is disturbed and the optic fibers are compressed. The patient loses parts of the peripheral visual fields, but at first does not notice this. A discovers that the eye sees only a narrow space in front of itself when, having damaged healthy eye, forced to close it. Only timely treatment can save vision in glaucoma. On the initial stage it may be medicinal. But if a cataract patient needs surgery for glaucoma, then both pathologies are treated through one incision. This operation is called phacotrabeculectomy - cataract removal with replacement of the lens with an artificial one with simultaneous operation to reduce intraocular pressure. True, it happens that the patient has all the signs of glaucoma, but they were provoked by a cataract, in which the lens has increased in size and compresses the optic fibers. In this case, the replacement of the lens becomes a treatment for glaucoma.
