List of prostate diseases in men: possible causes of prostate problems and treatment methods. Prostate diseases in men: symptoms and signs of prostate problems.
- This is an important and at the same time vulnerable organ.
She is susceptible to a number of diseases that arise due to an unhealthy lifestyle and a man’s inattention to his health.
Most pathologies are of an inflammatory nature. More details about what diseases are prostate gland, as well as what are the causes of diseases and methods of treating them, you can find out in.
The following factors influence the likelihood of developing prostate diseases:
- congestive processes in the pelvis caused by a sedentary lifestyle;
- nervous and physical overload of the body, reducing its defenses;
- abstaining from sex for too long;
- promiscuous sex life;
- smoking, alcohol consumption;
- improper diet with an excess of fatty, spicy and salty foods;
- the prostate is cold and provokes acute and chronic inflammation;
- infectious lesions of the body. They can be either bacterial in nature (streptococcus, tuberculosis, gonorrhea) or viral (influenza, papilloma);
- Traumatic lesions of the prostate occur with fractures of the pelvic bones, for example, with strong blows to the inguinal perineum. Prostate injuries can be caused by bougienage of the urethra, improper massage of the prostate and other diagnostic procedures performed in violation of the rules.
You can find out more about the causes of pain in the prostate gland.
Symptoms
It is performed without incisions, as the high-frequency laser is directed into the prostate through the urethra.
- This is another minimally invasive method. During this operation, the vessels of the prostate are blocked with medical polymers.
Other non-surgical methods include cryodestruction, ultrasound therapy, and thermotherapy.
Consequences
If infectious lesions of the prostate are not treated, the disease can spread throughout the body and cause serious systemic complications. Tuberculosis has the greatest likelihood of developing systemic complications.
IMPORTANT! Prostatitis can become chronic and lead to the appearance of cysts, abscesses and adenomas.
If the adenoma develops to the third stage, then there is a possibility of developing renal failure and rupture bladder, and this is deadly.
In general, all problems with the prostate are very unpleasant for a man, since even in the absence of serious complications they significantly worsen his quality of life.
To minimize the likelihood of developing prostate diseases, you need to:

- strengthen immunity;
- lead a moderate and orderly sex life;
- get checked regularly for STDs;
- exercise;
- eat healthy food;
- minimize stress.
- do not delay emptying the bladder for for a long time.
Useful video
The following video is about how to diagnose prostate diseases and their treatment.
Part 1:
Part 2:
Conclusion
There is a wide variety of prostate diseases in men, but the causes and treatment for most of them are similar. Despite the fact that this organ is not the most important in the body, disruption of its functioning can lead to serious systemic disorders. Therefore, one should not underestimate the importance of their prevention and timely diagnosis.
The prostate gland is an organ of the male reproductive system that performs a number of vital functions. It’s not for nothing that the ancient Greeks called the prostate the “second heart” of men. It secretes a special liquid, which makes up almost half the volume of the ejaculate and ensures sperm activity. Without her help, they are unable to travel their long way and take part in the conception of a new life.
It is generally accepted that the development of major prostate diseases is more typical for older patients. And this is in some way fair, but every year there are more and more men who suffer from various pathologies of this organ.
Classification of prostate diseases
The etiological factor became the basis for the division of diseases. Depending on the cause of a particular problem, there are:
- Infectious diseases of the prostate gland:
- spicy ;
- chronic bacterial prostatitis.
- Non-infectious:
- chronic pelvic pain syndrome or nonbacterial prostatitis;
- benign hyperplasia (adenoma);
- cancer (adenocarcinoma).
The main cause of the first group of diseases is harmful microflora that affects organ tissue. The reasons for such an invasion may be the following:
- violation of intimate hygiene rules;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- improper use of antibiotics, without following the instructions for their use.
As a result of such colonization of the prostate by microbes, a focus of chronic inflammation is formed with all the ensuing consequences and symptoms.
The condition for the development of the second group of diseases remains stagnation venous blood in the pelvis and the processes of formation of atypical cells.
Symptoms of prostate diseases
In addition to the different causes of the occurrence and progression of prostate pathologies, they are all united by a common pathogenetic mechanism for the formation of the main symptoms - this is increase in the size of the organ itself. Due to this anatomical change, there is an effect of compression of the urinary canal and small vessels that feed the prostate gland. All this leads to a number of common symptoms:
- Frequent and painful urination. This is the most common sign of male organ disorders.
- Local discomfort or pain in the perineal area. Due to the increased volume of the prostate, it compresses the peripheral nerve endings, thereby causing pain.
- Increase in local temperature. Blood stagnation increases the permeability of cell membranes, through which pro-inflammatory substances (histamine and prostaglandin) penetrate into the parenchyma of the organ. They take part in the processes of increased catabolism, as a result of which the temperature rises.
- Sexual dysfunction. Disorders such as premature or retrograde ejaculation, decreased libido, and impotence are common.
- Sometimes men have pain during defecation and pathological impurities in the urine(pus, mucus, blood).
All these phenomena are characteristic of almost all the diseases mentioned above. But it is worth considering each prostate disease more carefully.
Prostatitis

Inflammation of the male organ is probably the most common pathology in urological practice. Approximately every 40th man on the planet suffers from this disease. The reasons for this widespread are:
- Inactive lifestyle and sedentary office work. These factors lead to stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs and prostate, which increases the risk of infection;
- Defecation disorders such as constipation. Constant retention of feces in the rectum in close anatomical proximity to male organ promote the migration of pathogenic microbes into the prostate tissue;
- Hypothermia of the body, repeated many times. Relevant for drivers, security guards and other professions where unfavorable working conditions are possible;
- Too active sex life or its sharp limitation. In any case, there is a negative impact on reproductive system men;
- Frequent stressful situations, alcohol and smoking abuse, overeating. All this contributes to a general weakening of natural protective mechanisms and increases the risk of prostatitis.
As can be seen from the reasons, more patients are admitted to the clinic due to modern lifestyle. For successful treatment you need to change it.
The first signs developing inflammation prostate gland can be:
- a sluggish stream of urine that quickly falls down and does not reach 15 cm in length;
- difficulty urinating;
- lack of feeling complete liberation bladder;
- night desire to go to the toilet.
The remaining symptoms are similar to those described above. It is worth noting the fact that in young people who are sexually active, prostatitis in most cases occurs as an acute infection with a predominance of pronounced pain and intoxication syndromes with high fever. While in older people, the chronicity of the process with symptoms of dysuria and mild inflammation comes to the fore.
Laboratory symptoms of such a disease will be:
- increased level of leukocytes in the blood,
- increase in ROE,
- shift of the leukocyte formula to the left.
The urine will show neutrophils (inflammatory cells), bacteria, and possibly hyaline casts. In the case of pathological discharge, red blood cells or atypical forms of cells may be attached here.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome
The etiology of this disease has not yet been reliably established. The main theories proposed by scientists remain:
- bacterial;
- autoimmune;
- viral;
- somatotropic;
- chemical.
It is very difficult to say specifically, since there is no reliable evidence for any of them. Therefore, today abacterial prostatitis remains a diagnosis of exclusion and can only be made if it is impossible to confirm any of the other diagnoses.
Speaking about the symptoms of the disease, we must pay attention to the fact that pain and sexual dysfunction in men come to the fore, which is not typical for bacterial infection. Pain is observed during ejaculation and during physical activity. Localized in the perineal area with possible irradiation to the back and groin.
In laboratory diagnostics, no significant changes in blood tests are observed. Microscopic examination of urine reveals a small number of leukocytes and red blood cells.
The main disadvantage of this disease is the decrease in sexual function of men and sexual disorders that greatly reduce the quality of life. This becomes the first reason for visiting a doctor.
Benign hyperplasia or prostate adenoma

This process is characterized by the proliferation of parenchymal tissue of the organ with the formation of areas of compaction (nodes), which becomes the basis for the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
The main reason for this growth is the hormonal shift in the body of the stronger sex over time. The disease is more common in patients aged 50 years and older. At this time, in the body of men, the production of their own sex hormones (androgens) decreases and the production of female hormones (estrogens) prevails. The result is the occurrence of incorrect impulses in the main brain and impaired prostate function.
Due to the increase in the size of the organ, classic symptoms begin to develop with difficulty urinating and pain during this act.
It is only worth noting that the process is staged and involves progression over time. It manifests itself as follows:
- During the first phase, there is no pain when going to the toilet. The only change is the need to strain a little to relieve natural needs.
- The second degree of hyperplasia already leaves its mark on the frequency of urination - it increases while maintaining the normal amount of daily discharge. There is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- The third stage occurs when the prostate is so enlarged that It is almost impossible to go to the toilet on your own– a urinal is used. Moments of incontinence occur both during the day and at night.
Laboratory values of blood and urine may be normal. An ultrasound examination reveals a significant increase in the size of the organ. Its wall is smooth without infiltration into neighboring organs. General condition The patient is normal, if you do not take into account urinary disorders.
Adenocarcinoma or cancer
This is the most life-threatening prostate disease in men. It is still difficult to establish the main reason for the development of an atypical process in organ tissue. The main factors that can serve as a “trigger” for the development of the formation of a malignant neoplasm are:
- Genetic factor. It has been clinically proven that in a family where there have already been patients with cancer, the risk of a neoplasm in the heirs is several times higher than in a healthy population;
- Poor nutrition. This point remains highly controversial, but there are publications and scientific research, where the fact of more frequent development has been proven of this disease in persons who have taken large quantities of foods rich in animal fats and alcohol;
- Smoking. A still untested factor. However, due to its involvement in the development of other malignant tumors, it is also at risk in this case.
The general intoxication syndrome and harmful effect cells with uncontrolled growth.
In addition to the classic symptoms of urinary disorders and sexual dysfunction, specific signs of cancer. They include:
- symptoms associated with metastatic damage to other organs and systems (bone pain, swelling lower limbs, in rare cases - paralysis);
- the appearance of blood in semen;
- cachexia – general exhaustion of the body with pronounced loss of weight (up to 15 kg per month);
- anemic syndrome (pallor of the skin, dizziness, general weakness);
- loss of appetite;
- drowsiness;
- chronic fatigue.
Laboratory diagnostics reveal a very small amount of red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood, and a decrease in the level of leukocytes. Blood cells may appear in the urine.
The main marker of the disease is prostate-specific antigen (PSA). Its increase can most likely confirm the diagnosis of a tumor process.
Any pathology of the prostate gland in men requires adequate treatment. The main problem remains the incorrect attitude of the stronger sex towards their own health. They often try to lead a normal life even with the presence of early signs prostatitis or any other problem. This leads either to the transition of the pathology to the chronic stage or to the emergence additional complications. Only at this moment do patients remember medicine and are obliged to undergo therapy where it could have been avoided.
This problem becomes more and more urgent every year. Many men, as well as many women, are interested in this issue. After all, the incidence is growing, and the diagnosis of this disease, as a rule, occurs at later stages. And, as you know, the later the diagnosis is made, the more advanced the disease, and this applies to any disease, the more difficult the treatment and the worse the prognosis.
Therefore, we consider it necessary to draw your attention to such important problem, because treatment of prostate adenoma (PA) is possible, and in the early stages it is much more effective.
In this article we will consider in detail the causes of the development of this disease, factors contributing to the occurrence of prostate adenoma, symptoms, diagnostic methods, all treatment methods from traditional to the latest techniques. We will also describe methods of prevention and possible complications if a person does not pay attention to the symptoms that appear in time and does not consult a doctor.
A synonym for this disease is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), it is found in the medical literature and can be used in the text below. Some people confuse this disease with inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis); this is a mistake.
Prostatitis and prostate adenoma are different diseases and have different etiologies.
APZh is benign tumor prostate, which can form either from glandular epithelium, or from the stroma of the prostate gland.
Anatomy of the prostate gland
To better understand why certain symptoms occur with PDA, let’s tell you a little about the structure of the gland.
The prostate gland (prostate) is located in the pelvis under bladder in men. It has a spherical shape and covers the urethra. Macroscopic structure - the gland consists of two lobes and an isthmus. Its normal dimensions are 2*3*4 cm. The gland consists of glandular tissue, which is collected into lobules and connective tissue(stroma). The function of the prostate is secretory, that is, the production of fluid, which is necessary to maintain the normal functioning of sperm.
How common is the disease?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a very common disease. It most often develops in men aged 40 to 50 years. It is also rare in younger patients. According to doctors, about 80% of men sooner or later experience this disease. The risk of developing BPH increases with age.
Causes of adenoma
The cause of BPH is the male menopause. After 40 years, men experience hormonal changes in their bodies. The level of androgens (“male” hormones) decreases and the level of estrogens (“female” hormones) increases. All men always have both androgens and estrogens in their bodies, but during menopause their balance changes.
During this period, the level of estradiol increases; it is this substance that has the ability to stimulate the growth and reproduction of prostate cells.
Risk factors for developing BPH:
According to long-term observations, a number of factors have been identified that increase the risk of developing benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Male age over 40 years
- Presence of obesity (adipose tissue is a substrate for the production of estrogens)
- Presence of this disease in relatives
- Alcohol abuse
- Smoking
- Physical inactivity
- High blood pressure
- Poor diet – eating large amounts of spicy, fatty foods
Factors that do not affect the development of BPH:
There is no reliable connection between the incidence of this disease and the following factors:
- Sexual orientation
- Sexual activity
- Transferred inflammatory diseases pelvic organs, including sexually transmitted diseases
Symptoms of adenoma
In this section we will simply list possible symptoms benign prostatic hyperplasia; below they will be discussed in more detail.
- Frequent urination (see)
- Frequent night urges
- Sleep disturbance (see)
- Symptom of "sluggish stream"
- Intermittent urination
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
- The need for strong tension in the abdominal muscles when urinating
- Involuntary urination in small portions (see).
Classification of BPH
By location:
- Subvesical form - the tumor spreads towards the rectum.
- Intravesical form - the tumor spreads towards the bladder.
- Retrotrigonal form - the tumor is located under the triangle of the bladder.
Highlights different stages(degree) of adenoma development:
Stage 1 – compensated
Among the symptoms, patients note frequent urination, especially at night. The frequency can be up to 10 times a day and (or) up to 7 times a night. The urge is felt very strongly, but at the same time there is a delay in urination, a stream of urine flows out at a low speed, despite the efforts of the man. Sometimes there may be involuntary leakage of urine.
Emptying the bladder occurs due to the compensatory capabilities of the muscular wall of the bladder. This stage can be long, up to 9-10 years. But more intense progression often occurs. After the compensatory capabilities are exhausted, the next stage begins.
Stage 2 – subcompensated
At this stage, inflammation of the bladder occurs, which causes pain when urinating. Frequent urination persists, and involuntary leakage of urine becomes more frequent. There is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The stream of urine becomes not only sluggish, but also intermittent. There may be blood in the urine. In case of stress, alcohol consumption or hypothermia, it is possible complete absence urination. In this case, pain appears in the bladder area, radiating to the lumbar region or above the pubic bone.
Due to the fact that the patient has to strain a lot when urinating, rectal prolapse or hernia may occur. The walls of the bladder are greatly stretched and saccular formations appear, in which up to a liter of residual urine can accumulate. If not applied modern methods treatment of adenoma, then stage 3 of the disease occurs.
Stage 3 – decompensated
At this stage, it is necessary to use a urinal, since urine continuously leaks drop by drop from an overfilled bladder. Appear general symptoms– weakness, nausea, loss of appetite, thirst, weight loss, constipation may occur. When nitrogenous bases accumulate in the blood, urine smells from the mouth.
The volume of residual urine can reach two liters, overstretching of the walls of the bladder occurs, and the contractility of its walls decreases. Kidney dysfunction occurs. When urine stagnates, inflammation of the urinary tract may develop, which will manifest itself as an increase in body temperature. A patient with this stage urgently requires treatment of prostate adenoma not only with drugs, but also with surgical treatment.
Complications of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Often patients are afraid to see a doctor with such a delicate problem, or they worry that it will be necessary to remove the prostate adenoma, thereby only increasing the risk of complications that can be life-threatening.
Acute urinary retention
With strong compression of the urethra by the enlarged prostate gland, acute urinary retention develops. Triggering factors can also be hypothermia, acute respiratory infection, late emptying of the bladder, stress or drinking alcohol.
The clinical picture of acute urinary retention is the inability to urinate when the bladder is full. In this case, there arise severe pain in the suprapubic region, radiating to the lower back and penis.
If the patient is not provided with qualified medical care in a timely manner, acute urinary retention may be complicated by the development of renal dysfunction and coma.
If you experience signs of acute urinary retention, you should immediately go to the hospital!
Inflammation of the urinary tract
When urine stagnates or the bladder is not completely emptied, very favorable conditions are created for the growth of bacteria. This can cause urethritis, cystitis and pyelonephritis.
Urolithiasis
With stagnation of urine and a high level of salt concentration in the urine, the formation of microliths, and then stones in the bladder, is possible. They, in turn, can lead to blockage of the urethra, which will cause acute urinary retention.
Diagnosis of BPH
Collection of complaints and medical history and examination of the patient. Digital examination of the rectum allows you to determine the size, consistency of the prostate gland, pain on palpation or its absence.
Every man over 40 should have his prostate specific antigen level checked annually, even if he has no concerns. This test can help diagnose not only BPH, but also prostate cancer.
Laboratory research methods:
- Biochemical blood test
- General urine test
- Determination of prostate specific antigen (PSA, PSA) in the blood.
Determining the PSA level in adenoma is not only the most important method diagnostics, but also a method of monitoring the course of the disease.
Norms for the level of prostate specific antigen depending on the age of the man.
Instrumental research methods:
- TRUS – transrectal ultrasound examination. Allows you to detect enlargement of the prostate gland, nodules in its structure, the presence of stones in the bladder, and determine the volume of residual urine.
- Uroflowmetry - determination of the speed of urine flow during urination. Normally it is 15 ml per second and higher. When it decreases to 10 ml/s, we can talk about the presence of an obstruction to the flow of urine.
- X-ray - allows you to identify urolithiasis and changes in the renal collecting system.
I-PSS scale. It is a questionnaire of 7 questions about various symptoms BPH. The patient answers each of them, assessing the presence of each symptom and its severity from 0 to 5 points. Based on the sum of points, the doctor assesses the likelihood of BPH in a given patient.
Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Conservative treatment
- α – 1 adrenergic blockers. They are used to restore or improve the flow of urine through the urethra, as these drugs cause its expansion, relaxing the smooth muscles of the urethra.
- 5-α reductase inhibitors. They slow down the growth of the prostate, thereby reducing its volume. They are usually prescribed if the volume of the adenoma is very large. Have a number of serious side effects– erectile dysfunction, enlargement mammary glands and decreased libido.
- Herbal preparations slightly reduce the symptoms of the disease, affecting the muscles of the urethra, but do not in any way affect the growth of the tumor.
Medicines do not get rid of adenoma, but only slow down its growth or alleviate symptoms; it can only be cured medicines not possible.
Surgical treatment
There are many different operations used for prostate adenoma.
- Open prostatectomy– this is the removal of the prostate lobes, abdominal surgery, is performed under general anesthesia. Used when large mass prostate gland (more than 60 g) and a volume of residual urine of at least 150 ml. It is possible to carry out the intervention in 2 stages. The first step is to remove the prostate gland, forming a fistula up to the anterior abdominal wall, through which urine flows into a urinal. The second stage restores normal urine flow.
- Transurethral resection(TUR) - the operation is performed without any incisions. All manipulations occur through the urethra. The conditions for this type of surgical treatment are: the weight of the prostate is no more than 60 grams and the volume of residual urine is less than 150 ml. During transurethral resection, as a rule, the prostate is not completely removed and the patient is prescribed medications that will subsequently inhibit further growth of the gland. TUR is a less invasive procedure compared to open prostatectomy. But after this operation, complications are more common, such as bleeding, urinary incontinence, retrograde ejaculation, sclerosis of the bladder neck or urethral stenosis.
- Transurethral microwave therapy– a catheter is inserted through the urethra, through which microwaves are delivered. The gland tissue becomes very hot and coagulates. The method is used only for small adenomas. In the postoperative period, local swelling is observed and a catheter is installed to remove urine.
- Transurethral laser vaporization– as the name suggests, the operation is performed using a laser. A catheter is inserted through the urethra; when the laser is applied to the tumor, water evaporates from its cells, which leads to their death. The prostate decreases in size. The use of the technique is advisable only for small tumors.
- Transurethral needle ablation– through a cystoscope, the doctor inserts needles into the prostate tissue. Radio frequency waves are sent through them. This heats and destroys tumor tissue. The method is not used for large tumor sizes. The likely complications are the same as with transurethral microwave therapy - impaired urine outflow due to tissue edema.
- High intensity faux ultrasound(FUVI) – using a probe, a microscopic video camera and an ultrasonic wave emitter are inserted. Ultrasound has a thermal effect and destroys tissue. A significant complication is impotence, which develops in 1-7% of cases.
- Balloon dilatation– using a cystoscope, a balloon is inserted into the urethra, with the help of which the lumen of the urethra is expanded. This method is used in cases where conservative treatment ineffective and surgical treatment contraindicated. Balloon dilatation only reduces symptoms, but does not affect tumor growth.
- Stenting– the method is similar to the previous one, only a stent is inserted into the lumen of the urethra, with its help the outflow of urine is improved. The indications for the method are the same as for balloon dilatation.
- Cryodestruction– using a cystoscope, a freezing head is inserted through which liquid nitrogen is supplied. Prostate tissue is frozen at low temperatures and destroyed. To avoid damage low temperatures the urethra uses a warming element in its area.
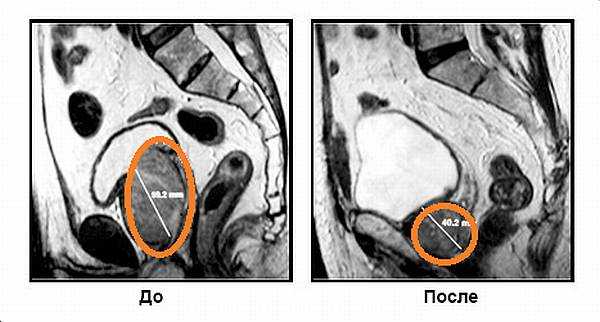
- Embolization of prostate arteries. The latest method used by endovascular surgeons. The prostate arteries are reached through the femoral artery using a catheter. Small spheres made of medical plastic with a diameter of 0.1-0.4 mm are fed into their lumen. They are carried by the blood current into small arterioles and clog them. The prostate tissue does not receive nutrition and dies, thereby achieving a significant reduction in prostate tissue.
The result of embolization of the prostate arteries. The orange circles indicate the prostate.
Ineffective treatments
These include traditional methods treatment of prostate adenoma. Among them are treatment with pumpkin juice, walnuts, fir water, hazel decoction, but they will not help get rid of the growing adenoma. These also include prostate massage for adenoma. Such methods will only allow you to waste time and reach a higher stage of the disease.
All minimally invasive and most safe methods Treatments are possible only for small adenomas. This means that the sooner you see a doctor when the first symptoms of the disease appear, the easier it will be to cure and the less likely there will be complications.
Prevention of BPH
There are several methods to prevent the development of adenoma:
Diet. Nutrition for adenoma should be balanced; foods should contain a lot of fiber, vitamins and microelements.
Moderate physical activity . Thanks to them, not only does venous congestion in the pelvic organs decrease, but they also help reduce body weight. Recommended hiking outdoors, active recreation.
Regular visits to the urologist. After 40 years, every man should visit a urologist once a year and take a PSA test. This may help in early diagnosis of this disease.
Forecast
With timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable. With a long course of the disease without medical care the prognosis is unfavorable. Complications arise, infections of the urinary system, stones form in the bladder, and acute urinary retention develops.
Also in severe cases there is renal failure, which can lead to death. We should not forget that there is a risk of malignancy, that is, a benign tumor can become malignant and in this case prostate cancer is already diagnosed.
An important place in urology is occupied by diseases of the prostate gland, which have long been known. Even among ancient writers one can find a description of impaired urination in elderly men.
The prostate, or prostate gland, is an organ located around the urethra under the bladder, consisting of 2 lobes, its shape resembles a chestnut. Takes part in the exchange and production of male sex hormones, which provide not only sexual function, but also the entire metabolism in the male body, and therefore the work of all systems and organs.
It’s not for nothing that ancient Greek doctors called the prostate the second heart of a man. The most common prostate diseases: prostatitis, benign hyperplasia or adenoma,.
Prostatitis and its varieties
It is considered the most common disease of the reproductive system in men. There is nothing surprising in this, because the factors that develop prostate diseases are very common in our lives.
 with inflammation of the urethra. Often the source is sexually transmitted diseases.
with inflammation of the urethra. Often the source is sexually transmitted diseases.
In some cases, the disease can be provoked purulent inflammation in the body (sore throat, boil, sinusitis, etc.). The secretion of the prostate has bactericidal substances, therefore, for the occurrence of inflammatory foci in the gland, some predisposing factors are also required, such as congestion or venous stasis, which begins with constipation, sedentary work, and hypothermia. Prostatitis can be acute or chronic.
Acute prostatitis
As a rule, it is easily diagnosed, as it has pronounced signs of the disease. The inflammatory process begins with the mucous membrane of the excretory ducts of the glandular lobe. Subsequently, the walls swell and the ducts become clogged. The virus penetrates the tissue and many small pustules appear.
Sometimes they merge into one large one, and the result is a prostate abscess, which can break into neighboring organs - the urethra, bladder or rectum. First, the patient will experience frequent urination, accompanied by painful sensations.
 With further inflammation, pain in the perineum intensifies, radiating to the head of the penis or anus.
With further inflammation, pain in the perineum intensifies, radiating to the head of the penis or anus.
Body temperature rises to 40ºС, weakness and chills appear. Sometimes when the lumen in the urethra, severe pain occurs during bowel movements and urination, and acute urinary retention occurs. You need to immediately contact a urologist and start correct treatment. In this case, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Chronic form
Occurs due to insufficient or incorrect. But more often it develops during and is characterized by a sluggish chronic inflammatory process, leading to scar-sclerotic changes in the prostate. The formation of an expanded cavity is characteristic, due to stagnation of secretions and blockage of the ducts.
Second stage
There is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The urge becomes more frequent day and night. In the morning I have to urinate in 2-3 passes. The stream is interrupted by drops and becomes vertical. Signs of impaired kidney function begin to develop - increased thirst, dry mouth.
Third stage
 Some of the residual urine increases to 2 liters. The bladder is stretched, the contours are visible in the form of a tumor, and its sensitivity decreases. Involuntary loss of urine at night and then during the day. Impaired kidney function causes loss of appetite, nausea and weakness. In the absence of adequate treatment, patients die from uremia.
Some of the residual urine increases to 2 liters. The bladder is stretched, the contours are visible in the form of a tumor, and its sensitivity decreases. Involuntary loss of urine at night and then during the day. Impaired kidney function causes loss of appetite, nausea and weakness. In the absence of adequate treatment, patients die from uremia.
Today, methods of treating adenoma are highly effective and diverse; the method of treatment depends on the stage and size of the adenoma. Treatment can be medication or surgery. Modern diagnostics helps stop prostate growth and helps avoid surgery. But you should remember that only a doctor can choose the optimal treatment method for you.
Prostate cancer
A malignant tumor that affects the prostate gland. It ranks 4th among cancer diseases in men. According to statistics, men over 50 years of age are more likely to get cancer. But, unfortunately, recently time goes by a tendency towards “rejuvenation” of this disease. In most cases, prostate disease is asymptomatic.
Then various disorders appear in the genitourinary area, the most common complaints being an increased urge to urinate at night. This results in the amount of urine excreted during the night exceeding the daily urine output. There is retention or incontinence of urine, as well as the presence of blood in it. There are cases when urination reaches 20 times a day, with the norm being 4-5 times, accompanied by severe pain.
Unlike prostate adenoma, cancer not only interferes with urination, but is also capable of metastasizing to other organs. When a tumor grows into the seminal vesicles, problems with potency appear. And, when the tumor reaches a large size, pain during bowel movements and constipation are possible.
The growth and development of metastases due to impaired lymphatic drainage is manifested by swelling of the penis, lower extremities and scrotum. Pain occurs when metastases appear in bone tissue(femur, lumbar region spine, pelvic bones).
With liver damage, symptoms depend on the size and number of metastases. With single metastases, the liver enlarges and dull pain occurs in the right side, and with multiple metastases, jaundice and liver failure appear.
Scientists have not yet developed any means to prevent cancer, so it is impossible to prevent it. But it can be detected at the earliest stages.
Please note that the symptoms of the disease (and they are similar to) will manifest themselves only in the last stages of the disease. Curing cancer today is only possible if it is detected early. To do this, men after forty need to undergo regular urological examinations. The examination is carried out on an outpatient basis and does not take much time or money.
IN recent years In medicine, enormous advances have been made in the treatment and diagnosis of the prostate gland. The sooner a man sees a doctor, the higher his chance of a full recovery. If there is a failure in treatment, then most likely it will depend on the patient’s lack of patience during treatment or on a late visit to the doctor than on the disease itself.
Prostate cancer is malignant neoplasm, which often occurs asymptomatically and progresses slowly, but the symptoms of prostate diseases can still be determined; to diagnose it, a blood test for prostate cancer can be performed. In the presence of tumors, the level of prostate specific antigen increases, which indicates the presence of cancer. Based on this study a specialist cannot diagnose cancer because PSA can also be elevated in prostatitis or prostate adenoma.
Causes of inflammation of the prostate gland
The development of any disease is caused by one reason or another. Diseases are mainly caused by the development of bacterial or viral flora in the body.
The development of prostatitis in men is caused by certain viruses. But experts agree that there are a number of reasons that provoke the development of this disease. Among the causes of cancer:
- poor environment;
- improper diet;
- bad habits.
All of the above causes disruption of blood flow in the capillaries, provoking the development of lipid peroxidation. Insufficient blood supply can cause urethral reflux (urine backflow through the ureters). As a result, urethral fever occurs, which develops into large inflammations.
Important! The main cause of inflammatory processes in the prostate gland is impaired blood flow and stagnation of blood in the capillaries, against the background of which the active development of infection occurs.
Symptoms of problems with the prostate gland may not manifest themselves in any way for a long time. If you find any abnormalities, immediately consult a specialist to ensure timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
TO early symptoms prostate cancer includes:
- problematic (difficult) or painful urination process;
- weakening of the urine stream;
- frequent urge to urinate.
These symptoms can be dangerous because they coincide with the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia, which is a natural change with age.
But, at the same time, at this stage, while the metastases are only in the gland, the disease can be completely cured. The emergence of new symptoms in diseases of the prostate gland indicates the growth of the tumor and the use of more complex therapy.
Symptoms of prostate tumors, with the growth of metastases:
- urinary incontinence;
- there may be blood in the urine;
- erectile function will decrease;
- the color of the sperm may be red or pinkish;
- pain in the pubic area;
- inflammation of the urethra or bladder, which is accompanied by painful urination.
For more information about the symptoms and types of prostatitis, watch the video.
Prostate carcinoma
Symptoms of prostate carcinoma are not specific; they coincide with other urological diseases.
For early stages carcinomas are characteristic:
- Difficulty urinating.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Urine leakage and involuntary urination.
- Pain in the pelvic area.
- Impotence.
- Blood in semen and urine.
It is also possible to experience swelling of the legs, constipation, general exhaustion, broken bowel movements, and paralysis of the lower extremities.
To treat this disease, the following methods are used:
- hormone therapy;
- radical prostatectomy (complete removal of the gland);
- radiation therapy.
There are also new methods of therapy, including: cryotherapy, local radiation therapy.
Presence of stones in the gland
The main symptom of prostate stones is pain in the perineal area. It may intensify during sexual intercourse or the process of defecation. There may be blood veins in the semen. And also:
- weak erection;
- pain during ejaculation;
- compaction in the gland and pain when palpating it.
Prostate abscess
Formation of pustules during inflammatory process in the prostate is called a prostate abscess. The appearance of such a disease is accompanied by an increase in temperature, fever, intoxication and pain radiating to the rectal area. Strong painful sensations interfere with the painless process of defecation and urination.
Abscesses are primary and secondary. Primary is formed due to the transfer of infection from another source of inflammation. A secondary abscess is caused by improper treatment of inflammation of the prostate gland.
Symptoms of prostate abscess:
- During the infiltrative stage, chills, fever and elevated temperature. Possible disturbance of consciousness, pain in the lower abdomen.
- During the purulent-destructive stage, symptoms weaken, which can subsequently cause rupture of the abscess.
Rupture of the abscess into the paraurethral tissue or peri-vesical space will lead to the development of phlegmon. The presence of pus in the urethra provokes the presence of a strong odor in the urine, pyuria, pus and cloudy urine.
Rupture of the abscess into the intestine will cause a rectal fistula, in which pus will be present in the stool.
Important! The rupture of the abscess does not lead to disinfection, so the process of suppuration will continue. Complications include peritonitis and sepsis.
All of the above symptoms of prostate diseases in men are always the same. They may not be clearly expressed, but in any case they should alert you. For any painful manifestations in the prostate area, you should consult a specialist for help.
